




An Overview of Class 10 Chemistry Ph Of Samples Experiment
Chemistry Experiment - pH of Samples
Chemistry employs a qualitative scale known as pH to categorize substances as acidic, basic, or neutral. pH scale is given by Søren Peder Lauritz Sørensen at the Carlsberg Laboratory in 1909. Acidic substances are those that have a pH value lower than 7. For instance, acidic foods like vinegar, tamarind, lemon, etc. More than 7 means that the substance is basic. Basic components like baking soda, limewater, ammonia, etc. are only a few examples. Contrarily, substances with a pH value of 7 are neutral, since they fall into neither the basic nor the acidic categories. Such as pure water. Hydrogen potential is referred to as pH. Highly potent bases can have a level of more than 14, while extremely potent acids can have a level lower than 0.
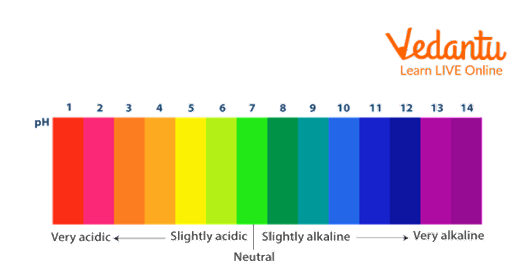
pH colour chart/pH indicator chart
Table of contents
Aim
Apparatus required
Theory Procedure
Observations
Result
Precautions
Aim
To determine the pH of the given samples using pH paper or a universal indicator. The following samples' pH values need to be determined:
Dilute CH3COOH
Dilute NaOH
NaCl
Dilute NaHCO3
Water
Lemon Juice
Apparatus required
Six test tubes
Test tube stand
Dilute acid CH3COOH
Dilute base NaOH
NaCl (salt) (Prepare by dissolving 10 mL of distilled water and 1 gram of salt)
Water
Lemon juice
Dilute NaHCO3
Glass rod
Measuring cylinder (10 mL)
Standard pH colour chart
pH paper
Glass rod
Dropper
Universal indicator
Theory
Sodium hydroxide's chemical name is NaOH. It can be found in laboratories as flakes or pellets. The basic sodium hydroxide is powerful. Sodium hydroxide entirely ionizes into a sodium ion and hydroxide ion upon dissolving in water. The sodium hydroxide solution has a pH that is higher than 7. NaOH(aq)→Na+(aq)+OH-(aq)
Acetic acid is another name for ethanoic acid. CH3COOH is its chemical formula. The acid is weak. It partially ionizes in an aqueous solution to produce hydrogen and acetate ions. A solution of ethanoic acid has a pH lower than 7. CH3COOH(aq)→H+(aq)+CH3COO-(aq)
There are acids, carbohydrates, and minerals in lemon juice. It has a pH lower than 7 and is acidic because of the presence of high amounts of citric acid.
Water has the chemical formula H2O. Since it is neither basic nor alkaline, its pH is 7.
Baking soda or sodium hydrogen carbonate are other names for sodium bicarbonate. NaHCO3 is its chemical formula. It partially ionizes when dissolved in water, generating sodium ions and bicarbonate ions. Sodium bicarbonate solution has a pH greater than 7.
NaHCO3(aq)→Na+(aq)+HCO3-(aq)
Procedure
Wash six test tubes with distilled water and put them on a test tube stand and label them A, B, C, D, E, F.
Add 2 ml CH3COOH to test tube A, 2 ml NaOH to test tube B, 2 ml NaCl to test tube C, 2ml NaHCO3 to test tube D, 2 ml of Water to test tube E, and 2 ml of Lemon juice to test tube F.
Label the six pH papers with the letters A through F.
Using a dropper, apply the corresponding sample solutions to the pH paper.
Note the colour change.
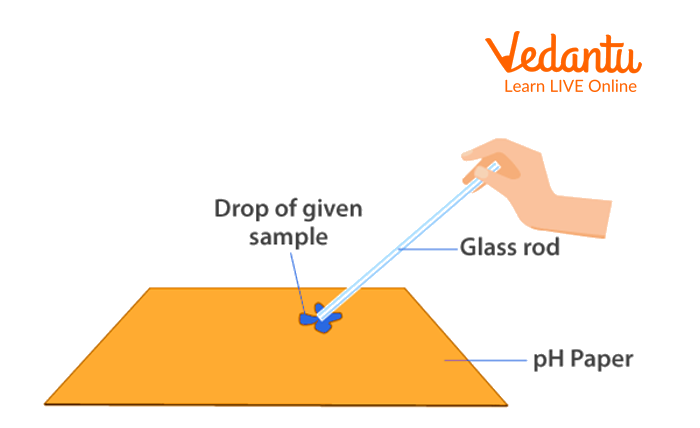
Observation
Results
Precautions
Make use of a freshly made test sample for the experiment.
A glass rod or dropper should be thoroughly cleaned before being utilized for another sample.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What do you mean by pH?
Ans. The hydrogen ion concentration in a solution is measured by pH.
2. At 25 °C (298 K), what is the pH of pure water?
Ans. At 25 °C, pure water has a pH of 7.
3. What pH do you think the dilute HCl and dilute NaOH solutions should have? Observe, then describe what you discover.
Ans. Because dilute HCl dissociates to produce H+ ions when it is dissolved in water, its pH is less than 7. Since diluted NaOH dissociates to produce OH- ions when it is dissolved in water, its pH is higher than 7.
4. When the soda water bottle is opened, the dissolved CO2 leaks out. As the gas escapes, will the pH of the solution rise or fall? Whatever your choice, explain it.
Ans. Carbonic acid and CO2 gas are dissolved in soda water bottles. Its pH is under 7. However, when we open it, CO2 gas is expelled and the acid concentration falls. The pH rises as a result.
Viva Questions
Identify the scientist who developed pH.
Ans. Sorensen.
What is the pH of human blood?
Ans. Human blood has a pH of 7.34 to 7.45.
What pH range does human saliva fall into?
Ans. Human saliva has a pH range of 6.0 to 8.0.
What is an indicator?
Ans. It is a substance that, when exposed to acid or basic, changes colour.
Identify two artificial indications.
Ans. Both phenolphthalein and methyl orange.
Identify two plants that are utilized to gather natural indicators.
Ans. Both hibiscus and red cabbage.
Which pH measurement technique is more accurate?
Ans. For more precise pH measurements, use a pH metre.
What would the pH of the water be if it were heated to a temperature of 50 °C?
Ans. The pH of the water would be 6.55 at 50 °C.
What constitutes the universal indicator?
Ans. Thymol blue, methyl red, bromothymol blue, phenolphthalein, and other colours are parts of the universal indicator.
If the pH level is 7, what colour will the pH paper be?
Ans. When the pH value is 7, the pH paper will be blue.
Practical Based Questions
Which of the following is not necessary to determine a solution's pH?
pH paper
HCl
Universal indicator
Standard pH value chart.
Ans. HCl is the one which is not able to determine the solution’s pH.
Which of the above solutions would you employ to check the pH of a specific sample?
Blue litmus solution
Red litmus solution
Universal indicator solution
Red and blue litmus solution together
Ans. A universal indicator solution is used to check the pH of a specific sample.
Which of the following is not a universal indicator component?
Methyl red
Thymol blue
Safranin
Phenolphthalein
Ans. Safranin is not a universal indicator component.
What among the following causes pH paper to turn red?
Milk of magnesia
Baking soda
Oxalic acid solution
NaCl solution.
Ans. The Oxalic acid solution causes pH paper to turn red.
What colour would a pH indicator paper become after being dipped in a grape juice solution?
Deep red
Blue
Orange
Violet
Ans. The possible colour of the pH paper is Orange.
Water's pH will be at 25 and 37 degrees Celsius, respectively.
6.8 and 7
1 and 6.8
7.8 and 6
6 and 7.8
Ans. The pH of water at 25 °C and 37 °C will be 1 and 6.8.
Tea and coffee are inherent:
acidic
highly acidic
basic
highly basic.
Ans. The nature of tea and coffee is acidic.
If the solution's pH drops from 6 to 4, it becomes:
less basic
less acidic
more acidic
neutral
Ans. It becomes more acidic when the solution's pH drops from 6 to 4.
What pH does saliva have after a meal?
7
6.8
5.8
Less than 4
Ans. The pH of saliva after a meal is 5.8
Curd contains the following acid:
Acetic acid
Oxalic acid
Lactic acid
Tartaric acid
Ans. Curd contains Lactic acid.
Conclusion
A sample's acidity or alkalinity will determine its pH. A pH metre is used to determine the pH of a sample. The metre gauges the sample's voltage before converting it to a pH reading. A chemical's pH solution is temperature-dependent. Temperature fluctuations cause a change in pH. From the above pH experiment we can conclude that a solution having pH less than 7 is an acidic, the solution having pH equal to 7 is neutral and the solution having pH greater than 7 is basic via pH paper test.
FAQs on Class 10 Chemistry Ph Of Samples Experiment
1. Why is a pH Paper Unreliable?
pH cannot distinguish between pH readings of 0 and 14. For instance, if a solution's pH is less than 0, the right value won't be shown.
2. What occurs when a person's body becomes acidic?
When body fluids become highly acidic, acidosis can happen. When the kidneys and lungs are unable to keep the body's pH level balanced, this sickness develops. Acidosis can lead to several health issues, including serious ones, including death.
3. Give some examples of pH indicator?
Some pH indicator examples are:-
Thymol Blue
Methyl Red
Bromothymol Blue
Phenolphthalein.
4. How do antacids function?
Hyperacidity results from too much hydrochloric acid in the stomach. An antacid is a product of nature. It eliminates extra acid and soothes discomfort brought on by hyperacidity.






































