In this article, we are going to study scabies, scabies insects, and the life cycle of scabies. We will also study the signs and symptoms of scabies, and the causes of scabies. After reading this article, readers will be able to tell
Scabies
Scabies insect
Causes of scabies
Scabies infection
The life cycle of scabies
Understanding Each Stage of the Scabies Mite Life Cycle
A microscopic mite that burrows into the skin causes the common skin disorder known as scabies. The primary sign of scabies is severe scratching, which is worst at night. A skin rash also develops in the locations where the mites have dug their way. The mite called Sarcoptes scabiei, which lives in the skin's epidermal layer in mammals, is the main cause of it. Understanding the biology of the mite, interactions between the parasite and the host, and strategies it adopts to get beyond the host's resistance has greatly increased during the past 40 years of research. A vaccine to prevent individuals at risk from contracting the disease, or at the very least, restricting its spread, is also being developed.
Scabies
What is Meant by Scabies?
Scabies is a skin disorder caused by Sarcoptes scabies or itch mites. The symptoms of scabies are itching and rashes. The disorder is easily curable but spreads quickly by direct contact. Scabies mostly develop in the skin folds of the body.
Scabies Insect
Sarcoptes scabiei is the name of the scabies insect. They feed by digging into the top layer of skin with their front legs and jaws, where they release their eggs. The baby insects emerge after three to four days and migrate to the top layer of skin, where they develop into adults.
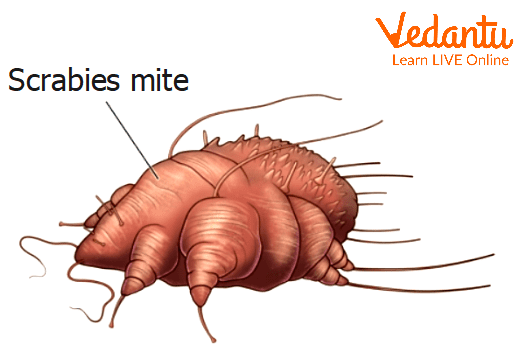
Scabies Mite
Scabies prefers warm areas, such as skin folds, the spaces in between fingers, underneath the fingernails, or the wrinkles around the breasts or buttocks. They may also be covered by accessories such as rings, bracelets, or wristwatch bands. This parasite, often known as an "itch mite," is spread by being near an infected individual. Sarcoptes scabiei is a parasite that can grow up to 0.35 mm in length yet is invisible to the unaided eye.
Scabies Life Cycle
The female mite lays two to three eggs every day beneath the skin after fertilization. The eggs are oval and can reach a length of 0.15 mm. In ideal circumstances, the eggs hatch in three to four days. Approximately, 10% of the eggs mature into adult itch mites.
The mite's larvae travel to the top layer of the skin when the eggs hatch and dig into the stratum corneum, the epidermis. As a result, molting pouches, the invisible burrows, are created. After hatching, the larvae have just three pairs of legs and live for three to four days. The larva later goes through a molt and becomes a nymph.
The mite has four sets of legs in its nymphal stage. Before becoming adult mites, the nymphs transition into considerably larger nymphs. The molting pouches are where you'll primarily find the nymphs and larvae of itch mites. Nymphs are also present in hair follicles and resemble adults in appearance.
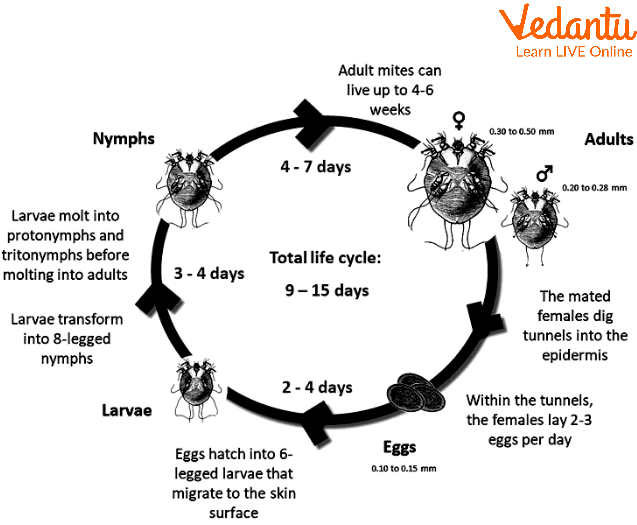
Life Cycle of a Scabies Mite
The adult stage of the nymph is marked by the appearance of a spherical, pouch-like, eyeless itch. The length of the female adult mites can reach 0.45 mm. The length of adult male mites is double that of females. Mites only mate once during their life.
After the male mite has gotten inside the female mite's molting pouch, reproduction in mites takes place. The female mite is fertilized for the rest of the duration of her life after mating.
These fertilized female mites leave their molting pouches behind and move to the surfaces of the body in search of an appropriate location to dig permanently. The mature mites cling to the skin using pulvilli that resemble suckers and are connected to the two sets of anterior legs.
After locating the ideal location, the female mite penetrates the skin and lays her eggs there. The fertilized female can remain in the host for up to one or two months after she has seeped into the skin.
Scabies Infection and its Symptoms
The adult itch mite plaguing the skin is what leads to human scabies. The most common way for the scabies mite to spread is through extended, close skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual. In congested areas where close bodily contact is common, scabies can spread quickly. Because scabies transmits so quickly, medical professionals frequently advise treating every member of the family or any close connections.
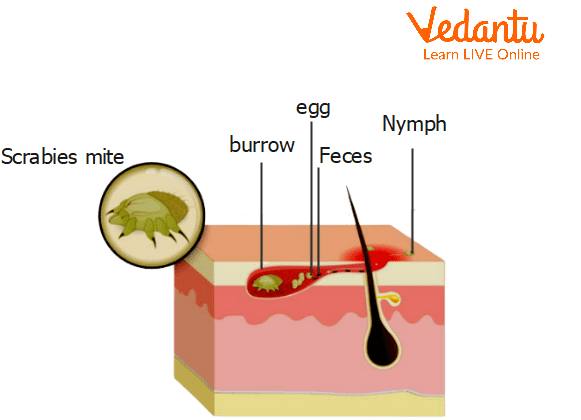
Scabies Under the Skin
Itching and tiny burrows created of pimples or blisters on the skin are sure signs of scabies. Skin creases are a frequent location for scabies. Scabies, however, can affect many different body parts. If you've already had scabies, symptoms could appear a few days after exposure. The scabies hive appears in many people. This hive produces tiny pimples that frequently line up. The bumps can resemble acne, blisters, tiny bites, or under-the-skin knots. Some people get scaly, eczema-like areas on their skin.
In the region of the mite's burrow, there is severe itching. The urge to itch could be more intense at night. It is simple to treat scabies. The scabies-causing mites and their eggs are killed by prescription skin treatments and tablets. However, the itching may continue for several weeks following treatment.
Interesting Facts
Scabies is the most common Infection and can infect anyone
It is a highly contagious infection that can transmit through skin contact
Scabies can be diagnosed by noninvasive methods just by looking at the rash
People who have weak immunity can get easily infected and will have a form of scabies
Important Questions
1. The itching disease, Scabies, is caused by which pathogen?
The itching disease scabies is caused by the human itch mite. Mites can burrow into the upper layer of skin where they can lay eggs and cause Infections
2. Does scabies Infections need contact isolation to prevent transmission of Infection?
Yes scabies needs contact isolation to prevent transmission of Infections to other healthy persons. These patients should be isolated till they are treated successfully.
3. In ideal circumstances, how many days do the eggs of scabies mites take to hatch?
These mites take around 3-4 days to hatch. After hatching these mites move to the outer surface of the skin where these mites mature into adults.
4. How long does it take scabies mites to reproduce?
It takes about 10 days for scabies mites to reproduce and make new adult scabies. First, it burrows under the skin and starts laying eggs within a few hours of burrowing.
Practice Questions
1. What are scabies symptoms?
2. Explain the life cycle of scabies
3. What is the lifespan of scabies insects?
4. What is the disease-causing pathogen of scabies?
Key Features
In this article, we have discussed scabies, scabies insects, and the life cycle of scabies.
Other parasite species, such as those that infect cats, horses, pigs, and other mammals besides Sarcoptes scabiei, also exist.
Scabies can cause skin irritation or inflammation, which can be upsetting. However, there are basic treatments for it.
Treatment for scabies includes antiparasitic medications such as permethrin. It should be administered every 2-3 for 1-2 weeks.


FAQs on Scabies Life Cycle Explained for Students
1. What is scabies and what is the organism that causes it?
Scabies is a contagious, itchy skin infestation caused by a microscopic mite named Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. This tiny parasite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs, leading to intense itching and a pimple-like rash. It is a common human parasitic disease found worldwide.
2. What are the four main stages of the scabies life cycle?
The life cycle of the scabies mite occurs entirely on the human host and consists of four distinct stages, typically completed in 10-17 days:
Egg: The adult female mite burrows into the skin and lays 2-3 eggs per day. These eggs are oval-shaped and remain in the burrow.
Larva: The eggs hatch into larvae within 3-4 days. The larvae, which have six legs, move to the skin's surface and create new, shorter burrows called molting pouches.
Nymph: Inside the molting pouch, the larva molts into a nymph, which has eight legs. The nymph molts one more time before becoming an adult.
Adult: The adult mite emerges from the pouch to mate. After mating, the male mite dies, and the female mite finds a suitable site to create a new burrow and begin laying eggs, starting the cycle over again.
3. How is a scabies infestation transmitted between people?
The primary mode of scabies transmission is through prolonged, direct, skin-to-skin contact with an infested person. It spreads easily among family members or in settings with close physical contact like schools and nursing homes. While less common, transmission can also occur by sharing contaminated items such as bedding, towels, or clothing used by an infested person.
4. What are the key symptoms that indicate a person might have scabies?
The most characteristic symptoms of scabies are:
Intense itching (pruritus): This is often severe and is usually worse at night, disrupting sleep.
Skin Rash: A pimple-like rash, tiny blisters (vesicles), or small, raised bumps on the skin.
Burrows: Thin, grayish-white or skin-coloured lines on the skin's surface, which are created by the female mites tunneling under the skin.
Common sites include the webbing between fingers, wrists, elbows, armpits, and along the beltline.
5. Why does the itching from scabies feel much worse at night?
The itching associated with scabies intensifies at night primarily for two reasons. First, the scabies mites become more active as the body temperature of the host warms up during rest or in bed. Second, the itching itself is an allergic reaction to the mites, their eggs, and their faeces. With fewer distractions at night, the brain's perception of this allergic itch becomes more pronounced, making it feel more severe.
6. How does the human body's immune response cause the scabies rash?
The visible rash and intense itching of scabies are not caused by the mites biting, but rather by the body's delayed hypersensitivity reaction to the presence of the mites and their byproducts (eggs, saliva, and faeces). The immune system identifies these as foreign substances and triggers an inflammatory response, leading to redness, swelling, and the formation of the rash. This is why in a first-time infestation, symptoms may take 4 to 6 weeks to appear as the immune system takes time to develop this sensitivity.
7. What is the difference between the main burrow of a scabies mite and a molting pouch?
A burrow is a relatively long, winding tunnel in the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of skin) created by an adult female mite for the purpose of laying her eggs. In contrast, a molting pouch is a much shorter, temporary burrow created by the larval and nymphal stages of the mite. They use these pouches for protection while they shed their exoskeletons and develop into the next stage of their life cycle.
8. Can a person get a permanent scabies infestation from an animal with mange?
No, a person cannot get a permanent scabies infestation from an animal. Mange in animals is caused by a different variety of scabies mite. While these animal mites can burrow into human skin and cause temporary itching and a rash, they are not adapted to our bodies. They cannot complete their life cycle or reproduce on a human host. Therefore, the infestation in humans is self-limiting and usually resolves on its own without medical treatment.
In this article, we are going to study scabies, scabies insects, and the life cycle of scabies. We will also study the signs and symptoms of scabies, and the causes of scabies. After reading this article, readers will be able to tell
Scabies
Scabies insect
Causes of scabies
Scabies infection
The life cycle of scabies










