In this article, we will discuss science drawing for class 7th. In Biology, diagrams are by far the most crucial component. We will also study a clean, labelled diagram of class 7th. After reading this article, readers will be able to explain the diagram of :
Photosynthesis
Human digestive system
Structure of heart
Human excretory system.
How to Draw and Label Class 7 Biology Diagrams for Exams
Biology diagrams play a key role in understanding and remembering scientific concepts, especially for students in CBSE Class 7. Accurate and well-labelled diagrams help make abstract processes clearer and improve retention for exams. Visual learning using diagrams is just as important as memorising definitions or formulas. In this guide, you'll find essential Class 7 biology diagrams, explanations, and science drawing tips to strengthen your concepts and boost your exam performance.
How Diagrams Simplify CBSE Class 7 Biology Concepts
Diagrams serve as visual representations that support theoretical explanations. Before exams, students can quickly revise labelled structures, making learning efficient and effective. Clear science drawings also train students to answer diagram-based questions and develop application skills, which are valued in the CBSE curriculum.
Core Biology Diagrams for Class 7
- Photosynthesis in plants
- Digestive process in Amoeba
- Circulatory system schematic
- Structure of the human heart
- Human excretory system
- Reproductive parts of a flower
- Pollination process in flowers
1. Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis allows plants to prepare food using water, carbon dioxide, minerals, and sunlight. The process takes place primarily in the leaves where chlorophyll captures sunlight. Roots absorb water and minerals, which are transported to leaves, while carbon dioxide enters through stomata. This combination produces food and oxygen.
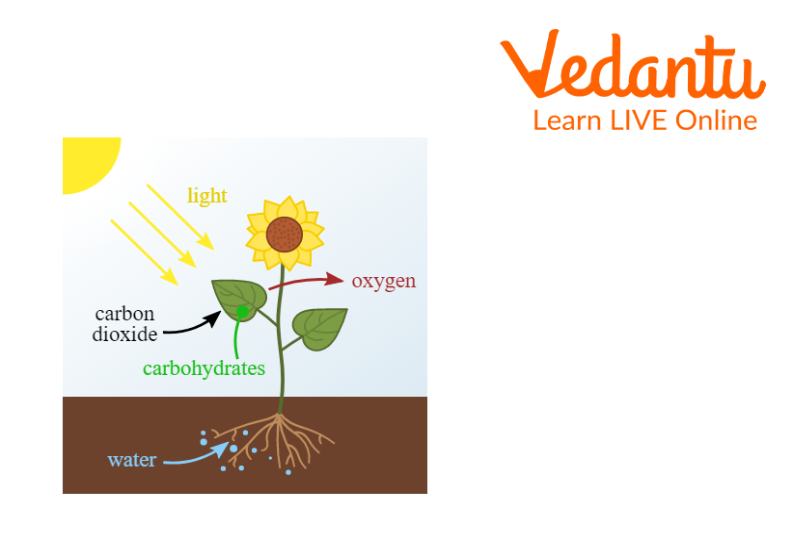
2. Digestion in Amoeba
Amoeba is a single-celled organism commonly present in stagnant water. It digests food by stretching pseudopodia to surround food particles, forming a food vacuole. Digestive juices in the vacuole break down the food so that nutrients are absorbed, enabling growth and energy.
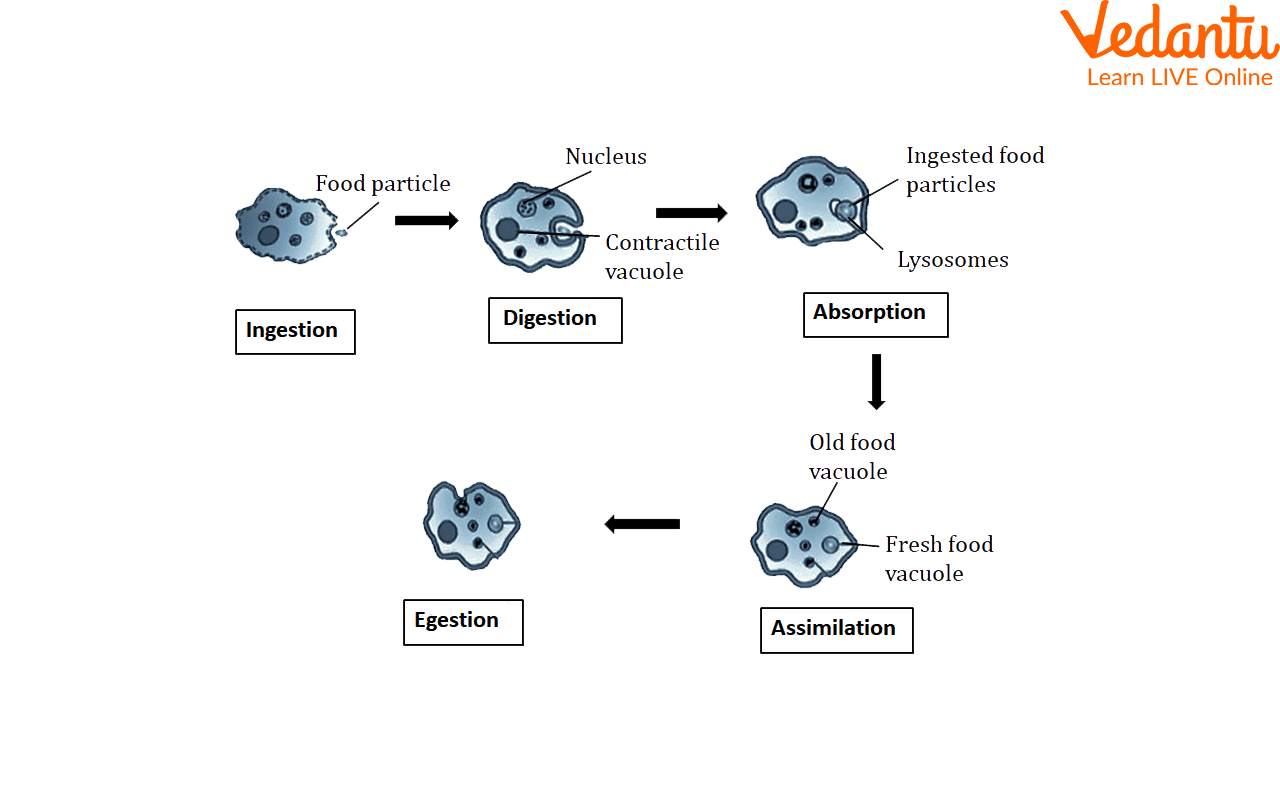
3. Schematic Diagram of Circulation
The human circulatory system has arteries, veins, and capillaries. Veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, while arteries carry oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. This double circulation ensures all body parts receive oxygen efficiently. Endothelial cells line the capillaries for smooth blood flow.
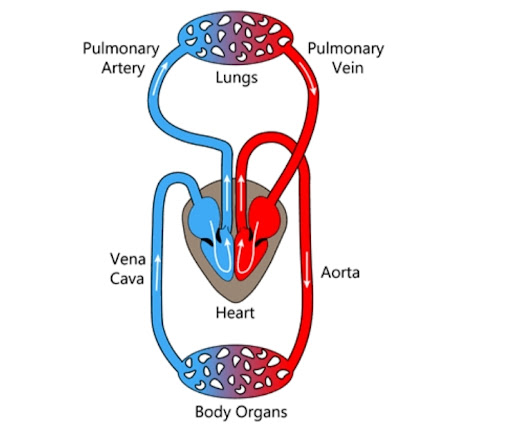
4. Structure of Heart
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood and stops the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. It has four chambers: two upper atria and two lower ventricles, separated by valves. This structure maintains effective blood circulation and supports healthy body function.
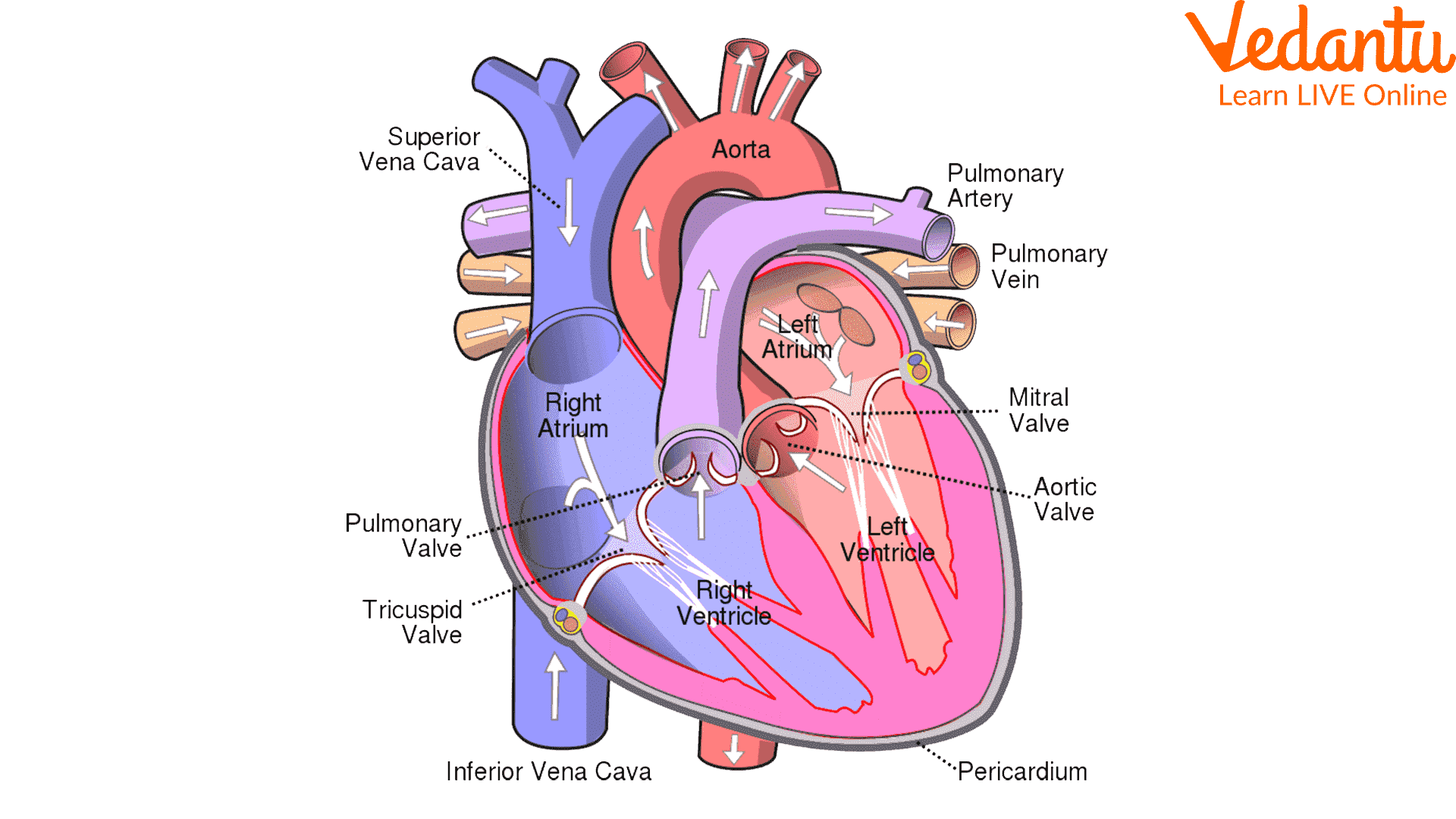
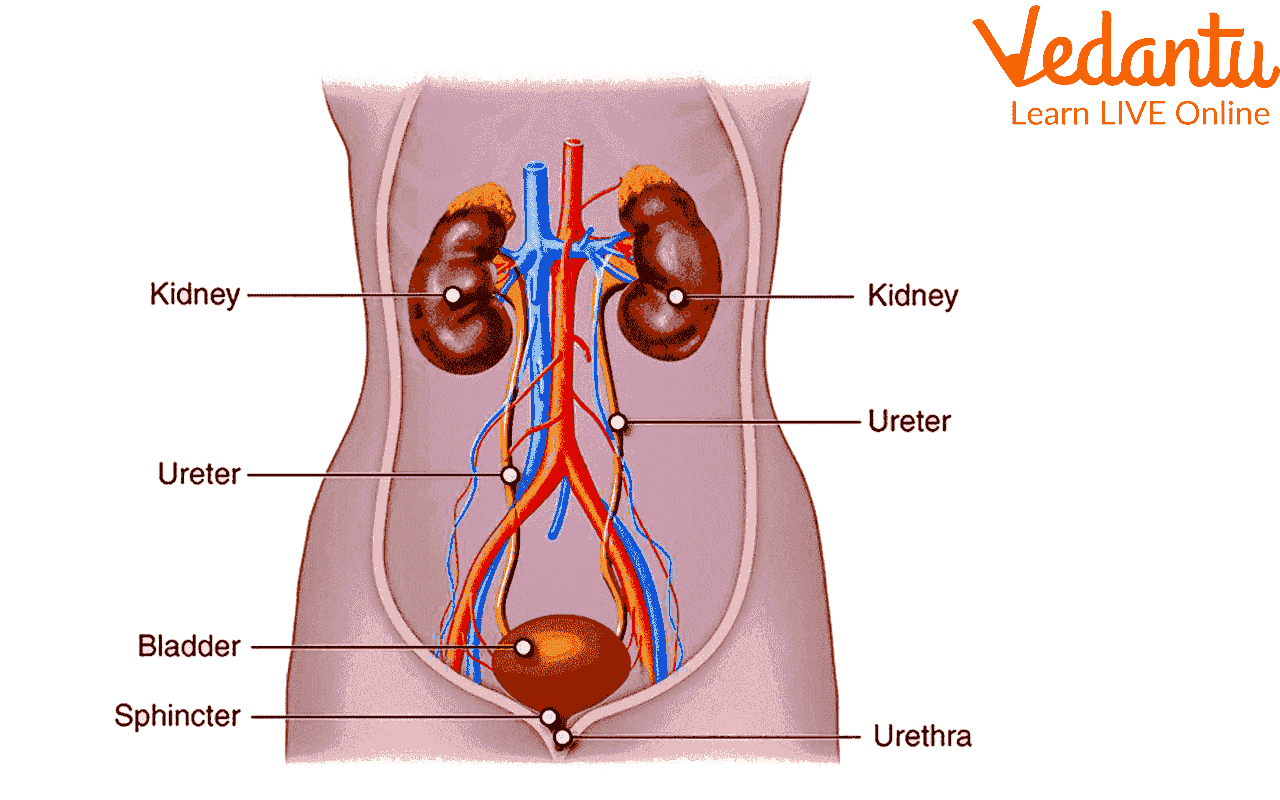
5. Human Excretory System
Excretion removes waste produced by body cells. The human excretory system includes two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra. Kidneys filter blood to form urine, which passes through the ureters to the bladder and leaves the body via the urethra. Urea is a major waste product expelled in urine.
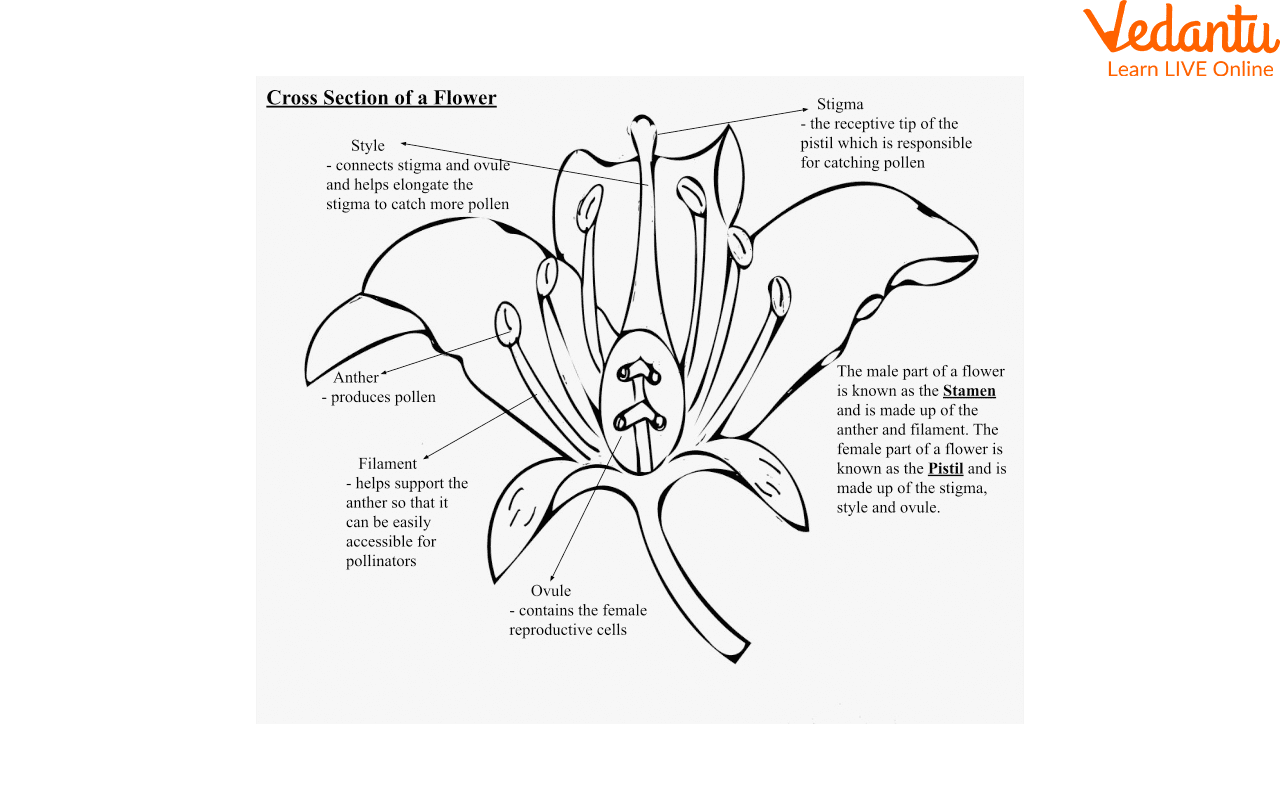
6. Reproductive Parts of a Flower
A typical flower has sepals, petals, stamens (male part), and pistils (female part). The stamen is made of anther and filament, producing pollen. Pistil includes stigma, style, and ovary (which contains ovules). Pollination transfers pollen to the stigma, enabling seeds to form.
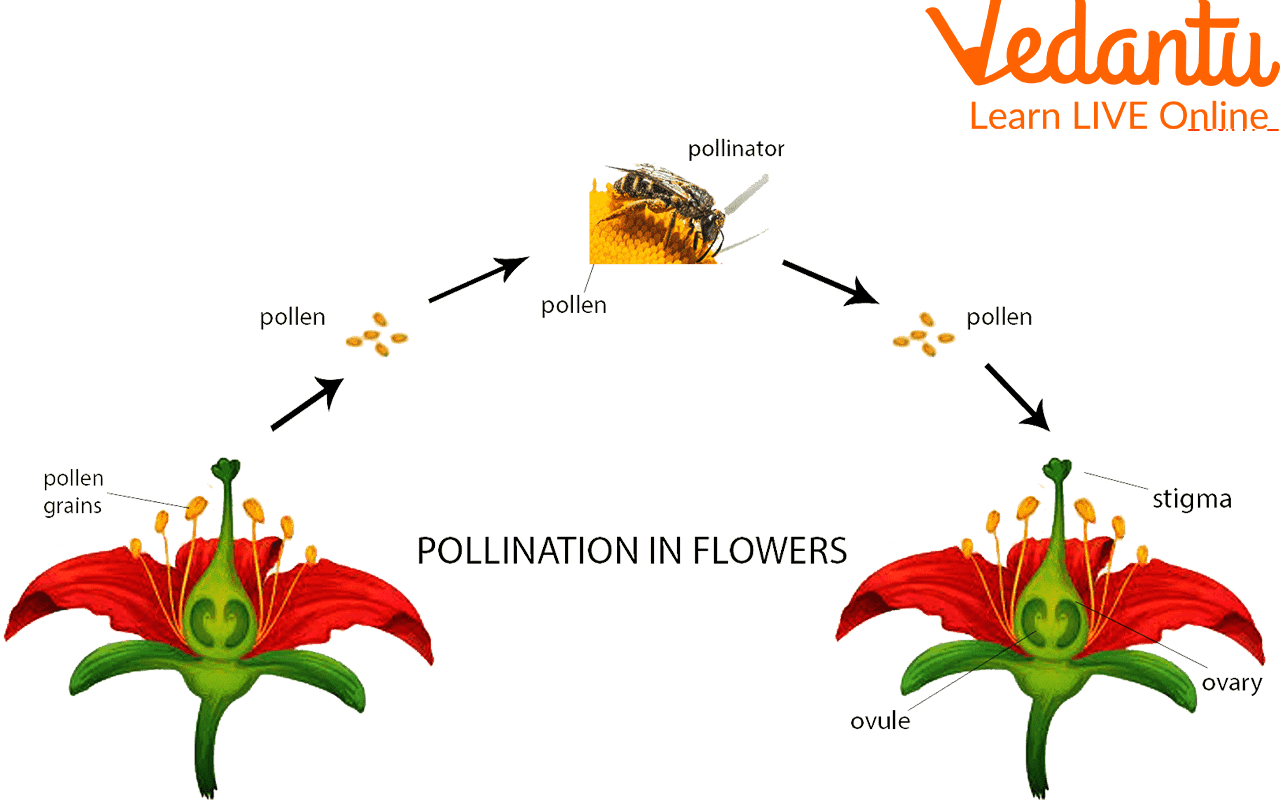
7. Pollination in Flowers
Pollination carries pollen from the anther to the stigma. This may occur within the same flower or between different flowers of the same species. After pollination, the ovules develop into seeds, and fruits form. Cross-pollination introduces features from both parent plants.
Step-by-Step: Drawing and Learning Diagrams
- Read diagram explanations and understand each labelled part.
- Practice by first tracing and then freehand drawing for neatness.
- Label every structure clearly using a ruler for straight lines.
- Revise regularly so diagrams can be recalled quickly in exams.
Key Concepts and Definitions
- Stomata: Tiny pores on leaves for gas exchange and transpiration.
- Photosynthesis: Process by which green plants make food from CO2 and water using sunlight.
- Pseudopodia: Temporary projections of Amoeba used for movement and feeding.
- Excretion: Removal of waste substances from the body.
- Pollination: Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma, leading to fertilisation.
| Diagram | Main Parts | Scientific Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Leaf, stomata, chlorophyll, roots | Basis for plant nutrition & producers |
| Heart Structure | Atria, ventricles, valves | Blood circulation and oxygen delivery |
| Human Excretory System | Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra | Waste removal and homeostasis |
| Flower Parts | Sepals, petals, stamens, pistil | Plant reproduction and seed formation |
Science Practice Questions
- Label the main parts of the human heart and explain their role.
- Draw and compare the reproductive organs of a flower.
- Explain the movement of water during photosynthesis with a diagram.
- Describe the process of digestion in Amoeba using a labelled drawing.
Explore More and Practice
Consistent practice and neat labelling are vital for mastering biology diagrams. Focus on understanding the function behind each part as you draw. For more revision and detailed explanations, visit Vedantu’s comprehensive science diagram resources anytime.


FAQs on CBSE Class 7 Science Biology: Important Diagrams and Explanations
1. What are the most important biology diagrams to learn for CBSE Class 7 exams?
Key biology diagrams for CBSE Class 7 include plant cell, animal cell, human digestive system, structure of heart, structure of flower, root hair, and schematic diagram of blood circulation. These diagrams are directly mapped from NCERT Science Class 7 chapters and are frequently asked in exams.
2. How can I remember diagram labels and their functions effectively?
To remember diagram labels and functions, use these strategies:
- Repeated practice: Redraw and label diagrams regularly from memory.
- Mnemonic devices: Use simple word cues or acronyms for sequences.
- Tables and charts: Compare similar diagrams (e.g., plant vs animal cell) using comparison tables.
3. Which chapters in the NCERT Class 7 Science book require diagram practice?
Important chapters for diagram practice include:
- Cell – Structure and Function
- Nutrition in Animals
- Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Reproduction in Plants
- Respiration in Organisms (for respiratory system basics)
4. What is the difference between the diagrams of plant cell and animal cell?
Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts, which animal cells do not. Plant cells are usually rectangular with a large vacuole, while animal cells are round or irregular in shape and lack chloroplasts and a prominent cell wall.
5. Are labelled diagrams compulsory in CBSE Class 7 Science exams?
Yes, labelled diagrams are often required in CBSE exams. Questions may ask you to draw, label, or identify parts of diagrams. Proper labelling and neatness help secure full marks and demonstrate conceptual understanding.
6. How do I draw a clear diagram of the human digestive system?
To draw the human digestive system:
- Start with the mouth, then draw oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus in sequence.
- Label each part clearly and indicate food pathway with arrows if required.
- Practice using NCERT illustrations for guidance.
7. What tips help in scoring full marks for diagram-based questions?
For full marks on diagram questions:
- Draw neatly with sharp pencil; use rulers for straight lines.
- Label all major parts on the right with straight lines.
- Follow NCERT recommended structure and orientation.
- Use correct terminology and make diagrams large enough for clarity.
8. What does the structure of a flower diagram show?
The structure of a flower diagram typically shows and labels the sepals, petals, stamens (male part: anther and filament), and pistil (female part: stigma, style, ovary). These indicate reproductive organs and help explain pollination.
9. Why are diagrams so important for biology learning in Class 7?
Diagrams help visualise biological structures and processes, making it easier to understand, remember, and apply concepts. They are crucial for answering exam questions clearly and for building strong foundational knowledge for future studies and competitive exams.
10. Where can I find practice worksheets and diagram resources for Class 7 Science?
You can access practice worksheets and diagram resources for Class 7 Science on Vedantu’s official website. These include printable worksheets, sample papers, and NCERT Solutions designed to improve diagram skills and exam performance.
11. What are stomata and how are they shown in plant diagrams?
Stomata are tiny pores on the leaf surface used for gas exchange and transpiration. In diagrams, stomata appear as small openings or ovals on the lower surface of the leaf, sometimes with guard cells illustrated around them.
12. How does mastering diagrams help in future competitive exams like NEET?
Mastering diagrams at this stage builds strong visual and conceptual understanding, which is essential for higher-level questions in exams like NEET and Olympiads. Diagram skills also help with memory retention, error-free answers, and efficient time management in competitive tests.
In this article, we will discuss science drawing for class 7th. In Biology, diagrams are by far the most crucial component. We will also study a clean, labelled diagram of class 7th. After reading this article, readers will be able to explain the diagram of :
Photosynthesis
Human digestive system
Structure of heart
Human excretory system.










