What Are the Main Causes and Effects of Tsunami Waves?
25 Amazing Facts About Tsunamis & Why We Observe World Tsunami Awareness Day 2025
World Tsunami Awareness Day is observed every year on November 5 to highlight the risks posed by tsunamis and to promote global awareness and preparedness. Initiated by the United Nations, this day serves as a call to action for communities, schools, and governments to educate people about tsunami safety. Understanding tsunamis is essential for minimizing disaster impact, especially for coastal regions. This page provides verified, student-friendly information—including facts about tsunami events, science, history, and practical tips—to help you stay informed and engaged for World Tsunami Awareness Day 2025.
What is a Tsunami?
A tsunami is a series of massive sea waves caused by the sudden displacement of water, most often after an underwater earthquake, volcanic eruption, or landslide. Tsunamis can travel across oceans at the speed of a jet plane and cause widespread destruction when they reach the shore. While sometimes called "tidal waves," tsunamis are not related to tides or everyday ocean waves—they are a unique and powerful natural disaster.
- Primary Keyword: Facts about tsunami
- Secondary Keywords: interesting facts about tsunami, 10 facts about tsunami
History and Significance of World Tsunami Awareness Day
World Tsunami Awareness Day was established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. The date, November 5, was chosen to commemorate the legendary Japanese story of "Inamura-no-hi" or "The Burning of the Rice Sheaves," in which a wise farmer saved his village from a tsunami. The observance aims to encourage the sharing of innovative approaches to risk reduction and to strengthen disaster preparedness globally. Schools, universities, and organizations worldwide take part in awareness activities—from educational drills and debates to creating informative posters.
World Tsunami Awareness Day 2025: Theme and Focus
Each year, World Tsunami Awareness Day adopts a new theme, focusing on different aspects of disaster risk reduction, disaster recovery, or safe community planning. As of 2025, the global theme is expected to emphasize “Building Tsunami-Ready Communities”, highlighting the need for early warning systems, education, and resilient infrastructure in coastal regions.
Top 25 Facts About Tsunamis
Here are some of the most important and interesting facts about tsunami events around the world—perfect for students, teachers, and anyone wanting to boost tsunami awareness in 2025.
- Tsunamis are most often caused by undersea earthquakes, but volcanic eruptions, landslides, and even meteorite impacts can trigger them.
- The word "tsunami" comes from Japanese, meaning "harbour wave."
- Tsunami waves in the deep ocean are often less than 1 meter high and go undetected by ships.
- As tsunamis approach land, the waves slow down and can build to heights of over 30 meters (about a 10-story building).
- Tsunamis can cross entire ocean basins at speeds up to 800 km/h (500 mph).
- The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami was one of the deadliest disasters in history, killing more than 230,000 people in 14 countries.
 Most tsunamis occur in the Pacific Ocean's “Ring of Fire” due to frequent seismic activity.
Most tsunamis occur in the Pacific Ocean's “Ring of Fire” due to frequent seismic activity.- Tsunamis are sometimes mistakenly called tidal waves, but they are unrelated to tides.
- The first wave of a tsunami may not be the largest; subsequent waves can be more powerful and destructive.
- Tsunami warning systems are in place in many parts of the world, especially the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- Before a tsunami hits, the sea often recedes dramatically from the shore—this is a dangerous sign.
- A tsunami’s wavelength can reach up to 1,000 kilometers, allowing it to travel vast distances inland.
- Tsunamis can flood coastal areas for minutes to hours, depending on geography and the wave’s energy.
- Japan, Indonesia, Chile, and the United States are among the countries most at risk for tsunamis.
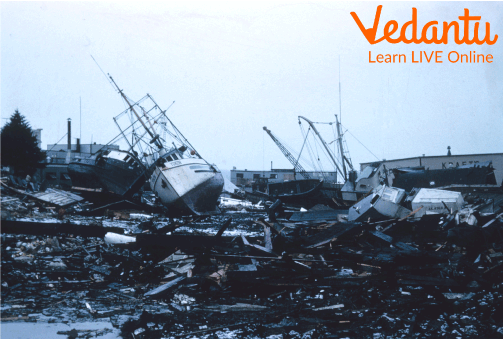 Tsunamis can move entire buildings, uproot trees, and wash away vehicles and bridges.
Tsunamis can move entire buildings, uproot trees, and wash away vehicles and bridges.- Scientists use ocean floor sensors and satellites to detect tsunamis and alert coastal residents.
- The International Tsunami Warning System was established to monitor seismic activity and reduce loss of life.
- Some tsunamis are so small they're barely noticeable; others can devastate entire coasts.
- Certain plants like mangroves and tidal trees can reduce the velocity of tsunami waves and protect shorelines.
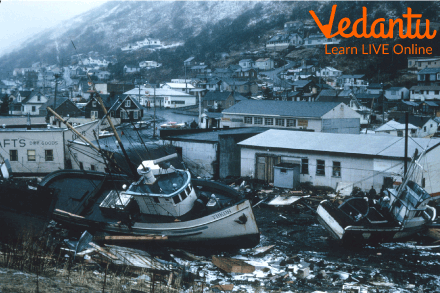 Tsunamis can affect not only humans but also wildlife, including marine and coastal ecosystems.
Tsunamis can affect not only humans but also wildlife, including marine and coastal ecosystems.- The earliest recorded tsunami comes from ancient Greece in 426 BCE.
- A tsunami can last anywhere from several minutes to over an hour, often occurring as a series of waves with dangerous intervals.
- People living close to the shore should know evacuation routes and participate in regular tsunami drills.
- International Days like World Tsunami Awareness Day help communities prepare for future tsunamis and recover more quickly after disasters.
- Staying informed and spreading tsunami facts encourages safer coastal communities worldwide.
Tsunami Awareness Day Activities for Students and Schools
World Tsunami Awareness Day offers many ways to participate:
- Host science fairs or debates on interesting facts about tsunami science and disaster safety.
- Create posters or infographics about “10 facts about tsunami” to raise awareness in your community.
- Organize evacuation drills or participate in online games and quizzes about tsunamis.
- Research and present on historical tsunamis and their effects on culture, wildlife, and the environment.
- Share stories or interviews of tsunami survivors as part of classroom projects or school events.
- Encourage community clean-ups and promote planting of tidal trees or mangroves for coastal protection.
Educational Takeaways & Student Tips
Knowing the facts about tsunami formation, warning signs, and safety procedures is essential for students—especially those living in or near coastal regions. Always move quickly to higher ground if you see the water recede suddenly, and never stay close to the shoreline during an alert. Sharing knowledge, participating in awareness campaigns, and practicing preparedness can help save lives.
For more environmental and disaster science resources, explore our World Earthquake Day or World Oceans Day blogs.
Quotes and Slogans for Tsunami Awareness
- “Better awareness, fewer losses: Know the facts about tsunamis.”
- “Run to higher ground, not towards the waves.”
- “Prepared communities are safer communities.”
- “Nature’s power is vast. Our knowledge is our shield.”
- “Tsunami awareness saves lives.”
- “Stay alert, stay informed, stay safe.”
- “Together for a tsunami-ready world.”
Conclusion
World Tsunami Awareness Day 2025 reminds us of the importance of science education, preparedness, and community action in minimizing the impact of natural disasters. By understanding key facts about tsunami formation, their history, and the best ways to stay safe, students and communities can play a direct role in saving lives and reducing risk. Share your knowledge, stay prepared, and be part of a more resilient future!
FAQs on 25 Amazing Facts About Tsunamis & Why They Matter
1. When is World Tsunami Awareness Day celebrated?
World Tsunami Awareness Day is observed every year on 5th November. It aims to raise global awareness about the dangers of tsunamis and the importance of early warning and preparedness.
2. When did the Disaster Management Act come into force in India?
The Disaster Management Act was enacted in India in 2005. It provides an institutional framework for disaster prevention, preparedness, and response to natural and man-made disasters.
3. When was India affected by the Tsunami?
India was affected by a major tsunami on 26 December 2004, due to an undersea earthquake near Sumatra. The tsunami caused significant devastation along the eastern coast and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
4. What is the main cause of the Tsunami?
Earthquakes are the primary cause of tsunamis. Most tsunamis form after underwater seismic activity forces a sudden upward or downward movement of the ocean floor, displacing large amounts of water.
5. Where did the word "Tsunami" come from?
The word "tsunami" comes from the Japanese language and means "harbour wave." It describes the phenomenon of large sea waves impacting coastal areas, especially harbours.
6. What are 5 interesting facts about tsunamis?
Here are 5 interesting facts about tsunamis:
- Most tsunamis are triggered by undersea earthquakes, but volcanoes, landslides, and meteorites can also cause them.
- Tsunami waves can travel at speeds up to 800 km/h (500 mph) in deep water.
- Out in the open ocean, tsunami waves may be less than 1 meter high but grow taller near the shore.
- The first wave is not always the largest; later waves can be more destructive.
- Planting mangroves and other tidal trees helps lower the speed and impact of tsunamis along coastlines.
7. What warning signs can help you identify a potential tsunami?
Warning signs of a tsunami include:
- A sudden and unexpected retreat of ocean water from the shore
- Strong or unusual ocean currents and swirling water
- Ground shaking near coastal areas due to an earthquake
If you notice any of these signs, immediately move to higher ground or inland for safety.
8. How does a tsunami differ from tides and regular ocean waves?
Tsunamis are caused by the sudden displacement of a large volume of water, usually from earthquakes or underwater events. They are not related to tides, which are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, or to wind-generated ocean waves. Tsunamis have much longer wavelengths and can travel vast distances with great force.
9. What are some effective tsunami survival tips?
To survive a tsunami:
- Move quickly to higher ground or away from the shoreline if you feel an earthquake or see the sea recede suddenly.
- Never go to the shore to watch incoming waves.
- Follow evacuation routes and listen to official warnings.
- Hold onto floating objects if swept up by the water and wait for rescue.
- Prepare emergency contacts and participate in local tsunami drills.
10. What is the International Tsunami Warning System?
The International Tsunami Warning System is a network of ocean floor sensors, satellites, and communication protocols used to detect earthquakes and tsunamis. It sends timely alerts to vulnerable coastal regions, helping to reduce risk and save lives through early warning and evacuation.
11. Why do we observe World Tsunami Awareness Day?
World Tsunami Awareness Day is observed to educate people about tsunami risks, promote early warning systems, and encourage disaster preparedness for coastal communities. It also commemorates stories of successful community action, like the Japanese legend of Inamura-no-hi.
12. How can students and schools participate in Tsunami Awareness Day?
Students and schools can participate by:
- Organizing science fairs or debates on facts about tsunamis
- Creating awareness posters and infographics
- Conducting evacuation and safety drills
- Researching real tsunami events and sharing findings
- Planting mangroves or supporting coastal clean-ups







