How Do Diffusion and Osmosis Work in Cells?
Living organisms depend on various transport mechanisms to move substances in and out of cells. Two key processes in this regard are diffusion and osmosis. Although both are forms of passive transport (they generally do not require energy), there are notable distinctions in how they operate, where they occur, and what types of molecules are involved. In this article, we at Vedantu provide you with an in-depth explanation of the difference between diffusion and osmosis, complemented by unique insights, osmosis and diffusion examples, and an osmosis and diffusion diagram to help you visualise these processes.
Overview of Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of particles (solute and/or solvent) from a region of higher concentration (or energy) to a region of lower concentration (or energy) until equilibrium is reached.
Osmosis, on the other hand, is a specific type of diffusion in which water (or another solvent) moves across a partially permeable membrane from a region with a higher concentration of the solvent to a region with a lower concentration of the solvent.
Both of these processes are critical in biology. For instance, diffusion and osmosis enable cells to acquire essential nutrients, eliminate waste, and maintain suitable conditions for various biochemical reactions.
Key Differences between Diffusion and Osmosis
The table below summarises the difference between diffusion and osmosis:
By understanding these distinctions in osmosis and diffusion, we get deeper insights into how cells regulate their internal environments, how plants draw water from the soil, and how our bodies ensure efficient exchange of gases and nutrients.
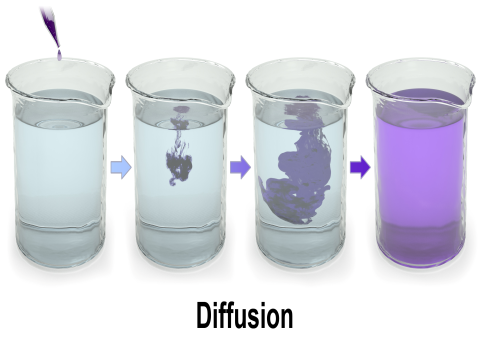
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion occurs in all states of matter – solid, liquid, and gas. In biological systems, diffusion is responsible for the movement of solutes like gases (e.g., oxygen and carbon dioxide) and small molecules (e.g., glucose under certain conditions) across cell membranes.
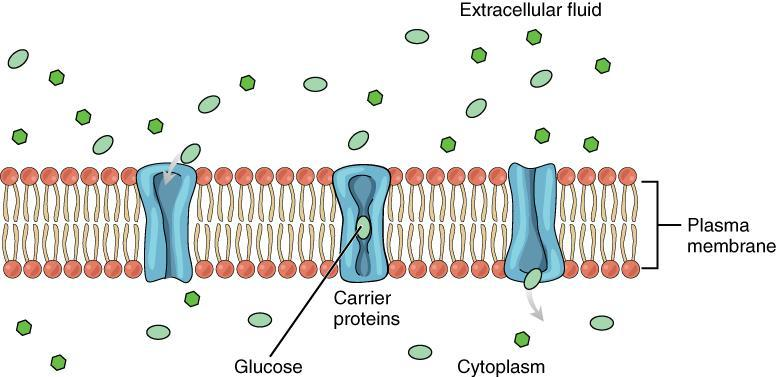
Simple Diffusion: No energy (ATP) is needed. Molecules move directly through the membrane or within the medium from higher to lower concentration.
Facilitated Diffusion: Although it is considered passive transport, it involves specific carrier proteins or channels in the membrane. Often, a small amount of energy may be required (ATP), especially when moving large or charged molecules through specialised proteins.
Example of Diffusion
Perfume in Air: When perfume is sprayed in a room, the scent molecules move from the area of higher concentration (near the spray) to the rest of the room where the concentration is lower.
Gas Exchange in Alveoli (Unique Aspect): In the lungs, oxygen diffuses from the alveolar air spaces (high concentration of oxygen) into the blood (lower concentration of oxygen), while carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction.
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is specifically the movement of solvent molecules (primarily water in biological systems) through a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher concentration of the solvent to a region of lower concentration. This membrane allows only certain molecules to pass through.
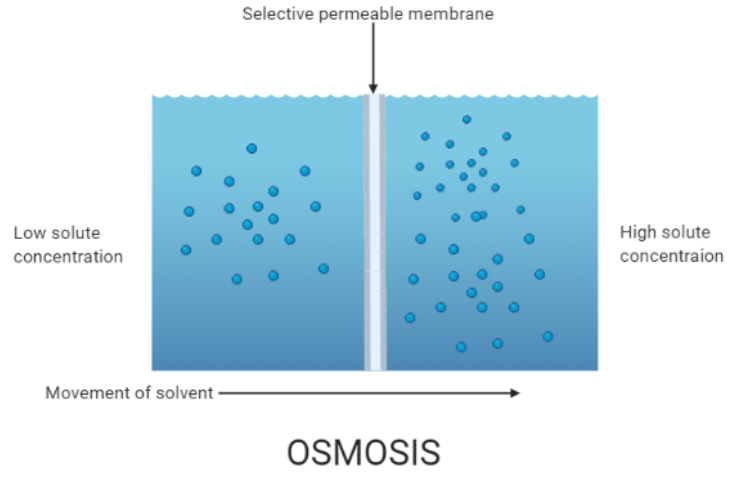
Key Points
Occurs only in a liquid medium in living organisms (primarily water).
Does not require additional energy under normal conditions.
Depends on solute potential, pressure potential, and water potential to drive water movement.
Example of Osmosis
Uptake of Water by Plant Roots: Plants absorb water from the soil, where water concentration is higher, and transport it into root cells, where water concentration is comparatively lower due to dissolved nutrients.
Red Blood Cells in Different Solutions (Unique Aspect): If RBCs are placed in a hypotonic solution, water enters the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to swell. In a hypertonic solution, water moves out, causing cells to shrink.
Osmosis and Diffusion Examples in Daily Life
To further your understanding, here are some everyday osmosis and diffusion examples:
Making Pickles: Cucumbers are placed in a saltwater solution; water moves out of cucumber cells by osmosis, causing them to shrink and become pickles.
Food Colour in Water: A drop of food colouring disperses in water by diffusion, leading to a uniformly coloured solution.
Reviving Wilted Vegetables (Unique Aspect): Placing wilted vegetables in fresh water helps them regain firmness through osmosis, as water moves into their cells.
Sugar Cube in Tea: A lump of sugar eventually dissolves and diffuses throughout the tea, ensuring it tastes sweet all around.
Importance of Diffusion and Osmosis in Living Organisms
Nutrient Transport: Diffusion and osmosis ensure that cells receive the nutrients they need (like glucose, and amino acids) and expel waste products (like CO₂).
Water Balance: Osmosis maintains proper hydration in cells. Plant cells rely on osmosis for turgor pressure, helping them keep their shape.
Gas Exchange: In animals, the exchange of O₂ and CO₂ in the lungs and tissues occurs by diffusion, facilitating respiration.
Homeostasis: Both processes help maintain stable internal conditions, a crucial aspect of living organisms.
Additional Unique Insights – Reverse Osmosis
Unlike normal osmosis, reverse osmosis (RO) involves applying external pressure to force solvent molecules from a more concentrated solution to a less concentrated one. This process is widely used for:
Water Purification
Desalination of seawater
Wastewater Treatment
By understanding reverse osmosis, you gain insight into how technology leverages fundamental biological principles for human benefit.
Also Read:


FAQs on Diffusion vs Osmosis: Definitions, Examples, and Key Differences
1. What is the main difference between diffusion and osmosis?
The primary difference is that diffusion refers to the movement of any type of particle (solute, solvent, or gas) from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. In contrast, osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that exclusively describes the movement of solvent molecules (usually water) across a semipermeable membrane from a high solvent concentration to a low solvent concentration. Diffusion can occur with or without a membrane, but osmosis always requires one.
2. Can you explain the key differences between diffusion and osmosis in a tabular format?
Yes, here are the key differences between diffusion and osmosis:
- Particles Moved: In diffusion, both solute and solvent particles can move. In osmosis, only solvent particles move.
- Membrane Requirement: Diffusion does not require a semipermeable membrane, whereas osmosis strictly requires one.
- System: Diffusion can occur in solids, liquids, and gases. Osmosis occurs only in liquid mediums.
- Concentration Gradient: Diffusion involves the movement of particles down their own concentration gradient. Osmosis involves the movement of solvent molecules down the water potential gradient.
- Example: The smell of perfume spreading in a room is an example of diffusion. The absorption of water by plant roots is an example of osmosis.
3. Why is osmosis considered a special case of diffusion?
Osmosis is considered a special type of diffusion because it follows the same fundamental principle: the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration to achieve equilibrium. However, it has two specific conditions that set it apart: it describes the movement of solvent molecules only (like water), and this movement must occur across a selectively permeable membrane. Therefore, osmosis is essentially the diffusion of water across such a membrane.
4. Do diffusion and osmosis require energy?
No, both simple diffusion and osmosis are forms of passive transport, which means they do not require metabolic energy (like ATP) to occur. The movement is driven entirely by the difference in concentration, known as the concentration gradient. However, a related process called facilitated diffusion uses protein channels to help substances cross a membrane but is still passive. In contrast, active transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient.
5. What are some real-world examples of diffusion and osmosis in living organisms?
In living systems, both processes are vital.
Examples of Diffusion:
- The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the alveoli of the lungs and in body cells.
- The transport of neurotransmitters across a synapse between nerve cells.
- The spreading of absorbed nutrients from the small intestine into the bloodstream.
- Plant roots absorbing water from the soil.
- Red blood cells maintaining their shape in blood plasma. Placing them in pure water causes them to swell and burst due to water influx.
- Kidneys reabsorbing water to regulate the body's water balance.
6. What would happen to an animal cell if it were placed in a highly concentrated salt solution?
If an animal cell, like a red blood cell, is placed in a highly concentrated salt solution (a hypertonic environment), the concentration of water molecules will be higher inside the cell than in the surrounding solution. Due to osmosis, water will move out of the cell and into the solution, following its concentration gradient. This loss of water will cause the cell to shrivel and shrink, a process known as crenation. This demonstrates the critical role of osmosis in maintaining cellular integrity.
7. How does a semipermeable membrane work to allow osmosis but not the free movement of solutes?
A semipermeable membrane, like a cell's plasma membrane, has microscopic pores of a specific size. These pores are large enough for small solvent molecules, such as water, to pass through freely. However, they are too small for larger solute particles (like sugar or salt ions) to pass through. This selectivity is what makes osmosis possible. It creates a situation where only the solvent can move to equalise the concentration on both sides of the membrane, leading to a net flow of water from the region of high water concentration to the region of low water concentration.
8. Can diffusion be stopped or reversed?
Diffusion continues until a state of dynamic equilibrium is reached, where the concentration of the substance is uniform throughout the system. At this point, there is no net movement in any particular direction, but particles continue to move randomly. The process can be effectively stopped or reversed by applying an external force or energy. For example, in reverse osmosis, pressure is applied to a solution to force the solvent to move against its osmotic gradient, a technique commonly used in water purification.










