How Does Genetic Drift Shape Evolution in Populations?
Genetic drift refers to random changes in the frequency of alleles (forms of a gene) within a population over generations. It tends to have a more pronounced effect in smaller populations because each individual’s genes represent a larger fraction of the entire gene pool. Unlike natural selection, which favours alleles that improve fitness, genetic drift is not influenced by how beneficial or harmful an allele is—it depends purely on chance.
In large populations, the impact of chance events on allele frequencies is generally diluted. However, in small populations, even minor random events (such as the loss of a few individuals) can significantly alter the genetic makeup of the group.
Types of Genetic Drift
Bottleneck Effect
The bottleneck effect occurs when a population’s size is drastically reduced due to events like natural disasters, disease outbreaks, or severe predation. This sudden reduction in population size can eliminate entire alleles if the individuals carrying them do not survive.
Population Size Drops: A large, genetically diverse population shrinks quickly.
Loss of Alleles: Certain alleles may be completely lost due to chance.
Reduced Variability: The surviving population exhibits lower genetic variation.
An example often cited is when a natural disaster, such as a volcanic eruption or earthquake, wipes out most of a species. The remaining few survivors pass on only the alleles they carry, reducing the overall genetic diversity.
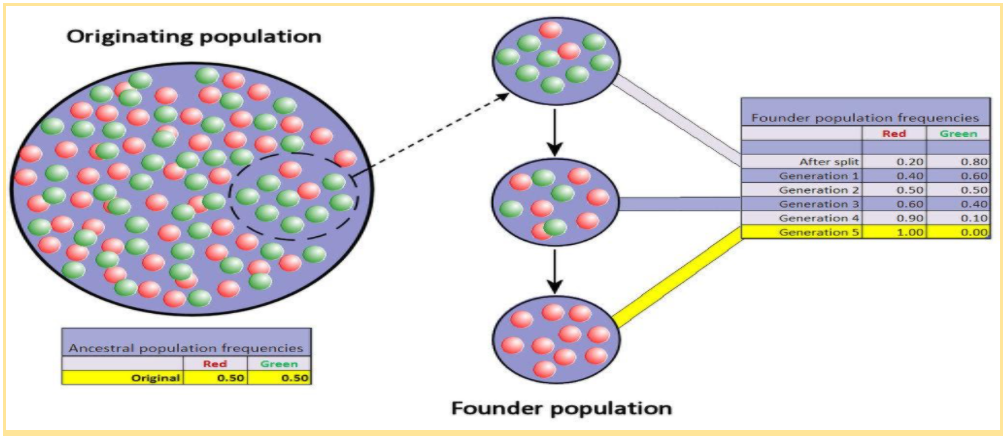
Founder Effect
The founder effect takes place when a small group of individuals establishes a new population in a geographically isolated location. Since this group is separated from the original population, there is no gene exchange between the two groups.
New Population: Formed by a few “founders” in an isolated region.
Limited Gene Pool: Allele frequencies in the new population may differ from the original population due to the small starting gene pool.
Potential Speciation: Over time, the new population can diverge so much that interbreeding with the original population may no longer be possible.
A classic founder effect example is when a few birds of the same species reach a distant island. Their genes become the starting point for all subsequent generations on that island, potentially leading to new species if genetic changes accumulate over many generations.
What Causes Genetic Drift?
Genetic drift arises primarily due to chance events in reproduction and survival. In smaller populations, these events have a more substantial impact on allele frequencies. Some key factors include:
Random Mating and Fertilisation: Not all alleles are equally passed on to the next generation simply because of the random pairing of gametes.
Random Mortality: A sudden death of individuals carrying certain alleles can remove those alleles from the gene pool.
Population Isolation: Limited gene exchange can amplify random fluctuations within small groups.
When individuals with certain alleles randomly survive and reproduce (even if those alleles do not confer any selective advantage), the prevalence of those alleles can increase purely by chance.
Genetic Drift Examples
Below are a few illustrative cases of genetic drift in various organisms:
The American Bison: Uncontrolled hunting drastically reduced bison numbers in the past, nearly driving them to extinction. After conservation efforts, the population rebounded but with much less genetic variation than before—an example of the bottleneck effect.
Rabbits with Different Fur Colours: Imagine a population of rabbits with both brown and white fur alleles. If a random event kills most of the white-furred rabbits, the brown allele could dominate the population by chance alone.
Eye Colour in Humans: Although blue eye colour can be inherited, it might become very rare or even lost in an isolated community if those carrying the blue-eye allele do not reproduce as frequently. This is a genetic drift example in humans, driven by chance rather than an adaptive advantage.
Birds with Different Beak Sizes: If a random event leads to the disappearance of birds with a certain beak size, only one beak-size allele could remain, reducing the gene pool’s diversity.
Flower Colour in Plants: Suppose a plant species produces both blue and yellow flowers. If a wildfire destroys most yellow-flowering plants, the blue allele might become predominant—another clear illustration of genetic drift in animals and plants.
In humans, isolated communities such as certain island populations or groups like the Amish have displayed unique genetic traits (e.g., higher frequency of specific genetic disorders) due to the founder effect.
Genetic Drift vs Gene Flow
While both genetic drift and gene flow affect allele frequencies in populations, they differ in how they operate:
Genetic Drift:
Operates by chance.
Has a more significant impact in small, isolated populations.
Tends to reduce genetic variation within a population over time.
Gene Flow:
Involves movement of alleles between populations (e.g., migration of individuals or transfer of pollen in plants).
Increases genetic variation within a population by introducing new alleles.
Can reduce genetic differences between populations by blending their gene pools.
When individuals migrate from one population to another and reproduce there, they introduce new alleles—a gene flow example that prevents the isolated changes seen in genetic drift.
Additional Insights on Genetic Drift
Population Size Matters: The smaller the population, the more pronounced the effects of genetic drift.
Interaction with Natural Selection: While natural selection favours alleles with a survival or reproductive advantage, genetic drift can randomly eliminate beneficial alleles or fix harmful ones if the population is tiny.
Long-Term Consequence: Persistent drift can significantly reduce genetic diversity, potentially making populations more vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes.
Quick Quiz
Try these questions to test your understanding of genetic drift. The answers are provided below:
Which concept refers to the movement of genes between two populations?
A. Genetic Drift
B. Bottleneck Effect
C. Gene Flow
D. Founder Effect
Which phenomenon reduces genetic diversity because most individuals of a population are wiped out suddenly?
A. Migration
B. Bottleneck Effect
C. Natural Selection
D. Gene Flow
In the founder effect, the new population is founded by
A. A large, diverse group of individuals
B. A random mutation in the gene pool
C. A relatively small group migrating to a new location
D. A sudden decrease in fitness
True or False? Genetic drift can eliminate even beneficial alleles from a population.
Answers
C
B
C
True
Related Topics You May Find Useful


FAQs on Genetic Drift Made Simple: Key Concepts, Examples & Impacts
1. What is genetic drift and what are its main features?
Genetic drift is an evolutionary mechanism that produces random changes in allele frequencies within a population from one generation to the next. Unlike natural selection, these changes happen purely by chance, not because an allele is beneficial or harmful. Its main features are:
It is a random, directionless process.
Its effects are most significant in small populations.
It can lead to the loss of genetic variation as alleles are lost or become fixed.
It does not necessarily lead to adaptation.
2. Can you provide a simple example of genetic drift?
Imagine a small population of ten rabbits, five with brown fur (allele B) and five with white fur (allele b). By pure chance, a fox happens to prey on three white rabbits. In the next generation, the allele for brown fur (B) will be much more common, not because it was better, but simply due to a random event. This shift in allele frequency due to chance is a classic example of genetic drift.
3. What is the founder effect, with a real-world example in humans?
The founder effect is a specific type of genetic drift that occurs when a new population is established by a small number of individuals (founders) from a larger parent population. This new population's gene pool may have different allele frequencies than the original population, simply by chance. A famous human example is the high incidence of polydactyly (extra fingers or toes) among the Old Order Amish communities in North America. The original founding members happened to carry this rare allele at a higher frequency than the general population.
4. How does the bottleneck effect cause genetic drift? Please provide an example.
The bottleneck effect is a form of genetic drift that happens when a population's size is drastically reduced by a random event, such as a natural disaster, disease, or habitat destruction. The small number of survivors may have a gene pool that, by chance, does not reflect the genetic diversity of the original population. An example is the Northern elephant seal, which was hunted to near extinction in the 1890s. The current population, descended from just a few dozen survivors, has very low genetic variation compared to other seal species.
5. What is the key difference between genetic drift and natural selection?
The key difference lies in the driving force behind the change in allele frequencies. Genetic drift is random, driven by chance events that are unrelated to an allele's traits. In contrast, natural selection is non-random; it favours alleles that provide a survival or reproductive advantage (adaptation) in a specific environment. In short, selection is about fitness, while drift is about luck.
6. How does genetic drift impact the genetic diversity of a population?
Genetic drift generally reduces genetic diversity within a population. Because the process is random, some alleles may be completely lost from the gene pool over generations, while others may become fixed (reaching a frequency of 100%). This loss of alleles decreases the overall genetic variation, which can make the population more vulnerable to environmental changes or diseases.
7. Does genetic drift always make a population less adapted to its environment?
Not necessarily, but it can. Since genetic drift is a random process, it is indifferent to whether an allele is beneficial, neutral, or harmful. By chance, it can lead to the loss of a beneficial allele or the fixation of a mildly harmful one, both of which would make the population less adapted. Conversely, a beneficial allele could become fixed by chance, but this outcome is not guaranteed, unlike with natural selection which actively promotes adaptive traits.
8. Can genetic drift occur in large populations?
Yes, genetic drift technically occurs in all populations regardless of size. However, its effects are far more pronounced in small populations. In a large population, random fluctuations in allele frequencies tend to even out and have a negligible impact on the overall gene pool. In a small population, a single chance event can cause a significant and lasting shift in allele frequencies.
9. How does gene flow interact with genetic drift?
Gene flow, the transfer of genetic material from one population to another, generally acts as an opposing force to genetic drift. While genetic drift can lead to populations becoming genetically different from one another, gene flow tends to make them more similar. It can reintroduce alleles that were lost due to drift, thereby increasing genetic variation and counteracting the isolating effects of genetic drift.
10. Can genetic drift alone lead to the formation of a new species?
Genetic drift can be a major contributing factor to speciation, especially when a small population becomes geographically isolated. In such a case, genetic drift can cause the isolated population's gene pool to diverge significantly from the parent population's over time. This genetic divergence, when combined with other evolutionary forces like mutation and natural selection, can eventually lead to reproductive isolation, which is the hallmark of a new species.










