




Redemption of Debentures Meaning
Companies and businesses traditionally utilised debentures to raise capital via public debt offerings. The debenture amount is guaranteed to be paid back to the lender at the end of the term, but the borrowers retain their lack of security. In India, a company or firm's collateral is used to obtain a loan. However, they are still not protected in the United States.
Meaning of Redemption of Debentures
Redemption of debentures means that debentures may be redeemed or paid back in full once their term has ended by repaying any outstanding obligations or loans owed to the debenture holder or even the lender who provided the loan.
Redemption of Debentures Journal Entries
Redemption of debentures includes a series of stipulations about the repayment of the debt or obligations, which were agreed upon by both parties. When a corporation's debentures mature, the company must repay the money borrowed from the holders of those debentures.
After the funds are repaid, the liability on the debenture account is discharged. Redemption of debentures journal entries:
1. Amount paid on redemption:
Debenture account Dr.
To bank account
2. For transferring properties
Profit and loss appreciation account Dr.
To Debenture Redemption Reserve account
Methods of Redemption of Debentures
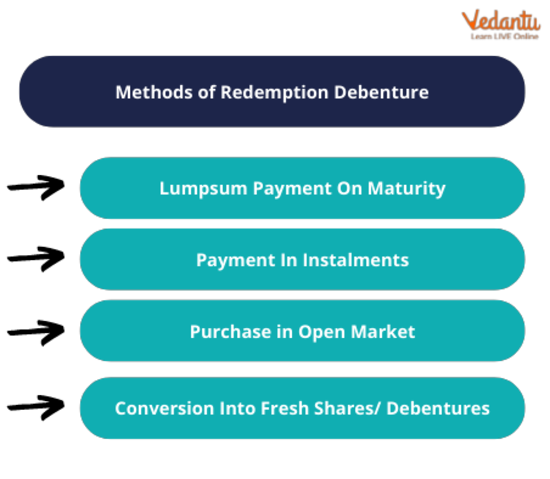
State the Types of Redemption of Debentures Methods
The amount owed to the person who owns a debenture when it comes due is called "redemption." The redemption involves giving back both the principal amount and the interest that was due on it. Companies could buy back the debentures at face value plus a profit. The company borrows money through debentures. This is a risk for the company. When this obligation comes due, it is paid off by a redemption process. Debentures can be redeemed in several ways. Each method of redemption of debentures has its way of keeping track of money. These ways of doing things can be put into the following groups:
Payment in one lump sum when the bond matures: - Under this method of redemption, the agreed-upon value of the debenture is compensated to the debenture holder all at once.
After maturity, instalment payments: - This is a different way debenture can be redeemed. The parties agree to save the debentures in instalments, which must be paid as agreed upon when the debentures were issued.
Redeeming the debenture by buying it on the market - You can also purchase debentures on the open market and use that to pay off your debt. This gives the option of redeeming the points at a lower price.
Converting debentures into fresh debentures or equity shares- Most debentures are redeemed by changing them into equity shares, preference shares, or even new debentures.
Sources of Redemption:
The following are the sources of redemption of debentures:
Companies Capital
Earned Profit
Change to Shares or Debenture
Earnings from the sale of new shares or bonds
Assets for Sale.
DRR and DRI
DRR and DRI
A debenture redemption reserve is a rule that says any company, firm, or business in the country which issues debentures must open a service for redeeming the debentures to display that they are making an effort to get their money back.
According to the Indian Companies Act of 1956, all businesses that issue debentures must set up a debenture redemption reserve well before a particular debenture matures. This Act says that companies must represent at least 25% of the face value of the debentures they have issued. Companies don't have to set aside money for the debenture redemption reserve immediately after issuing a debenture. After the debentures are paid off, the extra DRR has to be moved to the company's Capital Reserve.
If a company that gives debentures sets aside money for redeeming them, this is called a debenture redemption investment. Most of the time, the amount invested is at least 15% of the face value of the debentures that will be redeemed throughout the financial year. For DRR to be created, a company needs to invest the money in specific securities.
Conclusion
Debentures are a big part of how corporations get the money they need. Compared to other ways to earn money from the market, like preferred shares, bonus issues, equity shares, and rights issues, debentures are one of the most important ways to get money. Debentures may be less likely to default if provisions like DRR are made. The DRR ensures the company has enough money to pay the debenture holders and meet its other obligations. Debenture Redemption Reserve decreases the buyer's investment risk.
FAQs on Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) vs. Debenture Redemption Investment (DRI)
1. What is Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) as per the Companies Act, 2013?
Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) is a special reserve created from a company's profits that are available for distribution as dividends. The primary purpose of DRR is to safeguard the interests of debenture holders by ensuring the company systematically sets aside funds for their repayment. As per the Companies Act, 2013, and relevant SEBI guidelines, creating this reserve is a mandatory step before the redemption process begins for certain companies. It is important to note that DRR is an appropriation of profit, not a charge against it. For a detailed study of its application, you can refer to TS Grewal Class 12 solutions.
2. What is Debenture Redemption Investment (DRI)?
Debenture Redemption Investment (DRI) refers to the actual funds that a company must invest in specified, easily encashable securities. While DRR is a book entry to restrict profit distribution, DRI ensures that the company has liquid cash available when the debentures mature. This investment is made outside the company's regular business operations, earmarking funds specifically for the redemption payment, thereby preventing a cash crunch.
3. What is the primary difference between Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) and Debenture Redemption Investment (DRI)?
The primary difference between DRR and DRI lies in their fundamental nature and objective:
Nature: DRR is a book entry representing an allocation of profits to a reserve. It doesn't involve any cash outflow. In contrast, DRI is a tangible asset, representing an actual investment of cash into specified securities.
Objective: The goal of DRR is to ensure financial prudence by limiting the profits available for dividends. The objective of DRI is to ensure liquidity, making certain that the company has ready cash to repay debenture holders on the due date.
4. What are the current percentage requirements for creating DRR and making a DRI for the 2025-26 session?
As per the regulations applicable for the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus, the requirements are:
Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR): For companies that are required to create it, an amount equal to at least 10% of the value of outstanding debentures must be transferred to the DRR account before starting the redemption.
Debenture Redemption Investment (DRI): Companies must invest a sum that is not less than 15% of the nominal value of the debentures that are due for redemption in the current financial year. This investment must be made on or before the 30th of April of that year.
5. Why is it mandatory for certain companies to create a Debenture Redemption Reserve before redeeming debentures?
Creating a DRR is a legal safeguard mandated by the Companies Act to protect the financial interests of debenture holders. The primary reasons for this mandate are:
Financial Discipline: It compels the company to retain profits instead of distributing everything as dividends, ensuring funds are available for long-term debt obligations.
Creditor Protection: It serves as a financial cushion for debenture holders, providing them with an assurance that the company is financially preparing to meet its repayment promise.
Capital Preservation: By restricting dividend payouts, DRR helps maintain the company's capital base, preventing the erosion of funds that are crucial for redemption.
6. What happens to the DRR and DRI accounts after all the debentures are successfully redeemed?
Once the debentures are fully redeemed, the purpose of these accounts is fulfilled, and they are closed as follows:
Debenture Redemption Investment (DRI): The securities purchased as part of DRI are sold or encashed. The cash generated from this is used to make the final payment to the debenture holders.
Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR): Since DRR is an undistributed profit, the balance in the DRR account is transferred to the General Reserve. After this transfer, the amount becomes a free reserve, available for general corporate purposes like issuing bonus shares or declaring dividends.
7. Are all companies required to create a DRR? Which types of companies are exempt?
No, not all companies must create a Debenture Redemption Reserve. According to the Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014, the following entities are exempt from this requirement:
All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs) regulated by the RBI.
Banking Companies.
Other specified Financial Institutions.
Housing Finance Companies registered with the National Housing Bank.
Listed companies, for both publicly issued and privately placed debentures.
For practical problems covering these exemptions, you can review the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy.
8. How does the accounting treatment for DRR creation impact a company's financial statements compared to making a DRI?
The accounting treatments impact financial statements in distinct ways:
DRR Creation: This is an appropriation of profit. The entry debits 'Surplus in Statement of Profit and Loss' and credits 'Debenture Redemption Reserve'. This action reduces distributable profits and increases the 'Reserves and Surplus' on the liabilities side of the Balance Sheet. It has no impact on cash flow.
DRI Creation: This is a purchase of an asset. The entry debits 'Debenture Redemption Investment' (an asset) and credits 'Bank Account'. This reduces the company's cash balance and creates a new investment asset. It is recorded as a cash outflow under 'Investing Activities' in the Cash Flow Statement.
In summary, creating DRR affects the company's profit allocation, whereas making a DRI affects its liquid assets.





































