Water Bodies on the Earth’s Surface
Water bodies cover nearly 71 percent of our planet Earth's surface. Earth's water bodies are categorised based on their sizes or the salinity and freshness of the water. These water bodies include oceans, seas, rivers and streams, lakes, ponds, etc.
Oceans are the largest and comprise most of the Earth's hydrosphere. They are vast bodies of saltwater and hold almost 96.5 per cent of the total amount of water on Earth's surface.
The defining components of an ocean include its salinity, density, heat capacity, and temperature. The average depth of the ocean is approximately 12,100 feet or 3,688 metres. You would be surprised to know that an estimated 50 to 80 percent of all kinds of life on Earth are present under the ocean surface. Until now, humans could explore less than 10 percent of that.
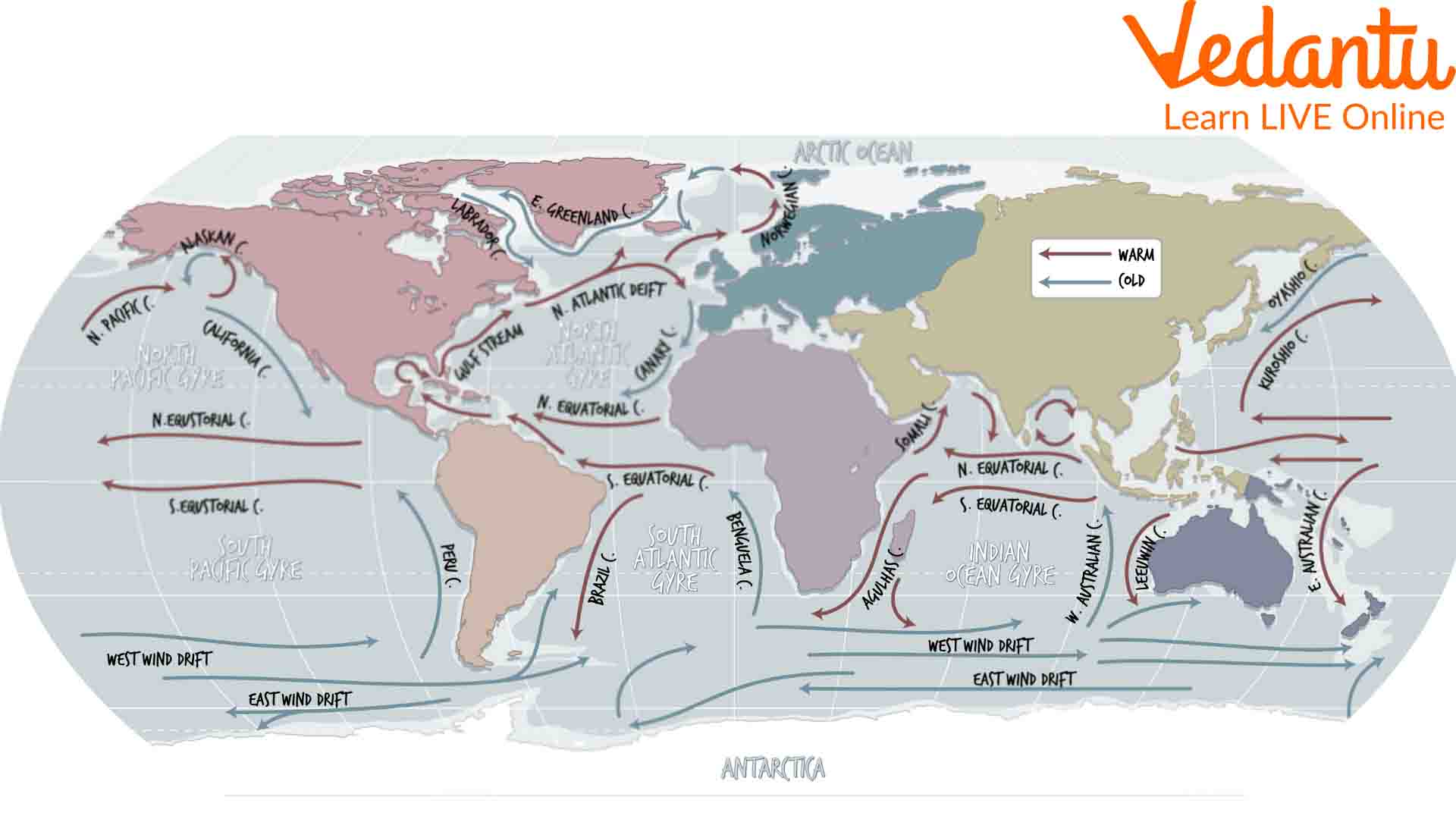
How Many Oceans are There in the World?
Almost 96.5 per cent of the whole world is covered by oceans stretching for vast areas on the surface of Earth. Conventionally speaking, there are four oceans on Earth. The oceans names are:
The Pacific Ocean: Covers over 60 million square miles and 4,000 metres of average depth.
The Atlantic Ocean: Covers over 41 million square miles and 3,646 metres of average depth.
The Indian Ocean: Covers over 27 million square miles and 3,741 metres of average depth.
The Arctic Ocean: Covers over 5 million square miles and 987 metres of average depth.
The Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian are considered the most commonly known ones. Recently, most countries, including the United States of America, have acknowledged the Southern ocean or the Antarctic ocean as the fifth ocean on the Earth's surface. So, it can be said that the Earth's surface is currently covered with five oceans.
Which is the Largest Ocean in the World?
Do you know among the five oceans, which is the largest ocean in the world? The Pacific Ocean is by far the largest and deepest ocean in the world, covering over 60 million square miles and comprising more than half of the planet's free water. It extends for an extensive stretch from the Arctic region in the north to the Antarctic region in the south. It lies between the continents of North America and South America on the east and Asia and Australia on the west.
The Pacific Ocean is a vast body of water with the deepest and most mysterious parts known to mankind and is home to some of the unique living creatures on Earth. Its basin is known as the 'Ring of Fire' because the regions along the ocean's edges are specifically noted as some of the most volcanically active regions in the world.
Discovery of a New Ocean: The Southern Ocean
Anthony de la Roché, during one of his visits to South Georgia in 1675, discovered the land for the first time south of the Antarctic Convergence and hence was the new ocean discovered. Although this new ocean name, the Southern Ocean, came up a long time back, and even though many scientists accepted its recognition, no one ever agreed on its existence.
Geographers from all over the world debated whether the waters surrounding Antarctica had the necessary traits that were unique to be identified as a separate ocean or if they were just southern stretches of the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian oceans.

According to Alex Tait, National Geographic Society Geographer, the Southern Ocean was thus never recognised by them officially. He and his society's map policy committee were trying to deal with the changes for years while witnessing the scientists and press related to ocean news make use of the name the Southern Ocean.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) officials declared that the federal agency has identified the Southern Ocean as the world's fifth ocean in the year 1999 when the U.S. Board on Geographic Names approved the name 'Southern Ocean'.
According to Dr Verena Meraldi, a biologist and chief scientist of Hurtigruten, acknowledging the Southern Ocean as an independent body of water and comprehending its role in global circulation has resulted in a huge step toward the betterment of scientific research projects and conserving all the species living in that ocean.
Important Facts about the Newest Ocean
Here are some important facts about the Southern Ocean that might enhance your knowledge of the same:
The Southern Ocean is the world's fourth largest ocean covering more than 8 million square miles and 3,270 metres of average depth. It holds over 17 million cubic miles of water approximately. It has a maximum depth of 7,432 metres in the South Sandwich Trench, which is southeast of the island of South Georgia.
Surrounding the South Pole and Antarctica, this newest ocean is the only water body on the planet that goes all the way around the globe.
The temperature in this new ocean found is somewhere between -2 and 10 degrees Celsius or 28 and 50 degrees Fahrenheit. It is the coldest and windiest of all the oceans on Earth. Parts of this ocean get frozen in the winter, thus forming huge sheets of ice. When the wind is very high, the ocean is choppier with giant waves.
It is one of the most productive feeding grounds in the entire world. Almost half of the water freezes during winter. When this enormous sheet of ice thaws during the springtime, it develops a distinctive layered surface of less salty water that allows plenty of phytoplankton (microscopic algae) to grow such that it appears like a milky substance when viewed from space.
These phytoplanktons form the base of the entire food web in the ocean, providing food for mammals, fish, and birds. Also, they produce almost half of the oxygen we breathe.
Conclusion
A water body represents any considerable accumulation or collection of water on the surface of Earth or any other planet in the Universe. By now, you are well aware of all the oceans of the world and the oceans' names. These vastly stretched water bodies cover most of the hydrosphere on the surface of Earth.
Although there are four commonly known oceans, the Southern Ocean has been identified as the fifth ocean of this planet. Besides being the coldest ocean, it is also the highest productive feeding basin on the planet.







