How Single Circulation Works in Animals
Do you know what are gills used for? Are gills only present in fish or do some other organisms have gills? Gills are used for respiration and they are present in most aquatic organisms for breathing. Gills are also used in single circulation and serve all fish. Blood only passes through the heart once in a single circulatory system, completing a full circuit through the body of the fish. The exchange of gases occurs in the gills, where the blood goes from the heart (carbon dioxide is released and oxygen is absorbed). To know more about single circulation, continue reading this article!!
What is Single Circulation?
Fishes have a single circulatory system. In the hearts of fish, there are two chambers: an atrium and a ventricle. Deoxygenated blood from the tissues is pumped to the gills for purification, where it is then returned to the heart to be given to the various bodily tissues with oxygen. Blood that has been deoxygenated returns to the heart from tissues. As a result, solitary circulation refers to the flow of blood along a single circulatory channel. Single circulation is exhibited by many aquatic animals such as all fishes, exocomets, hippocampus, etc.
Single Circulation in Fishes
A single circulatory system serves all fish. Blood only passes through the heart once in a single circulatory system, completing a full circuit through the body of the fish. The exchange of gases occurs in the gills, where the blood goes from the heart (carbon dioxide is released and oxygen is absorbed). The body's numerous organs receive oxygenated blood from the gills, which then returns to the heart via these organs. In single circulation, blood flows through the heart only once.
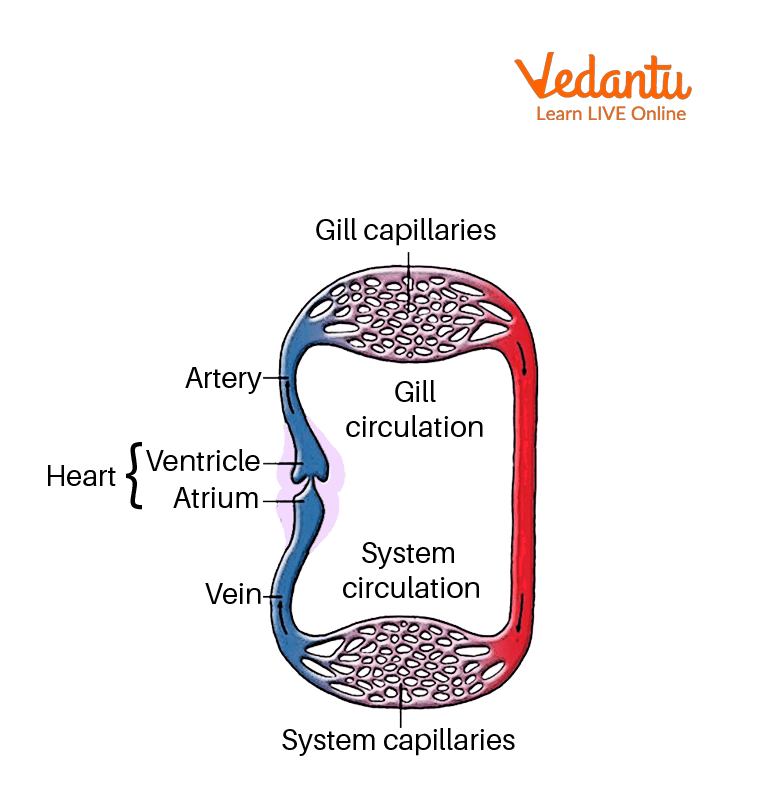
Single Circulation
Main Features of Single Circulation
The main features of single circulation are explained below.
In single circulation, blood only travels once to the heart for every circuit of the body.
A single circulatory system is present only in those animals who have two-chambered or three-chambered hearts.
Singles circulatory system present in aquatic organisms.
In single circulation, only deoxygenated blood goes to the heart.
Differences Between Single Circulation and Double Circulation
Single- and Double-Circulation Flow Diagrams
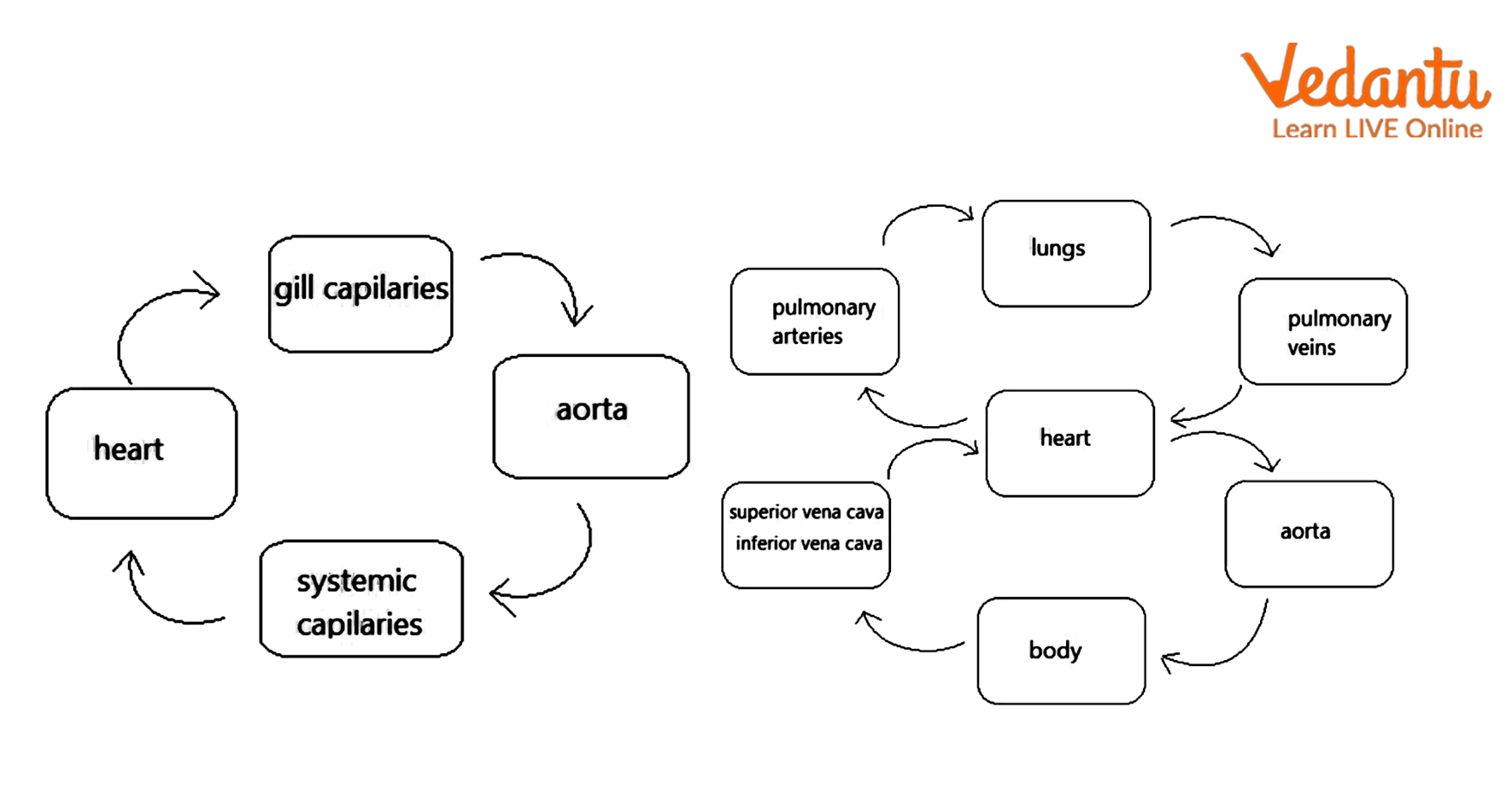
Single and Double Circulation Flow Diagram
Interesting Facts
About 100,000 km is the length of the circulatory system.
The RBCs have a size of 8 microns.
Heart rate is slower in larger mammals.
Outside of the body, the heart may beat for three to five minutes.
Blood comes in various red shades.
About 2.5 billion heartbeats have been recorded worldwide.
Important Questions
1. Do arteries carry only oxygenated blood?
Ans: Yes, all arteries carry oxygenated blood, but there is one exception: the pulmonary artery is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood.
2. Write the names of organisms exhibiting single circulation?
Ans: Single circulation occurs in fishes, reptiles, and other organisms.
3. Is single circulation open or closed?
Ans: Single circulation is a closed type of circulation.
Practice Questions
Do all veins carry deoxygenated blood?
Why is the double circulatory system better than the single circulatory system?
What is single closed circulation?
Conclusion
When the heart pumps blood to the gills for oxygenation, the blood then circulates through the rest of the body before returning to the heart. This process is known as single circulation. It is well known that some animals, like fish, have a single circulatory system. Additionally, they have two chambers in their hearts rather than the usual one atrium and one ventricle. As a result, solitary circulation has a substantial drawback since it delivers oxygen slowly, which slows down metabolism. In the twofold circulatory system seen through humans, blood circulates in two separate circuits.


FAQs on Single Circulation: Definition, Steps & Examples
1. What is single circulation?
Single circulation is a type of circulatory system where the blood passes through the heart only once for each complete circuit of the body. In this system, the heart, typically a two-chambered heart (one atrium and one ventricle), pumps deoxygenated blood to the gills for oxygenation. This oxygenated blood is then distributed to the rest of the body directly from the gills without returning to the heart first.
2. Which animals have a single circulation system?
Single circulation is a characteristic feature of animals with gills as their primary respiratory organ. The most common examples include:
- Fish (Class Pisces): This is the classic example where the two-chambered heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the gills.
- Cyclostomes: Jawless fish like lampreys and hagfish also exhibit single circulation.
These animals typically have lower metabolic rates compared to animals with double circulation.
3. How does single circulation differ from double circulation?
The primary difference lies in the number of times blood passes through the heart in one complete cycle. In single circulation, blood flows through the heart once. In double circulation (found in birds and mammals), blood passes through the heart twice. The first pass pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation), and the second pass pumps the newly oxygenated blood to the rest of the body (systemic circulation). This makes double circulation a more efficient, high-pressure system.
4. Can you describe the pathway of blood in a single circulation system like in fish?
The pathway of blood in a fish follows a simple, single loop:
- Deoxygenated blood from the body tissues collects in the atrium.
- The atrium pumps the deoxygenated blood into the ventricle.
- The powerful ventricle pumps this deoxygenated blood to the gills.
- In the gills, gas exchange occurs, and the blood becomes oxygenated.
- This oxygenated blood is then supplied directly to all body parts.
- After delivering oxygen, the deoxygenated blood returns to the atrium, completing the circuit.
5. What are the main limitations of a single circulation system?
The main limitation of single circulation is the low blood pressure and slower rate of blood flow to the body tissues. After passing through the dense capillary networks of the gills, the blood pressure drops significantly. This lower pressure means oxygen and nutrients are delivered less efficiently, which is only sufficient for animals with lower metabolic demands, like cold-blooded fish. It cannot support the high metabolic activity of warm-blooded animals like birds and mammals.
6. Why is the heart in fish known as a 'venous heart'?
The heart of a fish is called a venous heart because it exclusively receives and pumps deoxygenated (venous) blood. Unlike the four-chambered hearts of mammals, which handle both deoxygenated and oxygenated blood in separate chambers, the fish heart's atrium and ventricle only contain blood that is returning from the body and is yet to be oxygenated by the gills. The oxygenation process happens entirely outside the heart.
7. Why is single circulation sufficient for aquatic animals like fish but not for active terrestrial animals?
Single circulation is adequate for fish due to a combination of factors. Their poikilothermic (cold-blooded) nature means they do not need to expend energy to maintain a constant body temperature, resulting in lower metabolic demands. Furthermore, the buoyancy of water supports their body, reducing the energy needed for movement. In contrast, active terrestrial animals like mammals are homeothermic (warm-blooded) and require a highly efficient, high-pressure double circulation system to rapidly deliver large amounts of oxygen and nutrients needed to maintain body temperature and support more vigorous activity against gravity.










