Key Features and Functions of Culex Mosquito in Biology
Culex is a genus of mosquitoes that generally serves as a vector for spreading diseases to birds, humans, and many different animals. This topic is from Chapter 8: ‘Human Health and Diseases.’ Apart from being an important topic for Class 12, this topic is also important for different entrance-level exams.
We will discuss every detail of the Culex mosquito, starting from the Culex mosquito life cycle to the disease caused by the Culex mosquito in this article, along with some FAQs. This topic is full of facts and should be memorised and revised frequently to remember all the facts. Studying this topic will also help students understand the whole chapter accurately.
Culex Mosquito
Culex Mosquito has a size of around 4-10 mm. The body is divided into the head, thorax, and abdomen. The forewings are present in the abdomen region, and the second pair of wings is modified to halteres. Culex mosquito identification is important for the control of the disease. The first identification is based on whether the mosquito is anopheline or culicine. The proboscis of a mosquito is the main part involved in sucking blood from the host.
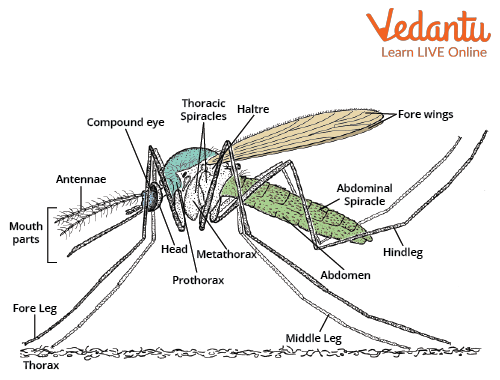
Culex Mosquito Diagram
Hierarchy Classification
Kingdom - Animalia
Phylum - Arthropoda
Class - Insecta
Order - Diptera
Family - Culicidae
Subfamily - Culicinae
Genus - Culex
Culex Mosquito Life Cycle
The life cycle of Culex mosquitoes is divided into 4 stages.
The first stage is the egg stage. Adult female mosquitoes lay eggs on the surface of fresh or stagnant water like barrels, ponds, unmaintained swimming pools, and marshy areas. The female Culex mosquito can lay 100-300 eggs one at a time, sticking together and floating on water.
The second stage is the larval stage. Larvae hatch from mosquito eggs, live in water, and are very active. Larvae shed their skin (moult) several times during this stage and feed on various things found in the water.
The third stage is the pupa stage. Pupae also live in water, and as they do not have external mouthparts, they do not feed during this stage. An adult mosquito emerges from the pupa stage.
The fourth stage is the adult stage. Adult female mosquitoes bite people and animals as they need blood to produce eggs. After feeding on blood, female mosquitoes lay eggs in water. It takes several days to feed and look for a place to lay eggs. They bite human beings only when other animals are not present near them. Since Culex bites animals and people, they live outdoors or near homes, dirty water, garbage areas, and dirty places.
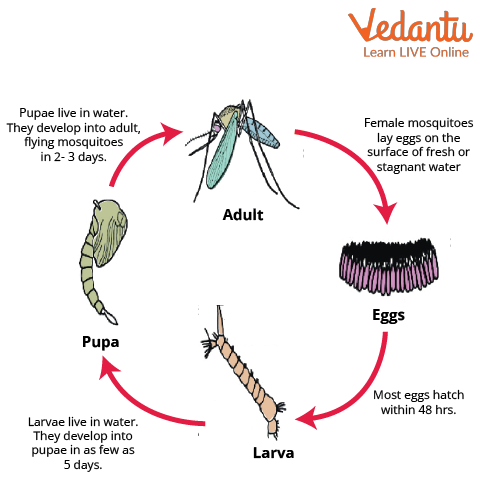
Culex Mosquito Life Cycle
Disease Caused by Culex Mosquito
There is a list of diseases caused by Culex mosquitoes. Arbovirus infections transmitted by various species of Culex include West Nile virus, Japanese encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, and Western and Eastern equine encephalitis. It is also under investigation if Culex species transmit the Zika virus. Nematode infections, mainly in the form of filariasis, may be borne by Culex mosquitoes and bloodsucking flies. The Culex mosquito causes many viral diseases in birds and horses.
Summary
The Culex mosquito genus is culex and belongs to the kingdom Animalia and phylum Arthropoda. The mosquito's body is divided into 3 regions: the head, thorax, and abdomen. The mosquito has a life cycle of 4 stages, starting from the egg, followed by larvae, pupa, and the adult stage. At adult age, only the mosquito can reproduce and form its offspring. The mosquito causes diseases like encephalitis, West Nile fever, and many more.
This article mentions all the necessary concepts related to Culex mosquitoes. This is an important topic for Class 12 under the chapter ‘Human Health and Diseases,’ and this article would help students understand the given topic. Apart from this, the student should study many other diseases for a better knowledge of the chapter.


FAQs on Culex Mosquito: Structure, Life Cycle, and Importance
1. What are the main diseases spread by the Culex mosquito?
The Culex mosquito is a primary vector for several serious diseases affecting humans. The most notable ones include Japanese Encephalitis, a viral brain infection; West Nile Virus, which can cause neurological disease; and Lymphatic Filariasis (often known as Elephantiasis), caused by parasitic worms. The mosquito transmits these pathogens when an infected female bites a human to take a blood meal.
2. How can one identify a Culex mosquito?
A Culex mosquito can be identified by a few key physical and behavioral characteristics:
- Appearance: They are typically dull in colour, usually brown or greyish-brown, and lack the distinct black and white stripes of the Aedes mosquito.
- Resting Posture: When resting on a surface, the body of a Culex mosquito is held parallel to the surface. This is a major difference from the Anopheles mosquito, which rests at an angle.
- Biting Time: Culex mosquitoes are most active and typically bite during the hours of dusk and dawn.
3. What is the difference between a Culex and an Anopheles mosquito?
The key differences between Culex and Anopheles mosquitoes are:
- Resting Posture: Culex rests with its body parallel to the surface, while Anopheles rests at a 45-degree angle with its head down and abdomen pointing up.
- Breeding Site: Culex mosquitoes prefer to lay eggs in rafts on the surface of stagnant or polluted water, such as in drains and ditches. Anopheles prefer cleaner, unpolluted water bodies.
- Eggs: Culex eggs are laid in clusters called rafts, while Anopheles eggs are laid singly and have floats on their sides.
- Diseases: Culex is a primary vector for Japanese Encephalitis and Filariasis, whereas Anopheles is the main vector for Malaria.
4. What are the key stages in the life cycle of a Culex mosquito?
The life cycle of a Culex mosquito consists of four distinct stages, a process known as complete metamorphosis:
- Egg: Female mosquitoes lay hundreds of eggs together in a floating cluster known as a 'raft' on the surface of stagnant water.
- Larva: The eggs hatch into larvae, which live in the water. They hang upside down from the surface and breathe through a siphon tube.
- Pupa: The larva develops into a pupa, which also lives in water but does not feed. This is a non-feeding, resting stage before adulthood.
- Adult: The adult mosquito emerges from the pupal case and, after its body hardens, flies away. The entire cycle can be completed in 7-10 days in optimal conditions.
5. Why are only female Culex mosquitoes considered dangerous to humans?
Only the female Culex mosquito bites humans and other animals because she requires the protein and nutrients from blood to produce and develop her eggs. The male Culex mosquito does not bite and feeds exclusively on plant nectars and juices for energy. Because the female is the one that takes blood meals from different hosts, she is solely responsible for transmitting disease-causing pathogens from an infected host to a healthy one.
6. How does the resting posture of a Culex mosquito help in its identification in the field?
The resting posture is a crucial visual cue for distinguishing between mosquito genera without laboratory equipment. A Culex mosquito rests with its body held parallel to the surface it is on. In contrast, an Anopheles mosquito, the vector for malaria, rests at a distinct 45-degree angle with its abdomen pointing upwards. This simple observation allows for quick field identification, which is vital for public health workers conducting vector control surveys.
7. What are the most effective measures to control the breeding of Culex mosquitoes?
Controlling Culex mosquito populations is most effective when targeting their breeding sites. Since they prefer stagnant and often polluted water, the primary control measures focus on eliminating these habitats:
- Source Reduction: Regularly eliminating standing water in containers like buckets, old tires, and clogged drains.
- Larviciding: Treating water bodies that cannot be drained with approved larvicides or introducing biological control agents like Gambusia fish, which feed on mosquito larvae.
- Improving Sanitation: Ensuring proper maintenance of drainage and sewage systems to prevent water stagnation in urban and rural areas. Targeting the larval stage is more efficient and environmentally sustainable than widespread spraying of insecticides to kill adult mosquitoes.
8. Explain the transmission cycle of Japanese Encephalitis by the Culex mosquito.
The Culex mosquito, particularly the species Culex tritaeniorhynchus, is the main vector for Japanese Encephalitis (JE). The transmission cycle is zoonotic, meaning it involves animals. The virus primarily circulates between mosquitoes and amplifying hosts, such as pigs and wading birds (like herons). The cycle proceeds as follows: an uninfected mosquito bites an infected animal and ingests the virus. The virus multiplies inside the mosquito. The now-infected mosquito then bites a human, transmitting the virus through its saliva. Humans are considered 'dead-end' hosts because the level of virus in their blood is usually too low to infect other mosquitoes that bite them, thereby breaking the cycle.










