How to Identify a Leopard vs a Cheetah: Physical and Behavioral Clues
When people think of big cats, two names often come to mind: the leopard and the cheetah. Because both species have spotted coats and share habitats in certain parts of Africa and Asia, many wonder about the difference between cheetah and leopard and jaguar or even the difference between leopard and cheetah spots. While all these wild cats belong to the Felidae family, they differ significantly in appearance, hunting techniques, social behaviour, and more. In this article, we will dig deep into leopard vs cheetah distinctions, and we will also touch upon topics such as the difference between leopard and jaguar and the difference between cheetah and tiger, ensuring you gain a holistic understanding of these majestic felines.
Overview of Classification and Distribution
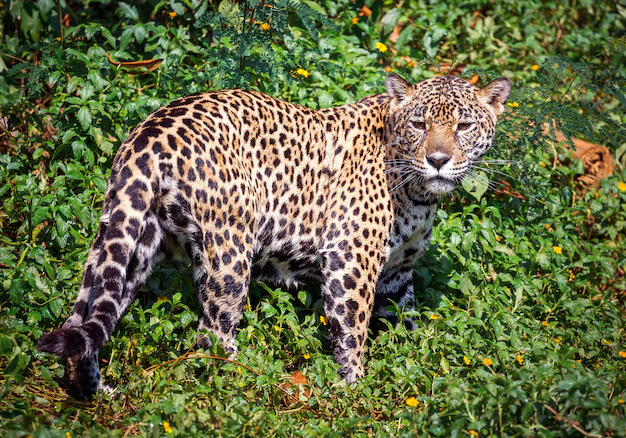
Leopard (Panthera pardus)
Habitat: Widely distributed across Africa, the Middle East, parts of Asia, and even remote regions in Siberia.
Preferred Environment: Adaptable to grasslands, dense forests, deserts, and mountainous regions.
Conservation Status: Listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List due to habitat loss and poaching.
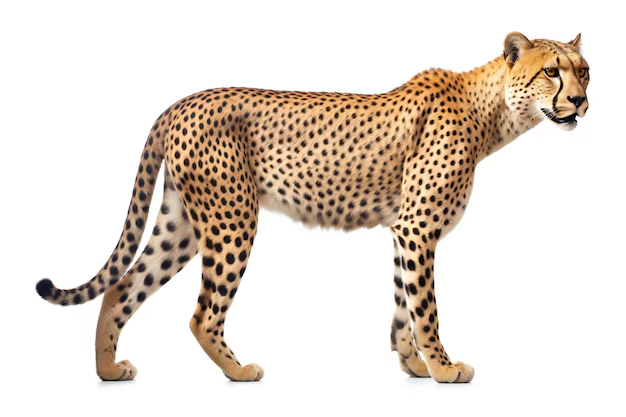
Cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus)
Habitat: Predominantly found in African savannahs; a small population persists in Iran.
Preferred Environment: Open grasslands, savannahs, and sometimes open forests.
Conservation Status: Listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List; threatened by habitat fragmentation, conflict with livestock farmers, and declining prey.
Major Physical Differences
One quick way to answer what is the difference between cheetah and leopard and jaguar is to look closely at their body shape and coat patterns. While jaguars have distinctly stockier bodies and rosettes with central spots, let’s first focus on leopard vs cheetah distinctions:
Body Build
Cheetah: Slender, aerodynamic frame, built for sprinting. Long legs and a flexible spine allow it to achieve remarkable acceleration.
Leopard: More muscular and stocky. They excel in climbing and ambush hunting, needing powerful limbs and robust shoulders.
Coat Patterns
Cheetah: Has small, solid black spots covering the entire body. The fur is somewhat coarse, suiting the open savannah habitats. This is a key difference between leopard and cheetah spots—cheetahs never develop rosettes.
Leopard: Features rosette-like spots (irregular circle shapes with lighter centres) across its coat. These rosettes provide excellent camouflage in forested or shaded habitats.
Facial Markings
Cheetah: Distinctive black tear-like streaks run from the inner corners of the eyes down to the mouth. They help reduce glare from the sun during daytime hunts.
Leopard: Absent of these tear marks; instead, leopards often have solid or rosette markings on the face.
Claws
Cheetah: Semi-retractable claws that function much like track spikes, offering traction during rapid sprints.
Leopard: Fully retractable claws, which help grip prey and climb trees effectively.
Hunting Strategies and Social Behaviour
Hunting Styles
Cheetah: A classic example of a pursuit predator. Famous for cheetah vs leopard speed comparisons, cheetahs can sprint up to 110–115 km/h over short distances. They usually hunt during the day to avoid competition with larger nocturnal predators.
Leopard: Stealthy, ambush hunter. Leopards excel at stalking prey under cover and pouncing unexpectedly. They can tackle prey at night, relying on powerful jaws and strong limbs to drag kills up trees.
Social Structure
Cheetah: Generally social compared to other big cats. Female cheetahs raise cubs alone, but male siblings may form coalitions that stay together for life.
Leopard: Solitary creatures. Adults mostly come together only for mating. Females raise cubs independently, defending a territory against other leopards.
Cheetah vs Leopard Speed
When people ask about cheetah vs leopard speed, the numbers speak for themselves:
Cheetah: The fastest land animal, reaching bursts of about 110–115 km/h. Their lightweight frame, elongated limbs, and non-retractable claws optimise them for speed.
Leopard: While leopards are no slowpokes (topping around 50–60 km/h), they rely less on outright speed and more on stealth and power.
What is the Difference Between Cheetah and Leopard and Jaguar?
So far, we have compared the leopard vs cheetah thoroughly. But you might still wonder about the difference between a leopard and a jaguar. Although leopards and jaguars can appear quite similar at first glance (both have rosettes), there are key distinctions:
Jaguar (Panthera onca):
Native Range: The Americas (from the southern United States to northern Argentina).
Physical Build: More robust and stockier than leopards, with larger rosettes that often contain a central black spot.
Behaviour: Known for a powerful bite force, capable of crushing skulls with a single bite. Often associated with aquatic habitats and very strong swimmers.
Hence, the difference between leopard and jaguar includes habitat, rosette patterns, and body size.
Difference Between Cheetah and Tiger in Table
Below is a summary table highlighting key differences between leopards and cheetahs:
Five Fascinating Facts You May Not Know
Vocalisations:
Cheetahs can purr, chirp, and hiss but cannot roar.
Leopards can roar (though not as loudly as lions).
Respiratory Adaptations:
Cheetahs have large nostrils and lungs for rapid oxygen intake during sprints.
Leopards’ respiratory system is strong enough for exertion, but they rely more on stealth than on prolonged chases.
Preferred Hunting Times:
Cheetahs are mainly diurnal hunters.
Leopards are mostly nocturnal, though they can adapt if needed.
Habitat Flexibility:
Cheetahs thrive in open spaces where speed is advantageous.
Leopards can live in diverse environments—from deserts to forests—thanks to their adaptability.
Global Reintroduction Efforts:
Several wildlife organisations are attempting to reintroduce cheetahs into regions like India.
Leopards remain one of the most widespread big cats but face increasing habitat pressure.
Interactive Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
1. Which big cat has tear-like streaks on its face?
a) Leopard
b) Cheetah
c) Jaguar
2. Who typically hunts during the day?
a) Leopard
b) Cheetah
c) Both
3. Which species is known for dragging its prey up trees?
a) Cheetah
b) Leopard
c) Tiger
4. Which cat can run up to 110–115 km/h?
a) Leopard
b) Jaguar
c) Cheetah
5. Which big cat has fully retractable claws?
a) Cheetah
b) Leopard
c) Neither
Check Your Answers
b) Cheetah
b) Cheetah
b) Leopard
c) Cheetah
b) Leopard


FAQs on Leopard vs Cheetah: Main Differences Every Student Should Know
1. What are the main physical differences between a leopard and a cheetah?
The primary physical differences between a leopard and a cheetah lie in their body build, coat patterns, and facial markings.
- Body Build: Leopards have a muscular, stocky build designed for power and climbing, while cheetahs have a slender, aerodynamic frame built for sprinting.
- Coat Patterns: Leopards are covered in rosettes (irregular, rose-like circles), which provide camouflage in forests. Cheetahs have simple solid black spots on their coat.
- Facial Markings: Cheetahs are easily identified by their distinct black “tear marks” running from their eyes to their mouth, which leopards lack.
2. How do the differences in speed between a cheetah and a leopard affect their hunting strategies?
Their contrasting speeds lead to completely different hunting methods. The cheetah, as the fastest land animal reaching speeds of up to 115 km/h, is a pursuit predator. It uses short, high-speed bursts to chase down prey in open grasslands. In contrast, the leopard, which is slower at around 60 km/h, is a stealthy ambush predator. It relies on its muscular build and camouflage to stalk prey silently and pounce at close range, often hunting at night.
3. Why do leopards have rosettes while cheetahs have solid spots?
The difference in coat patterns is a direct result of their adaptation to different environments and hunting styles. Leopards' rosettes are a form of disruptive camouflage that perfectly mimics the dappled sunlight filtering through the leaves of trees and dense bushland. This allows them to remain hidden while stalking prey or resting. Cheetahs' solid spots provide camouflage in open savannahs by breaking up their body outline against the uniform, grassy background during high-speed chases.
4. What is the difference in the claws of a leopard and a cheetah, and how does this relate to their lifestyle?
The claws of leopards and cheetahs are a key example of evolutionary adaptation. Leopards have fully retractable claws, like most cats, which they keep sharp for climbing trees and gripping prey. In contrast, cheetahs have semi-retractable claws that do not fully retract. These claws act like running spikes, providing extra traction and grip on the ground during their high-speed sprints.
5. What is the purpose of the black 'tear marks' on a cheetah's face?
The distinctive black tear-like streaks running from the inner corner of a cheetah's eyes down to its mouth are an adaptation for their diurnal (daytime) hunting habits. These marks are thought to reduce glare from the sun, functioning like natural anti-glare sunglasses. This helps them maintain focus on their prey during a chase in the bright, open savannah.
6. Are leopards and cheetahs solitary or social animals?
Leopards and cheetahs have different social structures. Leopards are classic solitary creatures, only coming together for mating. They live and hunt alone. Cheetahs, however, are more social. While females are solitary when raising cubs, male cheetahs, particularly brothers from the same litter, often form lifelong groups called coalitions to defend territory and hunt together.
7. Can leopards and cheetahs both roar?
No, only leopards can roar. Leopards belong to the genus Panthera, whose members have a specialised larynx and hyoid apparatus that allows them to roar. Cheetahs, belonging to the genus Acinonyx, lack this structure. Instead of roaring, cheetahs make other vocalisations such as purrs, chirps, and hisses.
8. How can you distinguish a leopard from a jaguar, since both have rosettes?
While both have rosettes, there are key differences to tell them apart. Jaguar rosettes are typically larger and more complex, often containing one or more black dots in the centre. Leopard rosettes are smaller and do not have central spots. Additionally, jaguars have a much stockier, more powerful build than leopards and are primarily found in the Americas, whereas leopards are native to Africa and Asia.
9. What is the difference between a leopard, a cheetah, and a panther?
A "panther" is not a distinct species of big cat. The term is used to describe melanistic (black) individuals of other cat species. A black panther in Asia or Africa is a melanistic leopard, while a black panther in the Americas is a melanistic jaguar. Therefore, the key difference is that leopards and cheetahs are distinct species, whereas a panther is a colour variant of a leopard or jaguar.
10. Which big cat is stronger, the leopard or the cheetah, and why?
The leopard is significantly stronger than the cheetah. A leopard's body is more muscular and robustly built for power, enabling it to take on large prey and famously drag heavy carcasses up trees to protect them from scavengers. The cheetah's physique is optimised for speed, not strength, featuring a lightweight frame and slender muscles designed for acceleration rather than powerful grappling.