




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers On Experiments Based On Ph Change Experiment
A solution's acidic or basic character can be determined using a pH scale. Danish chemist Srensen first proposed the idea of pH in 1909 as a practical way to express acidity. Neutral solutions have a pH of value 7. For example, drinking water will have a pH of 7. The pH is the measurement of the amount of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions in the water. So, the higher the hydrogen ion concentration, the pH value will be less than 7 and the higher the hydroxyl ion concentration, the pH value will be greater than 7. For example, vinegar will have a pH of vinegar range from 2 to 3 and of soap range from 9 to 10.
Table of Content
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Observation
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To determine the change in pH of hydrochloric acid at different concentrations:
0.1M HCl
0.001M HCl
0.00001M HCl
Apparatus Required
Test Tube
Test Tube Stand
pH Metre
Standard pH Colour Chart
pH Paper
Glass Rod
0.1M HCl
0.001M HCl
0.00001M HCl
Theory
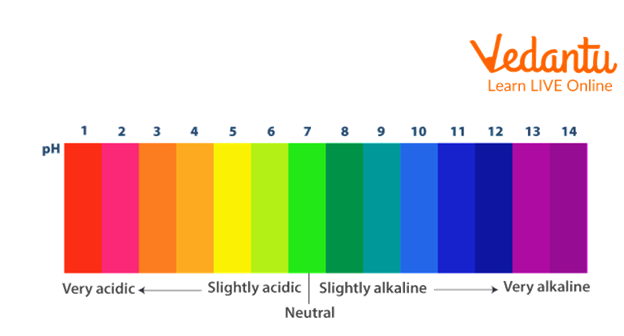
pH Scale
A solution's alkalinity or acidity can be determined using the pH scale, which measures hydrogen ion concentration.
A solution is considered acidic if its pH is less than 7.
A solution is considered basic if its pH is higher than 7.
A solution is neutral if its pH value is 7, indicating that it is at that level.
The pH Paper
We can use pH paper to determine whether a solution is basic, acidic or neutral.
A colour will appear when the pH paper is dipped into a solution whose pH has to be assessed.
The pH colour chart is used to compare this hue. We can also use universal indicator paper or universal indicator solution in place of pH paper.
The pH Metre
An instrument known as a pH metre tracks variations in the activity of hydrogen ions in a solution. The pH metre functions similarly to a voltmeter.
The combinatorial electrodes are capable of measuring voltage changes of the order of millivolts, also known as potential differences.
The loss of electrons that coincides with the loss of H+ results in changes in potentials.
Procedure
Take 0.01M HCl, 0.001M HCl and 0.00001M HCl in three test tubes.
With the aid of a glass rod, place two to three drops of the specified solution concentration on the pH paper.
Watch how the pH paper's colour changes.
Compare the pH paper's colour to the conventional pH indicator chart.
Note the sample's approximate pH value using the pH metre.
pH paper
Observations
Result
The pH value changes for different concentrations of HCl. And pH value increases on dilution.
Precautions
For the experiment, use a newly prepared test sample.
To obtain the correct pH readings, the concentration of acid should be different.
Before utilising a glass rod or dropper for another sample, it must first be completely cleaned.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What is the meaning of pH?
Ans: A metric for determining how basic or acidic a substance or solution is. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A pH value of 7 is considered neutral on this scale, meaning it is neither acidic nor basic. It is more acidic if the pH value is below 7, and more basic if the pH value is above 7.
2. What is a buffer solution?
Ans: The solution of reserve acidity or alkalinity that resists pH change upon the addition of a modest amount of acid or alkali is known as a buffer. There are acidic and basic buffers. And a mixture of aqueous solutions of CH3COONa and HCl can be an example of an acidic buffer.
3. Which indicator is used in pH metric titration?
Ans: Strong acid-strong base titration is done with a phenolphthalein indicator. Because it exhibits colour changes in the pH range of 8.3 to 10, phenolphthalein was chosen. It will be pink in basic solutions and clear in acidic ones.
4. What happens to a buffer on diluting?
Ans: On diluting a buffer solution, its pH doesn't change. On dilution, the ratio of the concentration of salt and acid (or base) remains unchanged.
Viva Questions
1. What impact does dilution have on the pH of an acidic solution and a basic solution?
Ans: The pH of an acidic solution rises with dilution, while the pH of a basic solution falls with dilution.
2. Does a raise in temperature have an impact on the pH of pure water?
Ans: With an increase in temperature, the pH value slightly declines. This is because as the temperature rises, the degree to which water dissociates increases, which in turn causes the concentration of hydronium ions to climb.
3. What would happen to the pH of the combination of any two acidic solutions?
Ans: The pH of the mixture would be in the range of the two solutions' pH values.
4. What is the pH of water?
Ans: Water is neutral, and its pH is 7.
5. What is an ionic product of water?
Ans: KW = [H3O+][OH-].
6. What is meant by an acid-base indicator?
Ans: An organic molecule that changes colour within a specific pH range is known as an acid-base indicator.
7. Does the addition of an acid or a base influence the value of the ionic product of water?
Ans: No, adding a little acid causes the hydronium ion concentration to rise and the hydroxyl ion concentration to fall. So, the ionic product of water doesn't change.
8. What will be the pH of lemon juice?
Ans: Lemons have an acidic pH due to their high citric acid content, and lemon juice has a pH between 2 and 3.
9. What is meant by a universal indicator?
Ans: It consists of a variety of indicators with various pH values. It exhibits several colour variations over a wide pH range. Each colour has an approximate pH that goes with it.
10. What will be the pH value for soap?
Ans: As soap is alkaline, its pH value ranges from 9 to 10.
Practical Based Questions
What is the range of the pH scale?
1 to 7
7 to 14
0 to 10
0 to 14
Ans: pH range is from 0 to 14.
What is the pH of a neutral solution?
<7
>7
0
7
Ans: pH of a neutral solution is 7.
The pH scale is used in which field?
Forestry
Medicine
Food
All of the above
Ans: pH scale is used in medicine, food and forestry.
Choose the correct statement about the buffer solution.
It is a solution whose pH does not change when a small amount of an acid or base is added to it.
It is a solution whose pH changes when a small amount of an acid or base is added to it.
It does not use pH value as a constant in a wide variety of chemical applications.
None of the above
Ans: pH of the buffer solution does not change in the addition of acid or base.
What will be the litmus test for a basic solution?
No change
Red litmus to blue
Blue litmus to red
None of the above.
Ans: For a basic solution, red litmus paper turns blue.
The pH of toothpaste is _____.
5 to 12
7 to10
1 to 7
7 to 14
Ans: pH of toothpaste is 7 to 10 (depending on additives).
Which of the following will be the strongest base?
pH= 12
pH=3
pH=9
pH=7
Ans: pH of the basic solution is greater than 7. Among the option bases, pH=12 will be the strongest base.
Addition of sodium acetate to acetic acid ____ the pH of the solution.
Decreases
Increases
No change
None of the above
Ans: The addition of sodium acetate to acetic acid increases the pH of the solution.
The ideal indicator for the titration of strong acid and weak base should have a pH range between
7-9
4-6
6-10
7-8
Ans: The ideal indicator for the titration of strong acid and weak base should have a pH range between 4 and 6.
What is the colour of acetic acid on pH paper?
Blue
Green
Yellow/orange
None of the above
Ans: The colour of acetic acid on pH paper is yellow or orange.
Conclusion
From the above experiment, we can conclude that pH is different for different concentrations of acid. For 0.1M HCl pH is 1, for 0.001M HCl pH is 3 and for 0.0001M HCl pH is 5. This shows pH value increases on dilution, so the acidity of the solution decreases.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers On Experiments Based On Ph Change Experiment
1. What happens as the pH value of a solution decreases?
It means that the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution increases as the pH value of the solution decreases.
2. What is meant by dilution?
Mixing an acid or base with water results in a decrease in the concentration of ions per unit volume. Such a process is called dilution.
3. How does pH impact a reaction's rate?
By altering the geometry of an enzyme's active site, every pH variation above or below the ideal pH has an impact on the pace of the reaction.
4. Does adding a base cause the acidity to rise or fall?
An acidic solution moves away from the centre of the pH scale and becomes less acidic as a base is introduced. This process is called neutralising the acid.
























