What Is the Structure and Function of a Prokaryotic Cell (Bacterial Cell)?
Prokaryotic cells are the earliest and simplest type of cells found on Earth. These tiny structures lack a true nucleus and most membrane-bound organelles, making them unique among living organisms. Understanding the structure, functions, and significance of prokaryotic cells is crucial for students in biology, especially in areas like microbiology, medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
Prokaryotic Cells Definition
Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have a well-defined, membrane-bound nucleus. Instead, their genetic material lies freely in the cytoplasm, usually in a single circular DNA molecule. Prokaryotic cells are found in unicellular organisms, primarily the bacteria and archaea kingdoms. They are known for their simple structure and remarkable adaptability to various environments.
Key Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells
The main features of prokaryotic cells help distinguish them from more complex eukaryotic cells. These distinguishing characteristics also form the basis for many biology class 12 topics.
- No membrane-bound nucleus; DNA resides in a nucleoid region.
- Absence of membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum.
- Cell wall usually present, providing shape and protection.
- Small cell size, generally between 0.1 to 5 micrometers.
- Simple internal structure with few compartments.
- Reproduce mainly by binary fission (asexual division).
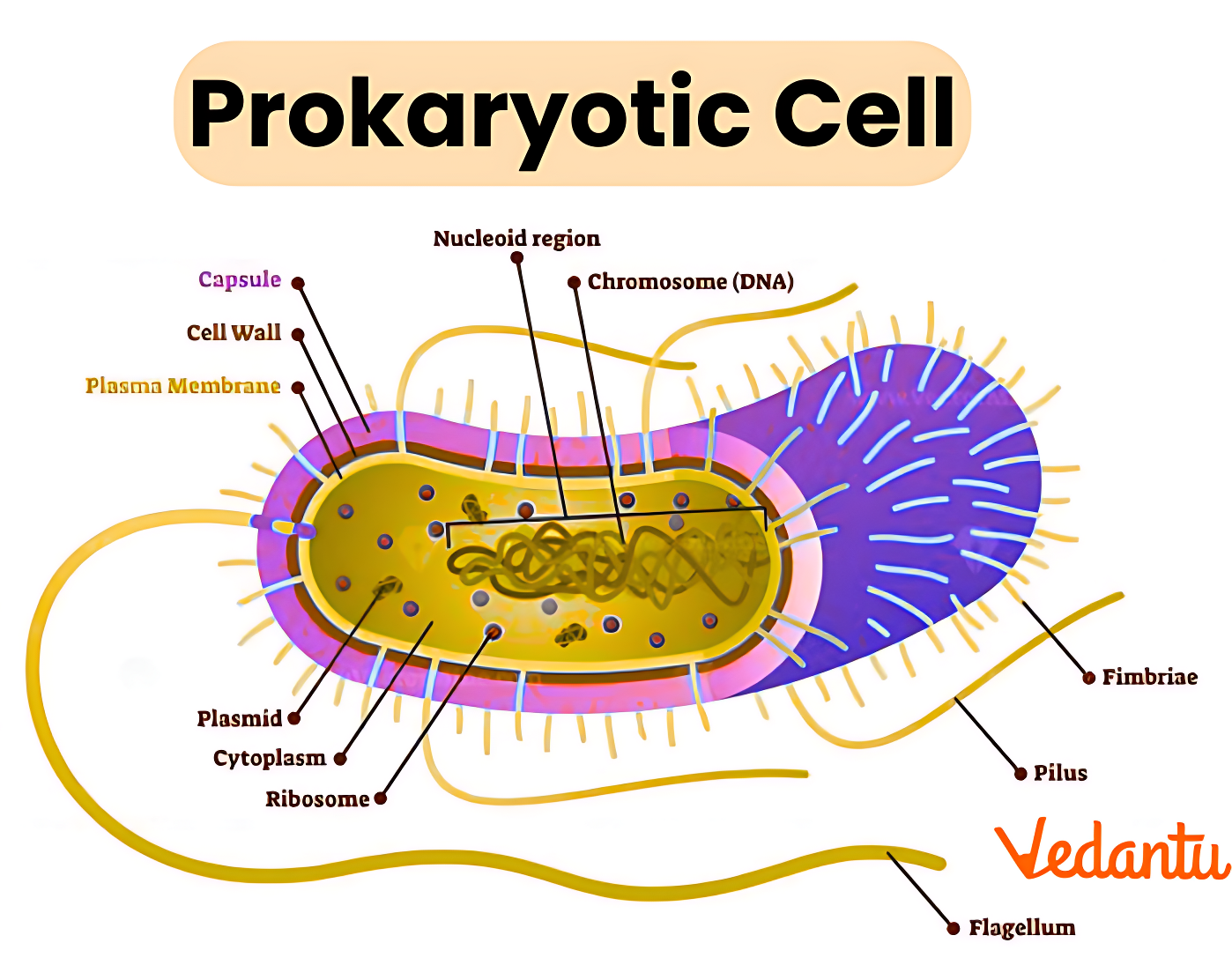
Structure of Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells have essential structures that carry out basic life functions. Here are the typical components found in a prokaryotic cell:
- Plasma membrane – Controls the entry and exit of substances.
- Cell wall – Gives rigidity and protects against external stress.
- Nucleoid – Irregular region containing the circular DNA.
- Cytoplasm – Gel-like fluid where chemical reactions occur.
- Ribosomes – Small structures responsible for protein synthesis.
- Plasmids – Small, extra circles of DNA found in some bacteria.
- Flagella or pili (occasionally) – Help in movement or attachment to surfaces.
Prokaryotic Cells Examples
Most prokaryotic cells belong to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Here are some common examples you’ll encounter in biology:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): Found in the human gut, often studied in microbiology.
- Streptococcus: Causes sore throat and other infections.
- Lactobacillus: Used in the production of curd and yogurt.
- Archaea: Such as Halobacterium, thrive in extreme environments like salt lakes.
These examples show the diversity and ecological roles of prokaryotes, from aiding in human digestion to causing diseases. To know more about the differences between microbes and their classification, visit Vedantu’s Kingdom Monera page.
Types of Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells are mainly classified into two groups based on their molecular and structural features:
- Bacteria: Found in soil, water, air, and living organisms. Includes both beneficial and harmful bacteria.
- Archaea: Often live in extreme environments and differ in cell wall composition compared to bacteria.
This classification is vital for understanding microbial diversity and for biotechnology applications.
Functions and Importance of Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells play essential roles in ecosystems, medicine, and industry:
- They recycle nutrients in soil and water through decomposition.
- Used in making dairy products, antibiotics, and enzymes.
- Some cause diseases, while others support human health.
- Involved in nitrogen fixation, making them crucial for agriculture (see nitrogen-fixing bacteria).
Recognizing the functions of prokaryotic cells makes it easier to connect food science and environmental issues to biology topics you learn in school.
Prokaryotic Cells vs Eukaryotic Cells
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No true nucleus; DNA in nucleoid | True membrane-bound nucleus |
| Cell size | Small (0.1-5 µm) | Larger (10-100 µm) |
| Organelles | Few, no membrane-bound organelles | Many, membrane-bound organelles present |
| Examples | Bacteria, Archaea | Plants, animals, fungi, protists |
Knowing the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells forms the basis for understanding advanced concepts like cell theory and modern genetics.
Reproduction in Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, primarily through a process known as binary fission. Here’s a simplified sequence:
- The DNA is copied.
- The cell grows larger.
- The cell membrane pinches inward.
- The cell splits into two identical cells.
This rapid means of reproduction allows bacterial populations to multiply quickly, which matters for both healthcare and environmental management.
Prokaryotic Cells in Human Life and the Environment
Understanding prokaryotic cells proves helpful in several real-world areas:
- Treating diseases by targeting bacterial infections with antibiotics.
- Useful in food processing and pharmaceuticals.
- Key in environmental conservation and bioremediation.
- Basis of advanced research like biotechnology and genetic engineering.
By studying prokaryotic cells, students can connect classroom lessons to broader scientific and practical issues.
Practice Questions: Prokaryotic Cells
Test your understanding of prokaryotic cells with these sample questions:
- Define prokaryotic cells and list two examples.
- Describe the structure of a prokaryotic cell.
- How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ?
- Explain why prokaryotic cells are important in the environment.
For more MCQs and questions, visit our biology MCQs page.
Prokaryotic Cells PPT and Diagrams
Teachers and students often use diagrams and presentations to understand the anatomy and function of prokaryotic cells. A clear prokaryotic cells diagram typically highlights the nucleoid, cell wall, plasma membrane, ribosomes, and sometimes flagella. If you’re preparing for a class presentation, include labelled diagrams and summaries. Explore more visual guides at CBSE Class 7 important diagrams.
Page Summary
Prokaryotic cells, lacking a true nucleus, represent the oldest and simplest type of living cells. They are fundamental in medicine, ecology, biotechnology, and daily human life. Understanding their definition, structure, examples, and roles provides an essential foundation for advanced biology topics and helps learners appreciate the vast diversity and impact of microbial life.


FAQs on Understanding Prokaryotic Cells
1. What are prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms that lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Key features include:
- No defined nucleus—genetic material is found in the nucleoid region
- No membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum
- Examples include bacteria and archaea
2. What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in various structural and functional aspects:
- Prokaryotes lack a nuclear membrane, while eukaryotes have a well-defined nucleus
- Organelles are membrane-bound in eukaryotes, but absent in prokaryotes
- Prokaryotic cells are usually smaller and simpler
- Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists; prokaryotes are mainly bacteria and archaea
3. What are the components of a prokaryotic cell?
Core components of prokaryotic cells include:
- Cell wall—provides shape and protection
- Cell membrane—controls movement of substances in and out
- Cytoplasm—jelly-like fluid filling the cell
- Nucleoid—region containing DNA
- Ribosomes—site of protein synthesis
- Optional structures: plasmids, flagella, capsule
4. What is the function of the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
The cell wall gives structural support and protection to prokaryotic cells. Its functions are:
- Maintains cell shape
- Prevents bursting in hypotonic environments
- Protects from mechanical damage and pathogens
- Made mainly of peptidoglycan in bacteria
5. Name two examples of prokaryotic organisms.
Bacteria and archaea are two main types of prokaryotic organisms. Examples include:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli)—a common bacterium
- Halobacterium—an archaean found in salty environments
6. How do prokaryotic cells reproduce?
Prokaryotic cells primarily reproduce through a process called binary fission. The main steps are:
- Replication of DNA
- Cell elongation
- Division of the cytoplasm
- Formation of two genetically identical daughter cells
7. What is the significance of plasmids in prokaryotic cells?
Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules found in many prokaryotic cells. They play important roles:
- Carry genes for antibiotic resistance
- Can be transferred between bacteria via conjugation
- Help in genetic engineering and biotechnology studies
8. How is genetic material organized in prokaryotic cells?
In prokaryotic cells, the genetic material (DNA) is usually a single, circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region. There is no membrane-bound nucleus, and plasmids may also be present as extra DNA.
9. Do prokaryotic cells have ribosomes? If yes, what are their functions?
Yes, prokaryotic cells have ribosomes. Their main roles include:
- Protein synthesis by translating mRNA
- Prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S in size, different from the 80S ribosomes in eukaryotes
10. What are archaea and how do they differ from bacteria?
Archaea are a unique domain of prokaryotes that differ from bacteria in several ways. Major differences include:
- Cell wall composition—archaea lack peptidoglycan
- Membrane lipids—distinct structure compared to bacteria
- Often live in extreme environments (e.g., extreme halophiles, thermophiles)
11. Which organisms are classified as prokaryotes?
Bacteria and archaea are the two groups classified as prokaryotes. All bacteria and archaea lack membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus.
12. What is the nucleoid in a prokaryotic cell?
The nucleoid is an irregularly-shaped region within prokaryotic cells that contains the cell's DNA. It is not surrounded by a membrane and is responsible for the organization of the chromosome.










