How Do Animals Reproduce Without Gametes? Explained with Examples
Asexual reproduction is a simple way for certain organisms to create new individuals using just one parent. In this process, there is no fusion of gametes, and the offspring are often exact copies (clones) of the parent. Although it is more common among single-celled organisms, some multicellular animals can also reproduce asexually under the right conditions.
Definition of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction involves producing new individuals from a single organism without the need for male and female gametes. Since only one parent is involved, genetic variation is minimal or absent. The newly formed offspring inherit the same genetic information as the parent.
Features of Asexual Reproduction
Single Parent Involvement: It does not require two parents.
Absence of Fertilisation: There is no union of male and female gametes.
Rapid Process: It usually takes less time compared to sexual reproduction.
Genetically Identical Offspring: The offspring are exact genetic copies (clones) of the parent.
Fast Growth Rate: Asexual offspring often reach maturity quickly.
5 Types of Asexual Reproduction in Animals
Below are 5 types of asexual reproduction in animals commonly observed in nature:
Fission (Binary Fission and Multiple Fission)
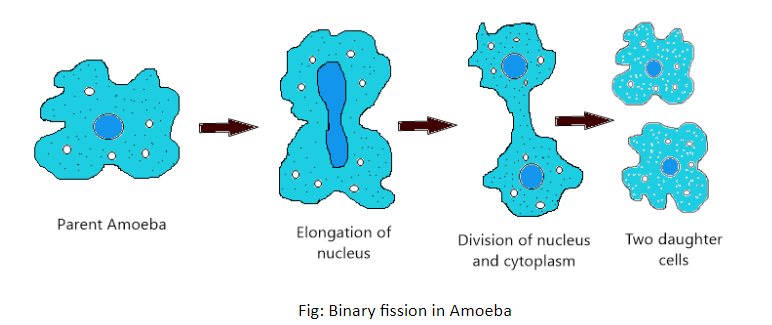
Binary Fission: The parent cell divides into two equal parts, each containing a nucleus. These two daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent. Amoeba and bacteria are classic examples.
Multiple Fission (in some protists): The nucleus divides multiple times before the cell splits into several daughter cells simultaneously.
Budding
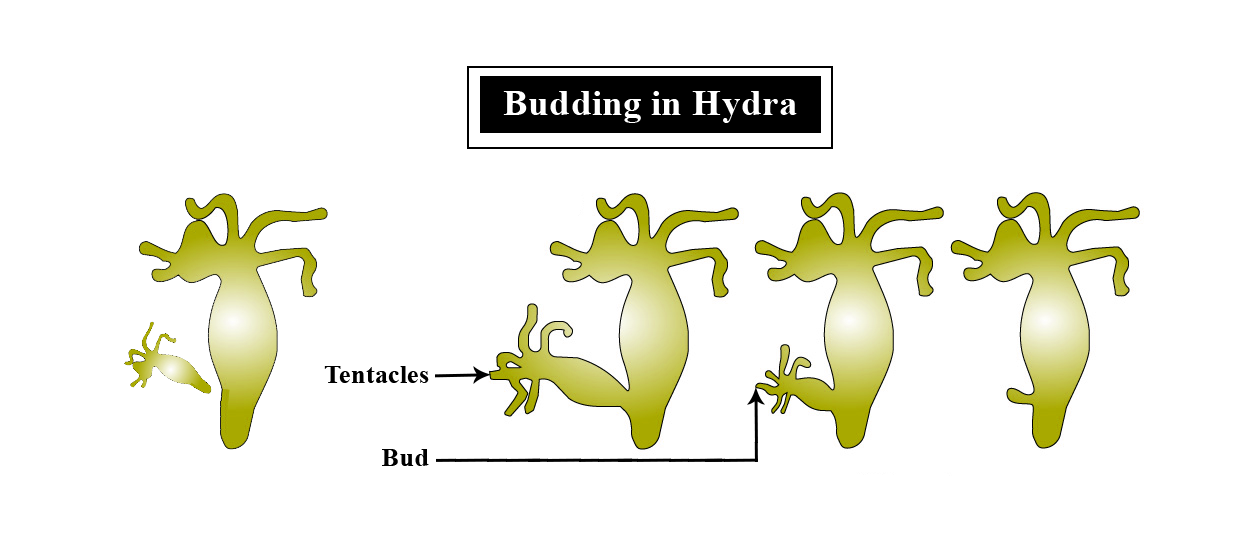
A small outgrowth or “bud” develops on the parent’s body. This bud receives nourishment from the parent until it can survive on its own. Once it matures, it detaches to become an independent organism. Asexual reproduction in animal budding is notably seen in Hydra.
Fragmentation
The parent body splits into two or more fragments, each capable of growing into a new individual. For instance, in Planaria, the body deliberately breaks into pieces, and each fragment regenerates into a complete organism.
Regeneration
In this process, a lost body part can grow into an entirely new individual. Many asexual animals, like some Echinoderms (e.g., starfish), exhibit remarkable regenerative abilities.
Parthenogenesis
In parthenogenesis, offspring develop from unfertilised eggs. While it is often considered an “incomplete form” of sexual reproduction, many scientists classify it under asexual modes because it does not involve sperm. Some insects (like aphids) and reptiles (like certain whiptail lizards) show parthenogenesis.
Asexual Reproduction Examples
Amoeba: Divides by binary fission.
Hydra: Forms buds that grow into new individuals.
Planaria: Shows fragmentation.
Starfish: Can regenerate an entire body from a single arm segment.
These asexual reproduction examples highlight the variety of ways animals can reproduce without two parents.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Asexual reproduction has its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
Differences Between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
While asexual reproduction in animals involves just one parent, animals that reproduce sexually need two parents and the fusion of male and female gametes. This fusion leads to genetic variation, which increases the ability of offspring to survive in changing environments.
Key Takeaways
Asexual reproduction in animals occurs through methods such as fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, and parthenogenesis.
No gamete fusion is involved, and the offspring are often exact replicas of the parent (clones).
Although it is fast and energy-efficient, asexual reproduction provides little genetic variation.
Animals that reproduce sexually usually show more genetic diversity, giving them a better chance of adapting to environmental changes.
Quiz (With Answers)
Which of the following is NOT a form of asexual reproduction?
A. Budding
B. Fission
C. Parthenogenesis
D. Internal fertilisation
Answer: D. Internal fertilisation (it involves gamete fusion, which is sexual).
In which method does a new individual form from an outgrowth on the parent’s body?
A. Fragmentation
B. Budding
C. Parthenogenesis
D. Binary Fission
Answer: B. Budding
Which organism is known for regenerating into a complete individual if cut into fragments?
A. Hydra
B. Planaria
C. Amoeba
D. Starfish
Answer: B. Planaria (though starfish can also regenerate arms, planaria is known for fragmentation, leading to completely new individuals).
Parthenogenesis involves:
A. Fertilisation of male gametes with female gametes
B. Formation of buds on the parent body
C. Development of offspring from unfertilised eggs
D. A nucleus dividing multiple times in a cell
Answer: C. Development of offspring from unfertilised eggs
Related Topics


FAQs on Asexual Reproduction in Animals: Key Types, Process & Examples
1. What is asexual reproduction in animals and what is its main purpose?
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction where a single parent produces offspring without the fusion of gametes. The primary purpose is to enable rapid population growth in stable, favourable environments, as it does not require finding a mate. The offspring produced are genetically identical to the parent.
2. What are the main types of asexual reproduction found in the animal kingdom?
The main types of asexual reproduction in animals include:
- Fission: The parent's body divides into two or more parts, seen in organisms like Amoeba (binary fission).
- Budding: A new individual grows as an outgrowth or 'bud' on the parent's body, as seen in Hydra.
- Fragmentation: The parent's body breaks into several pieces, each of which develops into a new adult, common in sponges and flatworms.
- Regeneration: The ability of a severed body part to grow into a complete organism, like in a starfish.
- Parthenogenesis: Development of an egg into an embryo without fertilization, observed in some insects, lizards, and birds.
- Gemmulation: The formation of internal buds called gemmules, which are resistant to harsh conditions, typical in freshwater sponges.
3. What are some clear examples of animals that reproduce asexually?
Common examples include Amoeba and Paramecium (fission), Hydra and corals (budding), Planaria and sponges (fragmentation), and some species of ants, bees, wasps, and lizards (parthenogenesis). Starfish can also reproduce asexually through regeneration if a part of the central disc is present in a broken arm.
4. How does binary fission in Amoeba differ from budding in Hydra?
The key difference lies in how the parent's body is divided. In binary fission, the parent cell (Amoeba) divides into two equal-sized daughter cells, and the parent identity is lost. In budding, a small outgrowth (bud) forms on the parent's body (Hydra), which then detaches to become a new, smaller individual while the parent remains intact.
5. Why is there very little genetic variation in offspring produced asexually?
Offspring from asexual reproduction show minimal genetic variation because they arise from a single parent. They inherit the exact same set of genes, resulting in offspring that are genetically identical clones of the parent. There is no mixing of genetic material from two different individuals, which is the primary source of variation in sexual reproduction.
6. How is regeneration in animals like starfish and planaria a method of reproduction?
Regeneration becomes a method of reproduction, also known as fragmentation, when an organism breaks into pieces and each piece has the ability to grow into a complete new individual. For example, if a Planaria (flatworm) is cut into multiple segments, each segment can regenerate the missing parts to form a whole new worm. This is more than just wound healing; it is the creation of new organisms from fragments.
7. What are gemmules, and what role do they play in the survival and reproduction of sponges?
Gemmules are tough, dormant internal buds produced by freshwater sponges. They are a means of asexual reproduction designed for survival in harsh environmental conditions like drought or extreme cold. Each gemmule contains a mass of archaeocytes (undifferentiated cells) protected by a hard layer. When favourable conditions return, the cells inside the gemmule emerge and develop into a new sponge.
8. What is parthenogenesis and in which types of animals is this unique form of asexual reproduction observed?
Parthenogenesis is a natural form of asexual reproduction where an embryo develops from an unfertilised egg. It is unique because it involves a female gamete (egg) but no male gamete. This process is observed in a variety of animals, including invertebrates like rotifers, aphids, ants, and bees, as well as some vertebrates like certain species of fish, amphibians, reptiles (e.g., Komodo dragons), and even birds (e.g., turkeys).










