How Do Plants and Animals Depend on Each Other in Nature?
The interdependence of plants and animals is a fundamental biological concept, describing how these two groups rely on each other for survival. Both plants and animals exchange gases, provide food, and recycle nutrients, forming the backbone of every ecosystem. Understanding this mutual dependence is essential for students to appreciate the balance of nature and the importance of biodiversity conservation.
What is the Interdependence of Plants and Animals?
Interdependence of plants and animals refers to the various ways in which plants and animals support each other's life processes. It includes basic needs such as food, shelter, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and involves more complex interactions like pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient recycling. Without this interrelationship, life as we know it would not be sustainable on Earth.
Why Do Plants and Animals Depend on Each Other?
Plants and animals are connected through a variety of cycles and relationships. Plants act as primary producers, turning sunlight into food using photosynthesis, while animals act as consumers. In turn, animals contribute to plant life by aiding in pollination, dispersal of seeds, and enriching soil nutrients through decomposition. This intricate web keeps natural systems balanced.
Key Ways Plants and Animals are Interdependent
Understanding the different forms of interdependence helps explain how ecosystems function. Below are the most significant connections between plants and animals:
- Food Source: Plants provide food (leaves, fruits, seeds) for herbivores. Carnivores obtain energy by feeding on herbivores, making plants the base of the food chain.
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Exchange: Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis, which animals use for respiration. Animals return carbon dioxide, essential for plant photosynthesis.
- Pollination: Animals like bees, butterflies, birds, and bats transfer pollen between flowers, enabling plants to reproduce.
- Seed Dispersal: Many animals help spread plant seeds, either by eating fruits and excreting seeds or by carrying them on their fur.
- Shelter and Protection: Plants provide homes and hiding places for animals; for example, birds nest in trees.
- Nutrient Cycling: Decomposing animal bodies return nutrients to the soil, which plants absorb to grow.
These connections form the basis for related science worksheets, diagrams, and charts showing interdependence in class 5 and class 4 curricula.
Interdependence in Different Ecosystems
Ecosystems are communities where both plants and animals coexist. The nature of their interdependence changes based on the ecosystem type:
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: Forests and grasslands are classic examples. Plants absorb nutrients from decomposing animal bodies, and animals—herbivores, carnivores, and insects—rely on plants for food and oxygen. Monkeys and birds help in seed dispersal. Insects like bees and butterflies pollinate flowering plants. For more on forests, visit terrestrial ecosystem and forest.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: In ponds, lakes, and oceans, algae and aquatic plants produce oxygen. Fishes and aquatic animals use this oxygen and return carbon dioxide, allowing plants to continue photosynthesis.
These reciprocal roles maintain ecological equilibrium across habitats and are often illustrated using diagrams showing the interdependence of plants and animals.
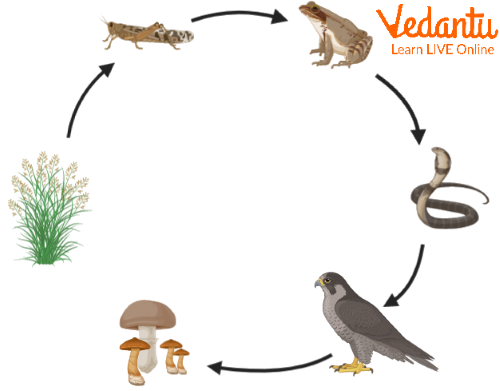
The Role of the Food Chain in Interdependence
Food chains clearly demonstrate how the survival of each organism is linked to others. Below is a simple food chain cycle seen in many science worksheets for class 5 students:
- Plants produce food via photosynthesis using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
- Herbivorous animals feed on plants and use the energy for survival and growth.
- Carnivorous animals consume herbivores to obtain energy.
- Decomposers (microorganisms, insects) break down dead plants and animals, returning nutrients to the soil.
This process repeats in a cycle, maintaining energy flow and nutrient balance, as detailed on our food chain and biogeochemical cycle resources.
Examples of Interdependence in Daily Life
Real-world examples make the concept clearer for students, whether in class 5 or higher grades:
- Bees and Flowers: Bees collect nectar and unintentionally transfer pollen, helping flowers form seeds and fruits.
- Squirrels and Oak Trees: Squirrels bury acorns for later but forget some, allowing new oak trees to sprout.
- Fishes and Algae: In ponds, fish depend on algae for oxygen, while algae get carbon dioxide from fish.
To see these relationships visually, check out interdependence of plants and animals diagrams or draw your own using examples around you.
Microorganisms: The Third Pillar of Interdependence
Microorganisms like bacteria and earthworms are crucial in soil formation and nutrient cycling. They decompose organic matter from plants and animals, releasing minerals that plants need. This contribution makes them essential for the overall cycle. Creating a chart showing interdependence of plants, animals, and microorganisms helps visualize this three-way relationship.
Maintaining the Gas Balance in the Biosphere
The exchange of gases between plants and animals is vital for life. Plants release more oxygen in photosynthesis than they consume during respiration. Animals rely on this oxygen, and the carbon dioxide they exhale is essential for plant growth. This cyclical exchange supports the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the biosphere. You can represent this as a cycle in a worksheet or drawing.
For deeper learning, explore oxygen cycle and carbon cycle on Vedantu.
Key Features of Plant and Animal Interdependence
- Plants and animals cannot exist independently; they rely on each other for vital needs.
- Animals need plants for food, shelter, oxygen, and protection from predators.
- Plants rely on animals for pollination, seed dispersal, and soil nutrient enrichment.
- Interdependence ensures the stability and sustainability of ecosystems.
Why is the Interdependence of Plants and Animals Important?
Without the interdependence of plants and animals, ecosystems would collapse. Removal of any one player—plants, animals, or microorganisms—would disrupt processes like photosynthesis, reproduction, and nutrient cycling. This would affect food production, air quality, and human health. Knowing this helps us appreciate the need for conservation and connecting biology to daily life and environment-oriented careers, including food science and biology research.
Practice Worksheets and Activities
For learners in class 5 and class 4, practicing with interdependence of plants and animals worksheets and worksheets on the food chain, along with drawing labelled diagrams, reinforces concepts visually. Making a poster or chart, or even completing MCQs about these cycles, is effective for revision. Find more diagrams in Vedantu's biology diagram section.
Related Topics and Further Reading
- Nutrition in Plants – Learn how plants make food and why it matters.
- Animal Kingdom – Discover diversity among animals and their adaptations.
- Conservation of Biodiversity – Understand why preserving species matters.
- Biosphere – Explore the global system where all interdependence occurs.
- Environmental Issues – How human activities impact nature’s balance.
- Acquired vs Inherited Traits – Notice how characteristics shift across generations.
If you’re interested in more advanced topics, Vedantu’s online courses can deepen your knowledge of biology and environmental sciences.
The interdependence of plants and animals is central to the health of natural and human-made environments. These mutual relationships enable ecosystems to thrive, influence agriculture, and sustain all life. Understanding and respecting these connections is vital for anyone aspiring to study science, protect the environment, or pursue related careers.


FAQs on Interdependence of Plants and Animals: Explained for Students
1. What is the interdependence of plants and animals?
Plants and animals are interdependent because each relies on the other to survive in nature.
Key points explaining this interdependence include:
- Plants provide oxygen through photosynthesis, which animals need to breathe.
- Animals give off carbon dioxide, which plants need for photosynthesis.
- Herbivores depend on plants for food, while carnivores eat herbivores.
- Animals help in pollination and seed dispersal, aiding plant reproduction.
2. How do plants and animals depend on each other for survival?
Plants and animals depend on each other mainly for food, oxygen, and pollination.
Examples of this dependence are:
- Plants give food and oxygen to animals.
- Animals produce carbon dioxide needed by plants.
- Certain animals help pollinate flowers.
- Birds and animals spread seeds of plants.
3. Why is oxygen important in the relationship between plants and animals?
Oxygen is essential because it is released by plants and taken in by animals for respiration.
The main roles of oxygen in plant-animal interdependence are:
- Plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis.
- Animals need oxygen to breathe and obtain energy from food.
- Without plants, the supply of oxygen would decrease and animals would not survive.
4. How do animals help in the reproduction of plants?
Animals assist in plant reproduction mainly through pollination and seed dispersal.
Key ways animals help are:
- Bees, butterflies, and birds transfer pollen from one flower to another, enabling fertilisation.
- Animals eat fruits and their movement spreads seeds to new places for germination.
5. What are the main benefits animals get from plants?
Animals benefit from plants by getting food, oxygen, and shelter.
The benefits include:
- Food: Herbivores eat leaves, fruits, and seeds; carnivores eat herbivores that depend on plants.
- Oxygen: Animals breathe in oxygen released by plants.
- Shelter: Plants provide homes and protection for many animals.
6. What is seed dispersal and how do animals help in it?
Seed dispersal is the process by which seeds are carried away from the parent plant to new locations.
Animals help in seed dispersal by:
- Eating fruits and discarding seeds elsewhere.
- Seeds sticking to their fur or feathers and being carried to other places.
7. Give examples of animals that help pollinate plants.
Many animals help in pollination, which is transferring pollen from one flower to another.
Common pollinators include:
- Bees
- Butterflies
- Birds (like hummingbirds)
- Bats
8. How does the interdependence of plants and animals help maintain the balance in nature?
Interdependence between plants and animals maintains balance in nature by regulating gases and food chains.
This balance is achieved through:
- Plants absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen; animals do the opposite.
- Animals relying on plants for food, while helping plants reproduce.
- This mutual dependence keeps ecosystems stable and biodiversity rich.
9. What would happen if there were no plants on Earth?
If there were no plants, all animals and humans would eventually perish due to lack of oxygen and food.
The effects would include:
- No oxygen production for breathing.
- No food for herbivores, leading to collapse of the entire food chain.
- No shelter for many animals and insects.
10. Explain the food chain showing the dependency of plants and animals.
The food chain starts with plants and shows how energy flows from plants to herbivores to carnivores.
A basic food chain is:
- Plants (producers) make food from sunlight.
- Herbivores (primary consumers) eat plants.
- Carnivores (secondary consumers) eat herbivores.










