Muscle tissues are made up of specialised cells that have the capacity to contract and relax. They help in movement of an organism.There are three types of muscular tissues- skeletal muscles, smooth muscles and cardiac muscles. This is one of the most important parts of our body that is composed of cells. From this article, we can learn that,
Muscular tissue’s function, its characteristics and its types.
A detailed diagram of muscular tissue.
How Do Muscle Tissues Work? Essential Facts for Students
Our body is composed of various cells and organs that function in several ways. Each part of our internal organs has a specific role in its own for the smooth functioning of our body. But, the main system that helps in the movement, as well as protection of our body, is nothing but the muscular tissue system. As a number of organs and tissues have specific duties for our body, these tissues act as a protective coat for skeletons and also carry various jobs that we are not able to do on our own. These tissues prevent any cracking, or breaking of bones easily and help in the movement of arms, legs etc. Let us learn about this in a detailed manner.
What is Muscular Tissue?
A tissue that surrounds the entire skeleton structure of our body is termed muscular tissue. These tissues are made up of several cells that have the ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts. These cells are highly supplied with blood vessels, which carry blood to the required parts of the body. These tissues also help in stretching and have good characteristics of contractility and elasticity. There are types of muscle tissues in our body that perform their respective functions.
Types of Muscular Tissue
It is said that there are more than 600 muscles in our body, all characterised by their work inside the body. Some can help you digest the food and some can protect your heart. Some of the main types of muscular tissue are:
Skeletal: These muscles cover the skeleton parts of the body. These tissues also help us in balancing the weight of the skeletons and make movement on our own. This is one of the muscular tissues that we have control over. These are part of the musculoskeletal system, also working with tendons and ligaments, helping with posture.
Cardiac: The muscles that line up the outline of the heart are called cardiac muscles. These muscles are delicate, as well as non-voluntary. They are responsible for pumping blood and making it travel through the cardiovascular system. We cannot control these muscles as it works with the internal organs. But, the heart tells it to stop the contract on its own.
Smooth: These are the muscles that line up the other organs of our body, like the stomach, bladder, and intestines. They play a vital role on their own without us knowing. For instance, we can fill up the urinary bladder or move waste to the intestines. They also help in the female, and male reproductive system and respiratory systems.
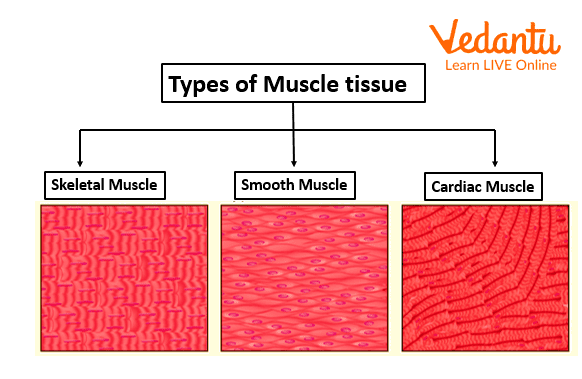
Types of Muscular tissue
Functions of Muscular Tissue
There are several tissues that work according to their functions. Some of the functions are:
Stability: These contribute to the joints, stabilising them. They also assist in lifting weights.
Mobility: Movements like walking, writing, running, etc. Are done with the help of the muscles.
Posture: Muscles help in straightening the posture of the body. Good posture relies on strong muscles, whereas bad posture relies on weak muscles.
Respiration: A normal activity like breathing too involves muscles. Diaphragm muscles help in steady respiration, helping the lungs with inhaling and exhaling air.
Circulation: Blood circulation also involves the help of muscle tissue. This happens when cardiovascular muscles pump blood to all parts of the body, involuntarily. The arteries and veins play a further role in the circulation of blood.
Digestion: Muscles on the abdomen and GI tract are involved in the process of digestion. When the digested food passes through the GI tract by peristalsis, the hollow muscles push the waste to the intestines to pass the food as stools.
Urination: The urinary bladder muscle is both smooth and skeletal muscle, that helps in holding urine and releasing it from the urinary bladder.
Characteristic of Muscular tissue
Muscles have various characteristics based on the work they do. They are:
Skeletal muscle: Long, striated and multinucleated (more than one nucleus) muscles.
Cardiac muscles: Muscles are short and narrow, rectangular in shape. They are about 0.02mm wide and 0.01mm long.
Smooth muscles: They are spindle-shaped and contain a single nucleus. They range from about 10 to 600 micrometres. They are elastic muscles.
Structure of Muscular Tissue
The Muscular tissues are bundled together and surrounded by tough connective tissues like epimysium. This epimysium surrounds the long nerve Fibre called fascicles, which is These epimysium surrounds the long nerve Fibre called fascicles, which is surrounded by perimysium. Another protective layer called endomysium surrounds the fibres. These layers of fibres in muscles help in muscle contraction.
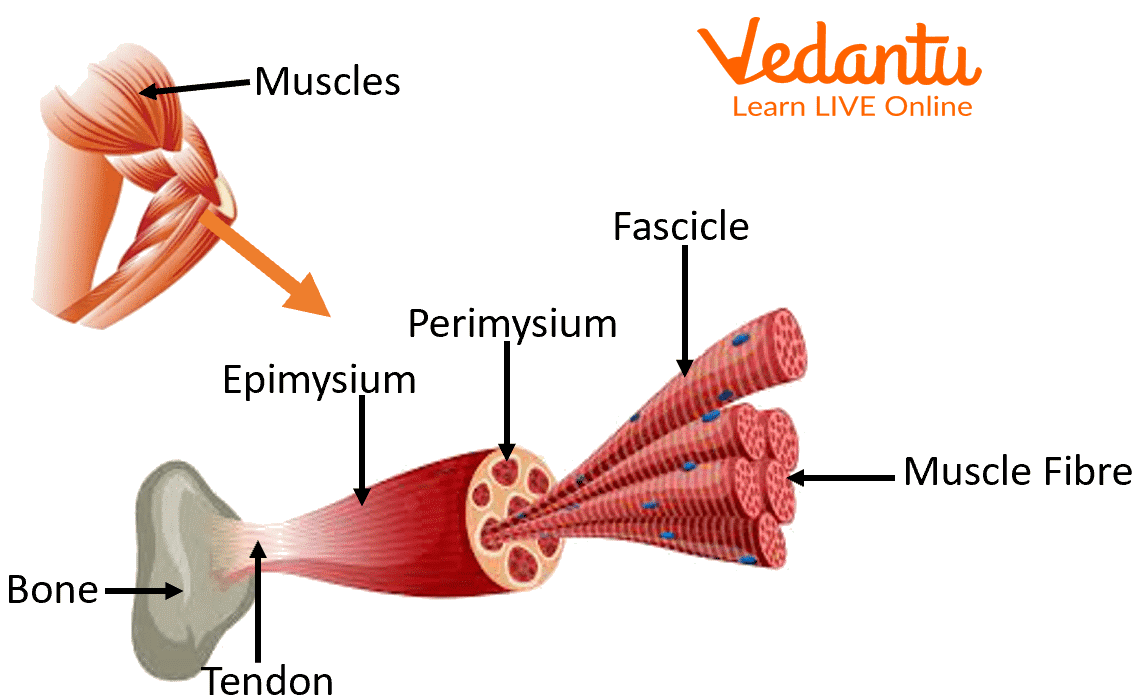
Structure of Muscular tissue
Interesting Facts
The largest muscle in our body is the gluteus Maximus
The strongest muscle in our body is the muscle of the tongue.
Muscles make up to 40% of the weight of our body.
The heart is the hardest working muscle in the entire body.
Key Features
Muscular tissue is composed of various fibres of tissues that work together.
There are mainly three types of muscles, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle.
Muscle helps us in day-to-day activities like waking, running, writing etc.
Some muscles are voluntary, while some are involuntary.


FAQs on Muscular Tissue Explained: Key Concepts, Types, and Functions
1. How are muscles made?
An individual muscle fibre is made up of blocks of proteins called myofibrils, which contain a specialised protein (myoglobin) and molecules to provide the oxygen and energy required for muscle contraction. Each myofibril contains filaments that fold together when given the signal to contract. This shortens the length of the muscle fibre which, in turn, shortens the entire muscle if enough fibres are stimulated at the same time. Skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles have very different functions, but they share the same basic composition.
2. What is the neuromuscular system?
The brain, nerves and skeletal muscles work together to cause movement. This is collectively known as the neuromuscular system. A typical muscle is serviced by anywhere between 50 and 200 (or more) branches of specialised nerve cells called motor neurons. This plug directly into the skeletal muscle. The tip of each branch is called a presynaptic terminal. The point of contact between the presynaptic terminal and the muscle is called the neuromuscular junction. The brain sends the signal to the motor neurons.
3. What are muscle disorders?
Muscle disorders may cause weakness, pain, loss of movement and even paralysis. The range of problems that affect muscles is collectively known as myopathy. Common muscle problems include Injury or overuse, including sprains or strains, cramps, tendonitis and bruising Genetic problems, such as muscular dystrophy Inflammation, such as myositis Diseases of nerves that affect muscles, such as multiple sclerosis Conditions that cause muscle weakness, such as metabolic, endocrine or toxic disorders; for example, thyroid, and adrenal diseases, alcoholism, pesticide poisoning, medications (steroids, statins) and myasthenia gravis Cancers, such as soft tissue sarcoma.
Muscle tissues are made up of specialised cells that have the capacity to contract and relax. They help in movement of an organism.There are three types of muscular tissues- skeletal muscles, smooth muscles and cardiac muscles. This is one of the most important parts of our body that is composed of cells. From this article, we can learn that,
Muscular tissue’s function, its characteristics and its types.
A detailed diagram of muscular tissue.










