




Absorption: An Introduction
Have you ever noticed that when we put some chalk sticks in water, it gets wet and when we break it, it remains dry from the core whereas, when we put some drops of water on a piece of cloth, it instantly gets soaked by it? Or have you seen that some materials do not let other substances penetrate into their volume while others do? The process that happened with the chalk sticks is called adsorption whereas, the process that happened with the piece of cloth is called absorption.
In this article, we are going to understand the concept of absorption, its types, processes, examples and the difference between absorption and adsorption.
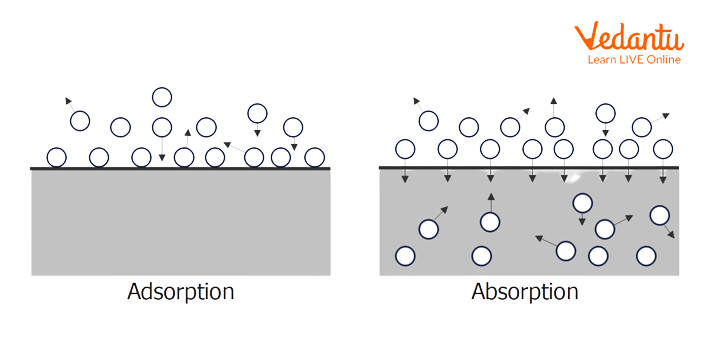
Absorption and Adsorption
What is Absorption?
The process in which one substance gets distributed throughout the volume of another substance is called absorption. In absorption, the substance which is absorbed by the other substance is called absorbate and the substance which absorbs the absorbate is called absorbent. Absorption is a type of bulk phenomenon. Absorption can be understood by some simple examples such as the absorption of water by a piece of cloth or sponge and chalk dipped in a liquid getting wet throughout its volume and the absorption of water by a towel.
Types of Absorption
The process of absorption is divided into two categories based on whether the absorbate and absorbent are reactive or nonreactive.
Physical absorption
Chemical absorption
Physical absorption – The absorption process in which there is no reaction between the molecules of absorbate and absorbent and only weak bonds are present is called physical absorption. For example, the absorption of water by a piece of cloth or sponge.
Chemical absorption – The absorption process in which there is a reaction between the molecules of absorbate and absorbent and strong bonds are present is called chemical absorption. For example, the absorption of ammonia gas by water and absorption of water by calcium carbonate.
Examples of Absorption
The process of absorption can be clearly understood by certain daily used examples which are explained below:
The absorption of water by calcium carbonate.
The absorption of oxygen by water for aquatic plants.
Absorption of water by a piece of cloth or sponge.
Removal of hydrogen sulphide from biogas is done by the process of absorption.
Absorption of sunlight by plants for photosynthesis.
Absorption of ammonia gas by water.
Carbon dioxide and oxygen are dissolved in the air or water through absorption.
Absorption of water by a towel.
A black surface absorbs heat through the process of absorption.
Absorption of heat by our skin.
Difference between Absorption and Adsorption
Conclusion
The process in which one substance gets distributed throughout the volume of another substance is called absorption. The process in which one substance gets accumulated on the surface of the other substance is called adsorption. Absorption is of two types – chemical absorption and physical absorption. In chemical absorption, there is a reaction between the molecules of absorbate and absorbent and strong ionic bonds are present. In physical absorption, there is no reaction between the molecules of absorbate and absorbent and only weak bonds are present. There are several examples of absorption which includes absorption of water by calcium carbonate and oxygen by water for aquatic life, removal of hydrogen sulphide from biogas through absorption etc. The difference between absorption and adsorption is that absorption is a bulk phenomenon and adsorption is a surface phenomenon. Absorption is an endothermic process while adsorption is an exothermic process.
FAQs on Difference Between Absorption and Adsorption for JEE Main 2026
1. Is absorption exothermic or endothermic in nature?
Absorption is generally an endothermic process whereas adsorption is an exothermic process. Absorption is endothermic because one substance gets distributed throughout the volume of another substance rather than just accumulating at the surface which requires more energy.
2. What is adsorption? Give an example.
The process of accumulation of a substance at the surface of another substance instead in the bulk is called adsorption. Adsorption is essentially a surface phenomenon. Solid state substances, mainly in a finely divided state, possess huge surface area which is required for adsorption and so, charcoal, silica gel, alumina gel, clay, colloids, metals in finely divided state, etc. act as good adsorbents (substance that adsorb another substance). For example, the adsorption of water vapour on silica gel and ammonia molecules on activated charcoal.
3. What are two absorption applications?
Absorption has various applications in almost all industries. Some of the daily applications of absorption are given below:
To absorb poisonous gases such as methane and carbon monoxide, activated charcoal is used in various products.
To remove hardness of water, ion exchange resin is used through the process of absorption.
























