How to Write Simple Sentences with Examples
A simple sentence is one of the most important sentence structures in English grammar. Simple sentences are easy to form and understand, making them essential for anyone learning English. On this page, you will learn the meaning, rules, and many simple sentences examples to help you master this basic yet powerful grammar concept.
What is a Simple Sentence? (Simple Sentences Meaning)
A simple sentence contains just one independent clause. This means it has at least a subject and a verb and expresses a complete thought. A simple sentence does not have dependent (subordinate) clauses. It can include objects, complements, and modifiers, but it always keeps its structure simple and direct. Simple sentences are the building blocks of more complex expressions in English.
Simple sentences help you communicate clearly and are used in both written and spoken English. Example: "The sun shines." This form is ideal for beginners, including simple sentences for kids and simple sentences for grade 1 learners. Learn more about basic grammar rules at Vedantu English Grammar.
Rules and Structure: How to Write Simple Sentences
| Component | Details | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Subject | Who/what the sentence is about | The dog |
| Verb | Action or state | barks |
| Object (optional) | Receives the action | The boy kicked the ball. |
| Modifiers(optional) | Add detail | She sings beautifully. |
A simple sentence must have a subject and a verb. It may include objects or other phrases, but will never have more than one independent clause. Compound elements (like compound subjects or verbs), such as "Tom and Jerry run," are still part of simple sentences in English grammar.
Simple Sentences Examples and Patterns
Using simple sentences examples is the best way to understand their structure. These sentences can describe people, actions, states, or feelings in one clear clause. They form the foundation for developing more complex writing and speech skills. Here are 10 simple sentences and more patterns you can follow in your daily English practice.
10 Simple Sentences Examples
The cat sleeps.
Birds fly.
She runs.
I like apples.
He smiled.
We play cricket.
The baby laughs.
It is raining.
Mina studies daily.
The flowers bloom.
20 Examples of Simple Sentences
John reads books.
Dogs bark.
The car stops suddenly.
My mother cooks well.
She dances gracefully.
We watch TV at night.
You help your friend.
Raj swims in the pool.
The teacher enters the class.
Sunflowers turn to the sun.
Milk is healthy.
My sister sings songs.
They walk to school.
The dog jumps over the wall.
We listen to music.
She writes a letter.
The boys play football.
He drives carefully.
Rain falls today.
The child smiles brightly.
You can use these simple sentences for students in classwork, written assignments, and creative writing. For more practice, visit English Worksheets for Kids.
Simple Sentences for Kids and Beginners
Simple sentences for kids are usually short and use easy words. These are often used in the early years, like simple sentences for kindergarten, grade 1, or 2nd grade. Practising these sentences helps children develop language confidence through repetition and clarity.
Simple Sentences for Kindergarten and Grade 1
I see a cat.
You are happy.
He is my friend.
She eats rice.
We jump high.
It is blue.
The dog runs.
They sit quietly.
Birds sing.
The moon shines.
For more child-friendly content, check out Vedantu Kids Topics, which includes simple sentences for 1st grade and vocabulary for early learners.
Simple Sentences in English Grammar: Types and Compound Elements
Simple sentences in English grammar can be short or long. As long as only one independent clause is present, it remains a simple sentence—even with compound subjects, compound verbs, or multiple objects. Here are a few variations you might see:
Compound Elements in Simple Sentences Examples
Anil and Ritu went to the market. (compound subject)
We ate pizza and drank juice. (compound predicate)
Ravi wrote a letter and made a call.
Simple sentences are effective for introducing new grammar points, such as determiners and pronouns.
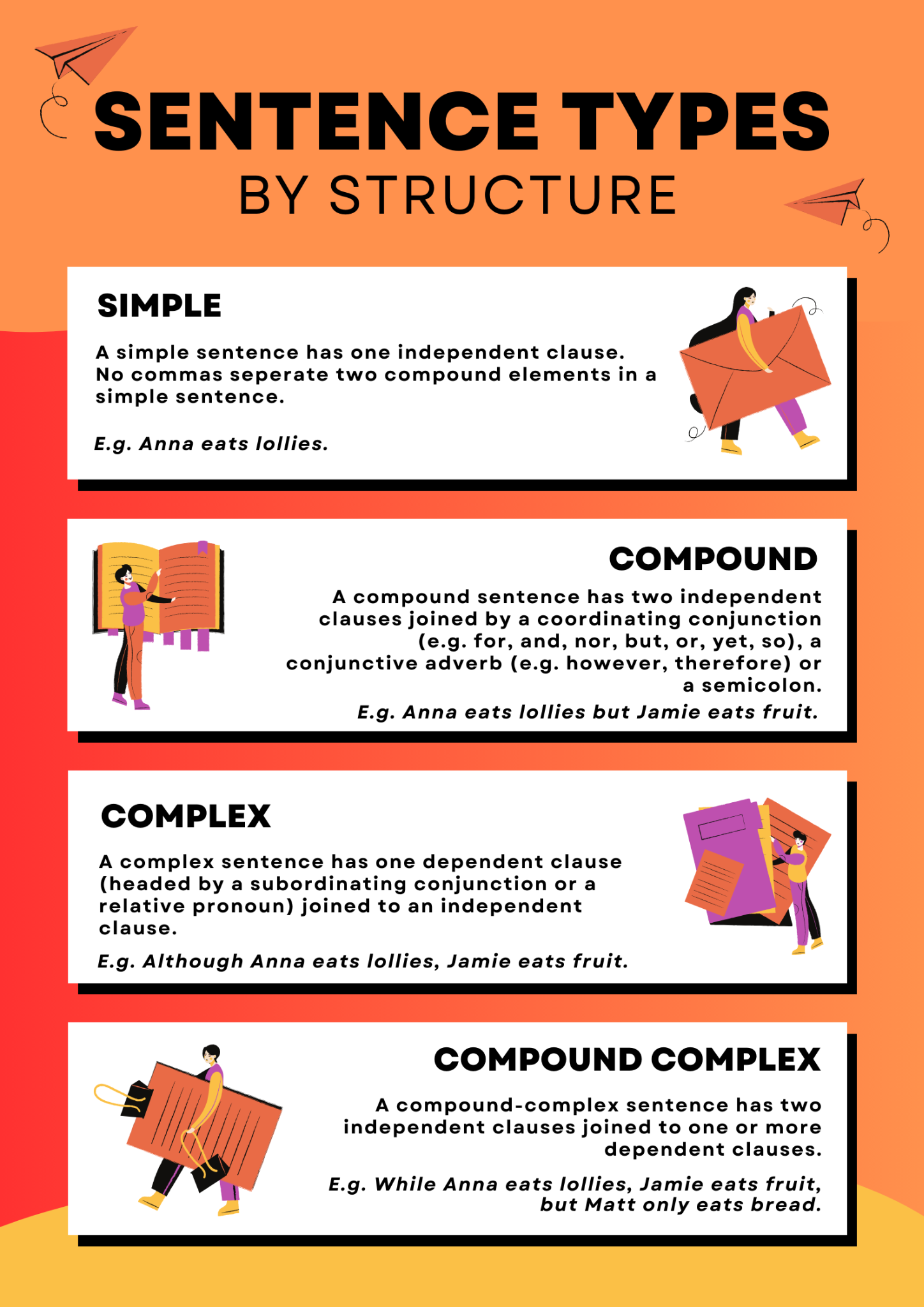
Simple, Compound, and Complex Sentences: Key Differences
Simple sentences differ from compound and complex sentences. A compound sentence joins two independent clauses (e.g., "I came, and he went"). A complex sentence joins a main clause with one or more dependent clauses (e.g., "I stayed because it was raining"). Learning these differences is vital for mastering English grammar.
Explore more about sentence types at Compound Sentences and Complex Sentences.
Simple Sentences Worksheet and Practice Tips
To get better at writing simple sentences, use worksheets and daily writing activities. These help learners identify the structure, use correct word order, and construct proper statements. Teachers use simple sentences worksheets to reinforce grammar topics and develop foundational writing skills.
Find a variety of worksheets at Worksheets for Kids and Grammar Exercises to practice more simple sentences in English grammar.
Simple Sentences in Other Languages
Learning simple sentences in other languages, such as simple sentences in Spanish or Hindi, helps students compare structures and understand how sentences are built universally. For early English classes, simple sentences are always the starting point before introducing complex ideas or other grammatical categories.
If you want to explore similar structures in Indian languages, browse topics on names of things for kids on Vedantu.
Why are Simple Sentences Important?
Simple sentences are vital for clear and precise communication. They are quick to read and easy for all ages, making them suitable for both beginners and advanced learners. They allow writers to focus on the message, reduce confusion, and build towards more advanced sentence structures confidently.
For guidance on sentence writing and improving clarity, refer to Sentence Structure and What Is a Sentence? on Vedantu.
Simple sentences are the foundation of English grammar. Learning to identify and use simple sentences examples prepares students for advanced writing and speaking skills. Practicing short, clear sentences daily helps learners of all ages communicate more effectively and confidently in English.
FAQs on What Is a Simple Sentence?
1. What are simple sentences?
Simple sentences are sentences that contain only one independent clause, expressing a single idea or thought.
Key features include:
- Consist of a subject and a predicate
- No dependent or subordinate clauses
- Clear, straightforward structure
- Often used for making direct statements
2. Give three examples of simple sentences.
Examples of simple sentences include:
- The sun rises.
- She reads books.
- Children play outside.
3. How do you identify a simple sentence?
A simple sentence can be identified by checking if it contains only one independent clause and no dependent clauses.
Steps to identify:
- Look for a single subject and a single predicate
- No use of coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or) to connect clauses
- Expresses a complete thought on its own
4. What is the difference between simple and compound sentences?
Simple sentences have one independent clause, whereas compound sentences contain two or more independent clauses joined by coordinating conjunctions.
- Simple sentence: I like apples.
- Compound sentence: I like apples, and she likes oranges.
5. Why are simple sentences important in English grammar?
Simple sentences are fundamental in English grammar for communicating clear and concise ideas.
They are important because they:
- Build a strong foundation for writing
- Make communication direct and easy to understand
- Help avoid grammatical errors in complex writing
6. Can a simple sentence have a compound subject or predicate?
Yes, a simple sentence can have a compound subject or predicate, as long as there is only one independent clause.
For example:
- John and Mary (compound subject) play and sing (compound predicate).
7. What are some tips for writing effective simple sentences?
To write effective simple sentences, focus on clarity and correctness.
Tips include:
- Use strong and precise subjects and verbs
- Avoid unnecessary modifiers
- Keep sentences short and focused
- Ensure each sentence expresses one clear idea
8. Are simple sentences always short?
While simple sentences are often short, they can be longer if they contain more details or compound elements.
Examples:
- Short: Birds sing.
- Long: Birds and insects chirp and buzz in the morning.
9. How do simple sentences help students improve their writing?
Simple sentences help students write clearly by focusing on one idea at a time, which enhances overall understanding.
Advantages include:
- Reduces grammatical errors
- Increases readability of texts
- Helps convey information quickly and directly
10. What are the main components of a simple sentence?
The main components of a simple sentence are the subject and predicate.
For example:
- Subject: The cat
- Predicate: sleeps