How Fragmentation and Regeneration Occur in Living Organisms
Fragmentation and regeneration are two captivating biological processes often seen in plants, simple animals, and even some advanced organisms. They play a vital role in survival, reproduction, and adaptation in various environments. Understanding the difference between fragmentation and regeneration helps us appreciate how diverse life on Earth truly is. In this guide, we will also discuss the difference between fragmentation and fission, the difference between fragmentation and budding, and the difference between regeneration and reproduction, with a special look at the difference between fragmentation and regeneration in planaria. Additionally, we will share real-life examples of fragmentation and regeneration to illustrate these concepts more clearly.
Also, read Reproduction in Plants
What Is Fragmentation?
Fragmentation is an asexual mode of reproduction where an organism splits into fragments, and each fragment develops into a fully formed individual. Key points include:
Commonly observed in organisms such as sponges, flatworms, and certain algae like Spirogyra.
Each fragment must contain sufficient cellular structure or tissue to grow independently.
It is a highly efficient way for organisms to increase their population quickly, especially under favourable conditions.
How Fragmentation Differs from Fission
Fission typically involves a single cell splitting into two (as in binary fission in bacteria).
Fragmentation, on the other hand, can involve a multicellular organism breaking into several pieces, each growing into a new individual.
This highlights the difference between fragmentation and fission: fragmentation involves multicellular, often more complex organisms, while fission usually occurs in unicellular organisms.
What is Regeneration?
Regeneration is the process where an organism can regrow or repair lost or damaged body parts. While it may look like a form of reproduction in some cases (for instance, planaria), regeneration often serves more as a survival mechanism. Key points include:
Most organisms display some degree of regenerative ability (like healing wounds), but only a few can regenerate entire limbs or sections of their bodies.
Example: A lizard can regrow its amputated tail, and a starfish can regenerate lost arms.
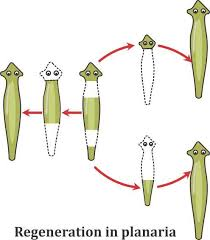
Certain species, such as planaria, can regenerate an entirely new individual if cut into several pieces, blurring the line between regeneration and reproduction.
Regeneration vs. Reproduction
While reproduction generally involves creating an entirely new organism, regeneration often focuses on repair.
However, in specific lower organisms (like planaria), regeneration leads to the formation of new individuals under certain circumstances, which can be mistaken for reproduction.
Hence, the difference between regeneration and reproduction is usually that regeneration is about restoring lost parts, while reproduction specifically aims to produce offspring.
Key Differences Between Fragmentation and Regeneration
This table effectively illustrates the difference between fragmentation and regeneration by focusing on how each process leads to different outcomes and purposes.
Also, read Asexual Reproduction
Difference Between Fragmentation and Regeneration in Planaria
Planaria are flatworms famous for their remarkable regenerative capabilities. When a planarian body is cut into multiple pieces, each piece can grow into a complete individual. In this sense, fragmentation directly triggers regeneration, resulting in the creation of new planaria. Therefore, the difference between fragmentation and regeneration in planaria blurs since the organisms use fragmentation as a reproductive strategy, and regeneration is the mechanism that completes the process.
Difference Between Fragmentation and Budding
Budding involves the formation of an outgrowth (bud) that remains attached to the parent until it matures and then detaches as a new individual (e.g., Hydra).
In fragmentation, the original body splits into fragments on its own, and each fragment develops into a new organism.
This emphasises the difference between fragmentation and budding: budding grows a small bud externally, while fragmentation breaks the original body into sections.
Difference Between Regeneration and Reproduction
Although regeneration can sometimes result in the formation of a completely new individual (especially in simpler organisms), it is primarily a repair mechanism. Meanwhile, reproduction (whether sexual or asexual) is the biological process specifically aimed at producing offspring. Thus, the difference between regeneration and reproduction lies in their biological intent: survival and repair versus the generation of new life.
Examples of Fragmentation and Regeneration
When looking for a clear example of fragmentation and regeneration, consider the following:
Fragmentation: Spirogyra (an algae) breaks into smaller filaments, each capable of growing independently.
Regeneration: A starfish losing an arm to a predator can regrow that arm; if certain conditions are met, the lost arm portion might even regenerate into a new starfish.
These examples show that some organisms use fragmentation purely for reproduction, while others rely on regeneration for healing or partial reproduction under specific circumstances.
Key Points
Partial vs. Complete Regeneration: Some organisms only regenerate superficial tissues, while others (like planaria and starfish) can regrow entire body structures.
Environmental Triggers: Certain species fragment under stress (e.g., sponges releasing gemmules in unfavourable conditions).
Cellular Basis: Advanced regenerative abilities often rely on pluripotent stem cells that can differentiate into various cell types necessary for regrowth.
These extra details showcase the broader contexts in which these processes operate, ensuring a well-rounded understanding beyond a simple chart or table.
Interactive Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
Which of these organisms commonly reproduces through fragmentation?
A. Hydra
B. Spirogyra
C. Amoeba
D. Paramecium
Regeneration typically helps an organism to:
A. Produce new spores
B. Regrow lost body parts
C. Perform photosynthesis
D. Increase oxygen intake
Which statement best describes the difference between fragmentation and budding?
A. Both involve outgrowths that detach from the parent.
B. Fragmentation needs external assistance, while budding does not.
C. In fragmentation, the body splits into pieces; in budding, a small bud grows and detaches.
D. Both are strictly sexual processes.
Planaria are well-known for which unique feature?
A. Bud formation
B. Complex organ systems
C. Advanced neural networks
D. Ability to regenerate from small fragments
Which of the following statements highlights the difference between regeneration and reproduction?
A. Regeneration repairs lost body parts; reproduction aims to create new individuals.
B. Both result solely in the formation of brand-new organisms.
C. Reproduction only takes place in mammals; regeneration takes place only in reptiles.
D. They are both forms of sexual reproduction.
Check Your Answers
B
B
C
D
A


FAQs on Difference Between Fragmentation and Regeneration Explained
1. What is the primary difference between fragmentation and regeneration?
The primary difference lies in the outcome. Fragmentation is a method of asexual reproduction where an organism breaks into pieces, and each piece grows into a new, complete individual. In contrast, regeneration is the process of regrowing a lost or damaged body part, which does not necessarily result in a new organism.
2. How are fragmentation and regeneration related processes?
Fragmentation and regeneration are often linked, especially in simpler organisms. For fragmentation to be a successful method of reproduction, the broken fragments must have the ability to regenerate the missing parts to form a complete organism. Therefore, regeneration is the underlying biological mechanism that makes reproduction via fragmentation possible in creatures like Planaria and Spirogyra.
3. How does fragmentation work as a method of reproduction in an organism like Spirogyra?
In Spirogyra, a filamentous alga, the long filament breaks into two or more smaller pieces or fragments due to mechanical disturbance or natural processes. Each of these fragments, containing at least one cell, has the capacity to grow through cell division into a new, fully developed Spirogyra filament. This is a classic example of asexual reproduction.
4. In Planaria, how does regeneration lead to reproduction after fragmentation?
Planaria exhibit a remarkable capacity for both processes. If a Planarian worm is cut into several pieces (fragmentation), each piece contains enough genetic information and specialised cells (neoblasts) to regenerate all the missing body parts. A fragment from the head section will regrow a tail, and a tail fragment will regrow a head, resulting in multiple new, genetically identical worms from the original one.
5. How does the ability to regenerate differ between simple organisms and more complex ones?
The ability to regenerate is generally more extensive in simpler organisms.
- Simple Organisms: Organisms like Hydra or Planaria can regenerate their entire body from a small fragment because they possess a large number of undifferentiated or totipotent cells.
- Complex Organisms: Organisms like lizards or starfish show limited, or restorative regeneration. They can regrow specific parts like a tail or an arm, but cannot regenerate an entire body from a single limb. In mammals, this ability is further restricted to tissue repair, like healing skin or regenerating parts of the liver.
6. To what extent can humans regenerate tissues, and how does this differ from the regeneration seen in starfish?
Human regeneration is very limited. We can regenerate certain tissues like the epidermis (skin), the lining of the gut, and parts of the liver. This is primarily a process of cell repair and replacement. In contrast, a starfish can perform organ-level regeneration. If it loses an arm, it can regrow a new one. Some starfish species can even regenerate a whole new body from a single severed arm, provided it contains a part of the central disc.
7. What is the role of specialised cells in the process of regeneration?
Specialised cells, often called stem cells, are crucial for regeneration. In organisms like Planaria, pluripotent stem cells called neoblasts can migrate to the site of injury and differentiate into any cell type needed to rebuild the lost tissue or organ. In more complex animals, regeneration depends on populations of adult stem cells that are more restricted in their potential but can still repair specific tissues like muscle, bone, or skin.
8. What is the key difference between fragmentation and budding?
The key difference is the formation process. In budding (e.g., in Hydra), a new individual develops from a small outgrowth or 'bud' on the parent's body, which then detaches. In fragmentation, the parent organism does not form a specific outgrowth; instead, its entire body breaks into multiple pieces, each of which then develops into a new individual. Budding is a deliberate outgrowth, while fragmentation is a division of the whole body.
9. What are the evolutionary advantages of using fragmentation as a reproductive strategy?
Fragmentation offers several evolutionary advantages, particularly in stable environments. It allows for rapid population growth since multiple offspring can be produced from a single parent without the need to find a mate. This method requires less energy than sexual reproduction and ensures that successful genetic traits well-suited to the current environment are passed on directly to genetically identical offspring.
10. Why is regeneration often limited to specific body parts (like a lizard's tail) and not entire limbs in higher animals?
Regeneration is limited in higher animals due to increased cellular and tissue complexity. Regrowing a complex structure like a limb requires a precise sequence of events involving multiple tissue types (bone, muscle, nerves, blood vessels) which is incredibly difficult to coordinate. A lizard's tail is a simpler, semi-autonomous structure designed to be lost (a process called autotomy). The genetic and cellular pathways for such complex regeneration have been largely suppressed during the evolution of vertebrates in favour of more efficient wound healing and scarring mechanisms.










