Key Characteristics and Classification of Living Things with Examples
Living things are organisms that display all the characteristics considered necessary for life, such as growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, and metabolism. From the tiniest bacteria to the largest animals and plants, these life forms shape every ecosystem on Earth. Understanding living things is a fundamental topic in biology, with real-world links to health, environment, and scientific progress.
What Are Living Things? – Definition
Living things are organisms or life forms that possess all the characteristics of life. These features include being made of cells, requiring energy, reproducing, growing, carrying out metabolic activities, responding to their environment, adapting, moving, and eventually, dying. In biological classification, living things belong to distinct domains, covering everything from bacteria to complex plants and animals.
Key Characteristics of Living Things
Biologists identify several essential characteristics that separate living things from non-living objects:
- Cellular Organization: All living things are made of one or more cells, the basic unit of life.
- Energy Requirement: They require energy to carry out various functions like growth and repair. Plants, for instance, use photosynthesis to make food.
- Reproduction: Living organisms can reproduce, either sexually or asexually, to create new individuals.
- Growth & Development: Every living thing grows and develops following a specific life cycle, such as observed in a human life cycle.
- Metabolism: They perform metabolic activities, which include all chemical processes necessary for life, like respiration and nutrient synthesis.
- Response to Stimuli: Living things can sense changes in their environment and respond accordingly.
- Homeostasis: They maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes (e.g., humans regulating body temperature).
- Adaptation & Evolution: Over generations, living things adapt to their environment, leading to evolution.
- Movement: Many living things, especially animals, can move independently. Plants show movement through growth responses.
- Death: Every living thing eventually completes its life span and dies.
These characteristics help students distinguish living things from non-living things. To explore more differences, see differences between living and non-living things.
How Did Living Things Originate?
Life began on Earth around 3.5–4 billion years ago. Scientists believe the very first living things emerged through a natural process called abiogenesis, where simple molecules formed complex organic compounds. These eventually evolved into the first primitive cells, marking the beginning of life.
Key scientific theories about the origin of living things include:
- Primordial Soup Hypothesis: States that Earth's early oceans contained organic molecules that assembled into life.
- RNA World Hypothesis: Suggests early life was based on RNA, which could store genetic information and act as enzymes.
- Endosymbiotic Theory: Proposes that complex cells (eukaryotes) evolved when simple cells began living inside each other.
Fossil records, such as ancient bacteria, support these ideas. To dive deeper, visit Evolution and RNA World Hypothesis.
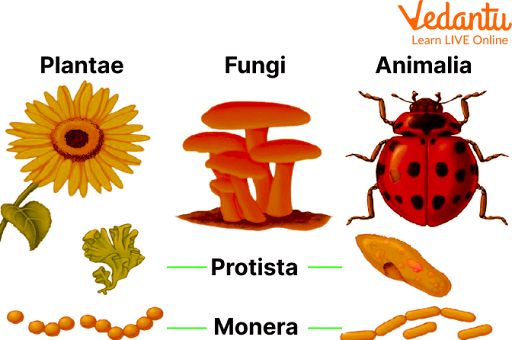
Classification of Living Things
Living things are grouped by their similarities and evolutionary relationships. Modern science divides all life forms into three major Domains:
- Bacteria (true bacteria – simple, single-celled, prokaryotic organisms)
- Archaea (ancient bacteria – single-celled, often found in extreme environments)
- Eukarya (complex cells with nuclei – includes animals, plants, fungi, and protists)
Within these domains, organisms are further classified into Kingdoms, Phyla, Classes, Orders, Families, Genera, and Species. For example, humans belong to the Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Chordata, and so forth. Explore Animal Kingdom Classification and Plant Kingdom for detailed charts.
Living Things Examples
There is a phenomenal diversity of living things on Earth. Here are some common examples:
- Bacteria (e.g., Lactobacillus)
- Plants (e.g., sunflower, mango tree)
- Fungi (e.g., yeast, mold)
- Animals (e.g., humans, birds, fish, insects)
- Protists (e.g., Amoeba, Paramecium)
Each group has its own features and plays a specific role in ecosystems and human life, including food, oxygen production, and medicine (e.g., antibiotics from fungi).
Non-cellular Life: Are Viruses Living Things?
Viruses are special cases. They have genetic material (DNA or RNA) and can reproduce, but only inside living cells. Outside a host, viruses cannot grow, move, or carry out metabolism. Most biologists do not classify viruses as truly living things, but study them for their impact on health and disease. Learn more at Virus and see the Tobacco Mosaic Virus for examples.
Differences: Living Things vs. Non-Living Things
| Feature | Living Things | Non-Living Things |
|---|---|---|
| Cellular Structure | Present (made of cells) | Absent |
| Metabolism | Carry out metabolic reactions | Do not perform metabolism |
| Growth | Grow internally and develop | Do not grow; may change by physical addition |
| Reproduction | Can reproduce | Cannot reproduce |
| Response to Stimuli | Respond to environment | No response to stimuli |
This table helps students clearly differentiate living things from non-living things, which is often asked in class and exams.
Living Things that Mimic Non-Living Things
Some amazing living things have evolved to look like stones, twigs, or leaves to protect themselves from predators. Examples include:
- Lithops ("living stone" succulents that resemble pebbles)
- Stonefish (venomous fish camouflaged as rocks)
- Leaf insects and certain butterflies (mimicry for survival)
Such adaptations show the diversity of survival strategies in nature. Explore Animal Adaptations and Adaptations in Plants for more real-life examples.
Importance and Applications of Studying Living Things
Understanding living things forms the basis of medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. For example, knowledge of living things:
- Helps develop better food production techniques.
- Guides healthcare and the study of diseases.
- Aids in biodiversity conservation and tackling environmental issues like climate change.
Learn more about the relationship between living things, environment, and health in Vedantu's articles on life science and biological science.
Living Things – Common Questions for Practice
Test your knowledge:
- List three major characteristics of living things.
- How do living things respond to stimuli? Give examples.
- Why are viruses not considered true living things?
- Name the domains in which living things are classified.
- Give two examples of living things that mimic non-living things.
Find more living things MCQs for practice and competitive exams on Vedantu.
Page Summary
Living things are complex, organized, and capable of growth, reproduction, response, and adaptation. They are the focus of biology and numerous applied sciences like medicine and agriculture. Recognizing their characteristics, classification, and real-world significance helps students understand and appreciate the natural world. Vedantu provides clear explanations and practical examples to support every learner's journey in biology.


FAQs on What Are Living Things?
1. What are living things?
Living things are organisms that exhibit life processes such as growth, movement, reproduction, and response to stimuli. Key characteristics include:
- Growth and development
- Respiration
- Response to environment
- Reproduction
- Excretion
- Nutrition
2. What are the main differences between living and non-living things?
The primary difference is that living things carry out vital life processes, while non-living things do not. Differences include:
- Living things grow, respire, reproduce, and respond to stimuli
- Non-living things lack these abilities
- Living things maintain homeostasis, non-living things do not
- Living things undergo cellular organization
3. What are the characteristics of living things?
Living things share several key characteristics:
- Growth
- Movement (sometimes limited in plants)
- Responsiveness to stimuli
- Reproduction
- Metabolism (including respiration and excretion)
- Cellular structure
4. Give examples of living things.
Common examples of living things include:
- Humans
- Animals (dogs, cats, birds, fish)
- Plants (trees, flowers, grasses)
- Fungi (mushrooms)
- Bacteria and protozoa
5. What do living things need to survive?
All living things need certain basic needs to survive:
- Food/nutrients
- Water
- Air (oxygen or carbon dioxide)
- Proper habitat or shelter
6. What is reproduction in living things?
Reproduction is the biological process by which living things produce offspring. This helps maintain the population and continuation of a species. Types of reproduction include:
- Asexual reproduction (single parent, identical offspring)
- Sexual reproduction (two parents, offspring with mixed traits)
7. Why do living things need food?
Living things need food to obtain energy for all vital life processes such as growth, movement, and reproduction. Food provides:
- Nutrients for body maintenance
- Fuel for metabolic activities
- Materials for tissue repair and growth
8. Do all living things move?
All living things show some form of movement, although the type and extent can vary:
- Most animals move their entire bodies to search for food or escape danger
- Plants show movement by growing toward light or water, or by opening and closing their flowers and leaves
9. How do living things grow?
All living things grow by increasing in size and complexity through cell division and development. This growth involves:
- Increase in number and size of cells
- Development of new body parts
- Maturity over time
10. What does it mean to respond to stimuli?
To respond to stimuli means that living things can react to changes in their environment. Examples include:
- Plants bending towards sunlight
- Animals running away from danger or moving towards food
- Humans shivering when cold










