How big or small can an ecosystem be?
An ecosystem is a dynamic community where living organisms interact with each other and their physical surroundings. Studying the ecosystem reveals the balance that supports all life on Earth. From understanding everyday environments to preparing for ecosystem MCQs in exams, this topic empowers students to connect biology with environmental issues, agriculture, and real-world sustainability.
Ecosystem Definition
Ecosystem refers to a biological community of organisms together with the non-living (abiotic) environment they inhabit and interact with. This includes relationships among plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, soil, water, air, sunlight, and minerals. Energy flows and nutrient cycles are central to the functioning of any ecosystem. The term is widely used in biology class 12, ranging from ecosystem short notes to ecosystem diagrams and ecosystem ppt presentations.
Structure of Ecosystem
Understanding the structure of an ecosystem involves identifying its main components. These are classified as:
- Biotic Components: All living things like plants, animals, microorganisms.
- Abiotic Components: Non-living factors such as soil, water, air, minerals, temperature, and sunlight.
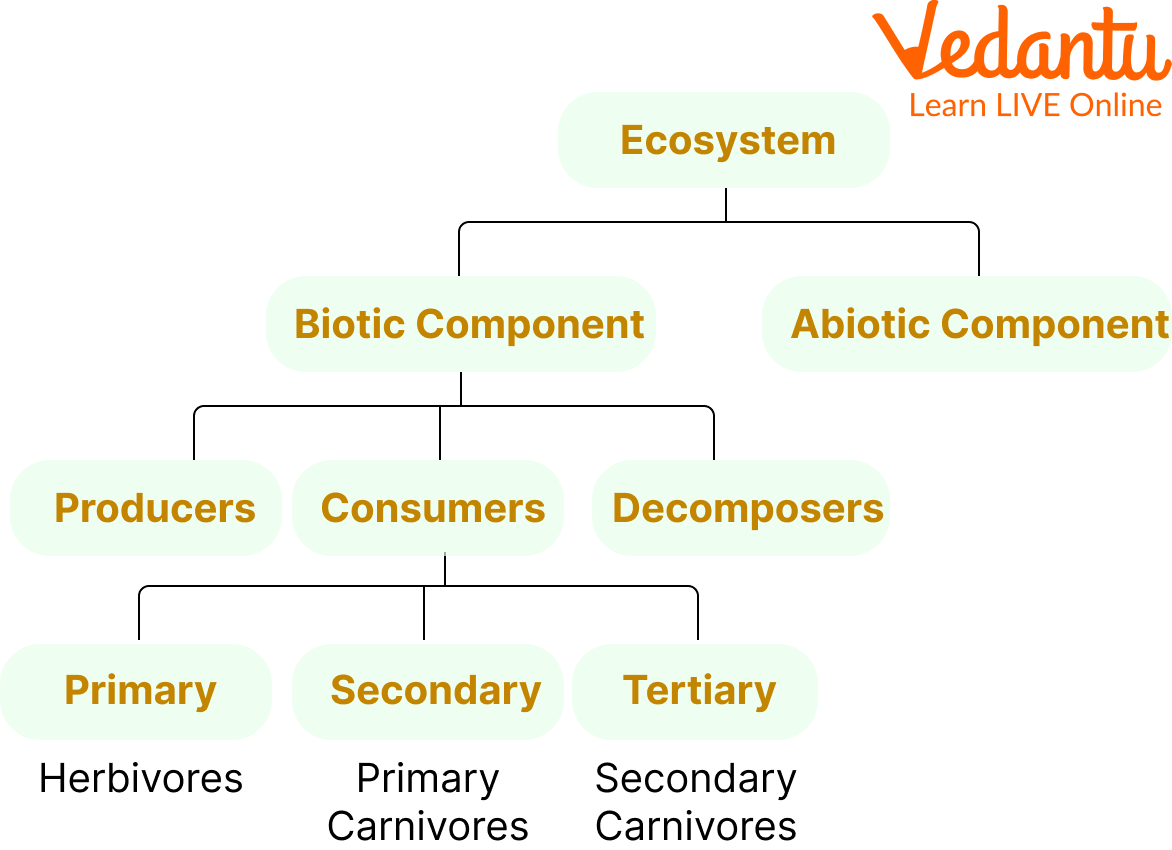
Producers (like green plants) use sunlight to make food. Consumers depend on plants or other animals for energy. Decomposers break down dead material, recycling nutrients for reuse.
Scales and Size of Ecosystem
An ecosystem can exist at many scales, from the tiny (a puddle, a moss patch) to the enormous (forests, oceans, or the Earth itself). There are no fixed boundaries for ecosystems, and often, one merges gradually into another through a transition zone called an ecotone. For instance:
- A small pond or the back of a tree can be an ecosystem.
- A forest, wetland, or large lake is a medium-scale ecosystem.
- Rainforests or coral reefs are large, complex ecosystems.
- The entire biosphere, including land, water, and air, is the largest ecosystem.
Physical barriers such as mountains, lakes, or deserts often influence the boundaries between different ecosystems.
Types and Examples of Ecosystems
Ecosystems can be broadly categorized based on where they are found. Here are two major types, along with ecosystem examples:
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: Found on land. Examples include forests, grasslands, deserts, and mountains. Learn more about terrestrial ecosystems.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Occur in water. This includes freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds) and marine (oceans, estuaries) ecosystems. Explore details at Vedantu's aquatic ecosystem page.
These divisions help us study how different living beings adapt and survive in specific environmental conditions.
Ecosystem Functioning and Processes
Every ecosystem operates through certain key processes that maintain life and energy balance. The main processes are:
- Energy Flow: Sunlight is captured by plants, passed to herbivores, then to carnivores, and finally to decomposers.
- Nutrient Cycling: Elements like carbon, nitrogen, and water move in cycles between living and non-living components.
- Decomposition: Dead matter is broken down, returning nutrients to soil or water.
- Trophic Levels: Organisms are grouped based on how they get energy, forming food chains and food webs.
Human actions such as agriculture, deforestation, and pollution directly affect these ecosystem processes. For current challenges, see effects of climate changes and pollution and calamities.
Ecosystem Diversity and Importance
Ecosystem diversity means the variety of unique ecosystems within a region. For example, India has deserts, forests, grasslands, wetlands, and islands. Maintaining this diversity supports:
- Clean air and water
- Balanced climate and soil fertility
- Pollination and food production
- Medicinal resources and materials
- Biodiversity conservation
Preserving ecosystem variety is vital for sustainable development. For deeper class 12 understanding, check out autotrophs and heterotrophs and life science.
Ecosystem Diagram
Ecosystem diagrams visually show the interaction between producers, consumers, decomposers, and abiotic factors. They help students grasp food chains, food webs, and nutrient cycles. To improve your ecosystem notes or ecosystem PPT presentation, try drawing labelled diagrams showing energy flow from the sun to plants, animals, and decomposers, or review CBSE class 7 important diagrams at Vedantu.
Ecosystem Questions and MCQs
Prepare for exams with practice ecosystem questions, MCQs, and case studies. Important areas include:
- Defining ecosystem and its components
- Identifying examples of various ecosystems
- Explaining energy flow, food chains, and food webs
- Describing ecosystem services and human impacts
Vedantu offers ecosystem MCQs, short notes, and questions for competitive exams and board studies.
Significance and Applications of Ecosystem Study
Ecology and ecosystem knowledge extends into many fields:
- Environmental science: Understanding global warming and natural resource management.
- Food science: Sustainable agriculture and food web insights. Learn more at food science.
- Medicine: Discovery of drugs from plants and microbes within specific ecosystems.
- Human health: Clean air, water, and stable climates come from healthy ecosystems.
Ecosystem study also helps in conserving endangered habitats and meeting global challenges such as food security and biodiversity loss.
Page Summary
Ecosystems unite living and non-living components to create self-sustaining environments for all life. Studying ecosystems helps us understand energy flow, species diversity, and environmental balance. This knowledge supports conservation, health, agriculture, and real-world problem solving. For further exploration, Vedantu provides detailed notes, diagrams, and MCQs tailored for student success.


FAQs on What is an ecosystem and how is it structured?
1. What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with each other and with their non-living environment.
Key points to remember:
- Biotic factors: living components, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Abiotic factors: non-living components, like air, water, soil, and sunlight.
- Energy flows through food chains and food webs in an ecosystem.
- Ecosystems maintain a balance through the interaction of their components.
2. What are the main components of an ecosystem?
The main components of an ecosystem are biotic (living organism) and abiotic (non-living elements) factors.
- Biotic: plants, animals, microorganisms
- Abiotic: sunlight, temperature, water, soil, minerals, air
3. How do producers, consumers, and decomposers work in an ecosystem?
Producers, consumers, and decomposers each play an important role in the ecosystem.
- Producers (like green plants) make food using sunlight via photosynthesis.
- Consumers (animals) eat producers or other consumers for energy.
- Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) break down dead matter and recycle nutrients back to the soil.
4. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain shows a single, linear pathway of energy flow, while a food web illustrates multiple pathways and interconnections between organisms.
- Food chain: Simple, one-way flow; producer → primary consumer → secondary consumer → decomposer.
- Food web: Complex, includes several interconnected food chains within the same ecosystem.
5. What are the types of ecosystems?
Ecosystems can be classified based on their environment.
- Terrestrial ecosystems: Forests, grasslands, deserts
- Aquatic ecosystems: Freshwater (ponds, lakes, rivers) and marine (oceans, seas)
6. Why is energy flow in an ecosystem unidirectional?
Energy flow in an ecosystem is unidirectional because energy enters as sunlight, is converted by producers, and flows from one organism to another without being recycled.
- Once used, energy is lost as heat at every trophic level.
- Nutrients are recycled, but energy does not return to the original source.
7. What are trophic levels?
Trophic levels are the steps in a food chain or food web, showing the feeding position of organisms.
- Producers (First trophic level): Plants and algae
- Primary consumers (Second level): Herbivores
- Secondary consumers (Third level): Carnivores
- Tertiary consumers (Fourth level): Top predators
8. What happens if one component of an ecosystem is removed?
Removing any component can disrupt the balance of the ecosystem.
- Predators control prey populations; removing them may cause overpopulation of herbivores.
- If a producer is removed, food and oxygen decrease for higher levels.
- Decomposers recycle nutrients; without them, waste accumulates and plants lack nutrients.
9. How do humans affect ecosystems?
Humans impact ecosystems in various ways, often leading to ecological imbalance.
- Deforestation destroys habitats.
- Pollution contaminates air, water, and soil.
- Overhunting and overfishing disturb population balance.
- Climate change alters habitat conditions and species survival.
10. What is ecological balance in an ecosystem?
Ecological balance refers to the stable state where all organisms and environmental factors coexist in harmony.
- Population sizes remain in equilibrium.
- Nutrients and energy circulate efficiently through various cycles.
- Human interference can disrupt this balance, leading to environmental problems.
11. Define biotic and abiotic components with examples.
Biotic components are the living organisms in an ecosystem, and abiotic components are the non-living factors.
- Biotic: Plants, animals, bacteria, fungi
- Abiotic: Sunlight, temperature, water, soil, air
12. What do you mean by the term 'producers' in an ecosystem?
Producers are green plants and some algae that prepare their own food by using sunlight in the process called photosynthesis.
- They form the base of the food chain.
- Provide energy and nutrients to all other organisms in the ecosystem.










