Nervous System Diagram: Key Parts and How They Work Together
The human nervous system is a complex and fascinating network that enables every thought, action, and response. Acting as the command centre for our body, it not only controls voluntary actions like moving your limbs but also manages involuntary processes such as breathing and digestion. In this comprehensive guide, we break down the nervous system function, explore the nervous system diagram, and discuss each of the nervous system parts and their functions in a simple, educational tone. Whether you’re a student or an enthusiast, this page provides clear insights into topics such as the central nervous system, as well as downloadable resources like nervous system PDF and nervous system ppt for further study.
Understanding the Nervous System: Function, Parts & Organs
Living organisms adapt to their surroundings by detecting stimuli and responding appropriately. This response is coordinated by the nervous system, a complex network that ensures rapid communication between the brain and the rest of the body. Imagine touching a hot surface—the sudden pain is your nervous system function in action, protecting you from further harm.
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is the body’s electrical communication network. It detects external stimuli such as sound, light, and temperature, and relays messages to the brain via neurons. Each neuron, the basic signalling unit, plays a vital role in this process. From sending signals in a split second to controlling crucial bodily functions, the nervous system organs work together to keep us safe and aware.
Nervous System Diagram and Parts
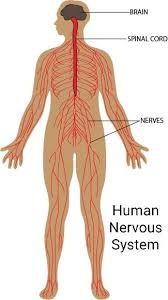
A clear nervous system diagram shows two main divisions:
Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprised of the brain and spinal cord, the CNS is the control hub. It processes information and directs responses.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This includes all nerves that branch out from the CNS to the rest of the body, controlling both voluntary movements (via the somatic nervous system) and involuntary actions (through the autonomic nervous system).
In our detailed nervous system diagram, you can explore every component—from the central nervous system to the peripheral nerves, highlighting the nervous system parts and functions in depth. For additional study materials, you can download our comprehensive nervous system PDF or view a dynamic nervous system ppt.
Detailed Look at the Central Nervous System
The central nervous system is essential for processing sensory information and coordinating responses. It consists of:
Brain: The control centre for thinking, decision-making, and memory.
Spinal Cord: A bundle of nerve fibres that transmits messages between the brain and peripheral organs. It is also key in reflex actions.
Peripheral Nervous System and Its Subdivisions
The peripheral nervous system connects the CNS to the rest of the body. It has two main subdivisions:
Somatic Nervous System: Manages voluntary movements by sending signals to skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System: Oversees involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiration. This system works in tandem with other body systems, including the respiratory system and excretory system, ensuring our internal environment remains balanced.
Integration with Other Body Systems: The nervous system does not operate in isolation. It communicates with the respiratory system to regulate breathing and with the excretory system to manage waste removal processes. This intricate cooperation ensures homeostasis and effective bodily functions.
Fun Facts about the Nervous System
Speed of Signals: Some neurons can fire signals at speeds exceeding 428 km/h, making the nervous system one of the fastest communication networks in the body.
Neuronal Diversity: Although neurons come in various shapes and sizes, each one plays a critical role in transmitting and processing information.
Brain Energy: The human brain, while only about 2% of body weight, consumes roughly 20% of the body’s energy, highlighting its importance in our overall physiology.
Real-World Applications of the Nervous System
The study of the nervous system parts and functions is not just academic—it has real-life implications:
Medical Diagnostics: Understanding the nervous system function aids in diagnosing conditions like neuropathies and neurodegenerative diseases.
Technology and AI: The structure of neural networks has inspired modern artificial intelligence, improving machine learning algorithms.
Everyday Safety: Recognising how the nervous system works can explain why pain is crucial for avoiding injuries, and ensuring we respond appropriately to dangerous situations.


FAQs on Nervous System: Complete Student Guide to Structure & Functions
1. What is the main job of the human nervous system?
The main job of the human nervous system is to act as the body's command centre. It controls and coordinates all essential functions, from movement and thoughts to automatic processes like breathing and digestion, by sending and receiving electrical signals.
2. What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system is divided into two main parts:
- The Central Nervous System (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. It acts as the main processing centre.
- The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), which consists of all the nerves that branch out from the CNS to the rest of the body, connecting it to the limbs and organs.
3. What is a neuron and why is it important for the nervous system?
A neuron, or nerve cell, is the basic building block of the nervous system. It is important because it transmits electrical and chemical signals, called nerve impulses, which allow different parts of the body to communicate with each other and with the brain.
4. What is the difference between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
The key difference lies in what they control. The somatic nervous system governs voluntary actions that we consciously control, like walking or picking up a book. The autonomic nervous system manages involuntary functions that happen automatically, such as heartbeat, breathing, and digestion.
5. How does a reflex action, like touching a hot object, work so quickly?
A reflex action is so fast because it follows a shortcut called a reflex arc. The signal travels from your hand to the spinal cord, which immediately sends a command back to the muscles to pull away. This happens before the signal even reaches the brain, making the reaction almost instant to protect the body from harm.
6. What are the three major parts of the human brain and their main roles?
The three main parts of the human brain are:
- The Cerebrum: The largest part, responsible for higher functions like thought, language, memory, and voluntary movements.
- The Cerebellum: Located at the back, it coordinates motor control, balance, and posture.
- The Brainstem: Connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls vital automatic functions like breathing and heart rate.
7. Why can't we consciously control our heartbeat or digestion?
We can't consciously control these functions because they are managed by the autonomic nervous system. This system works automatically to regulate vital bodily processes without needing our active thought, ensuring our survival even when we are asleep or focused on other tasks.
8. How does the nervous system work with the muscular system to help us move?
To create movement, the brain sends an electrical signal down the spinal cord and through a motor neuron. This neuron connects to muscle fibres. When the signal reaches the muscle, it causes the muscle to contract, resulting in movement. This close coordination allows for everything from walking to writing.










