




Why Do the Moon's Phases Change? A Simple Guide for Students
Have you ever seen the sky at night? If yes, you must observe a glowing somewhat circular body like this:

Moon
The Moon is one of the brightest objects that you see at night. The Moon is one of our nearest neighbours in space. It is nearly about 250,000 miles away from us.
The moon, unlike the sun, does not emit any light. When you see the moon, you see the sun’s light reflected off it.
The different phases of the moon are determined based on how much of the moon is visible from the earth. Except during an eclipse, half of the moon is always illuminated by the sun, but we only see a fraction of it. This is the moon's current phase.

It takes nearly a month for the Moon to orbit the earth (27.3 days to complete a revolution, but 29.5 days to transition from one New Moon to another New Moon). The Moon completes its 27.3-day orbit of Earth while the Earth and Moon move around the Sun.
Have a Look at the Moon
The Moon's atmosphere has no oxygen. The surface of the moon is made up of rocks and dust. These rocks resemble those found on the surface of the earth. On the Moon's surface, there are several holes. These are called craters.

Surface of the Moon
Different Phases of Moon
Since we have walked the earth, we have been looking at the changing moon with wonder. But what would be the reasons for the appearance of the moon to change?
The answer has to do with the position of not just the moon but the sun and the earth as well. This is also what causes eclipses and tides.
Remember that the sun is the centre of our solar system and the earth is revolving around the sun as the year goes by and rotates on its axis.

The moon, on the other hand, revolves around the earth and rotates on its own axis. The moon circles around the earth every 28 days or so. It rotates for about 28 days as well. As a result, the same side of the moon faces the earth at all times.
The Moon does not emit its own light, but rather reflects sunlight. The sun does not always illuminate the half of the moon that faces the earth.
As the moon moves around the earth, it seems to change its shape. Does the moon actually change its shape? No, it does not. The moon has no light of its own. The light we see is actually sunlight bouncing off the moon's surface. At any time, half of the moon is lit up by the Sun's light while the other part is in darkness. As the moon goes around the earth, different portions of its lit side are visible. Thus, only its appearance on the earth changes and not its actual shape. We call it different phases of moon.
Names of Phases of Moon
There are four phases of the moon. Let’s see the different phases of moon diagram one by one.
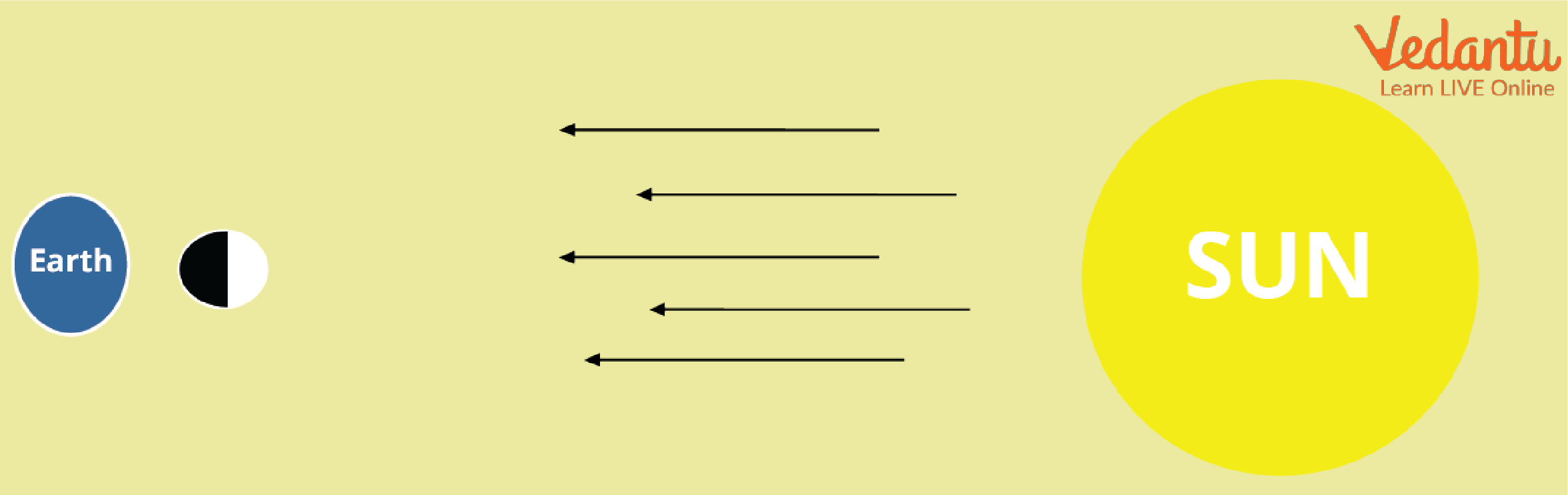
New Moon
The light coming from the sun reaches the side of the moon that is away from the earth.
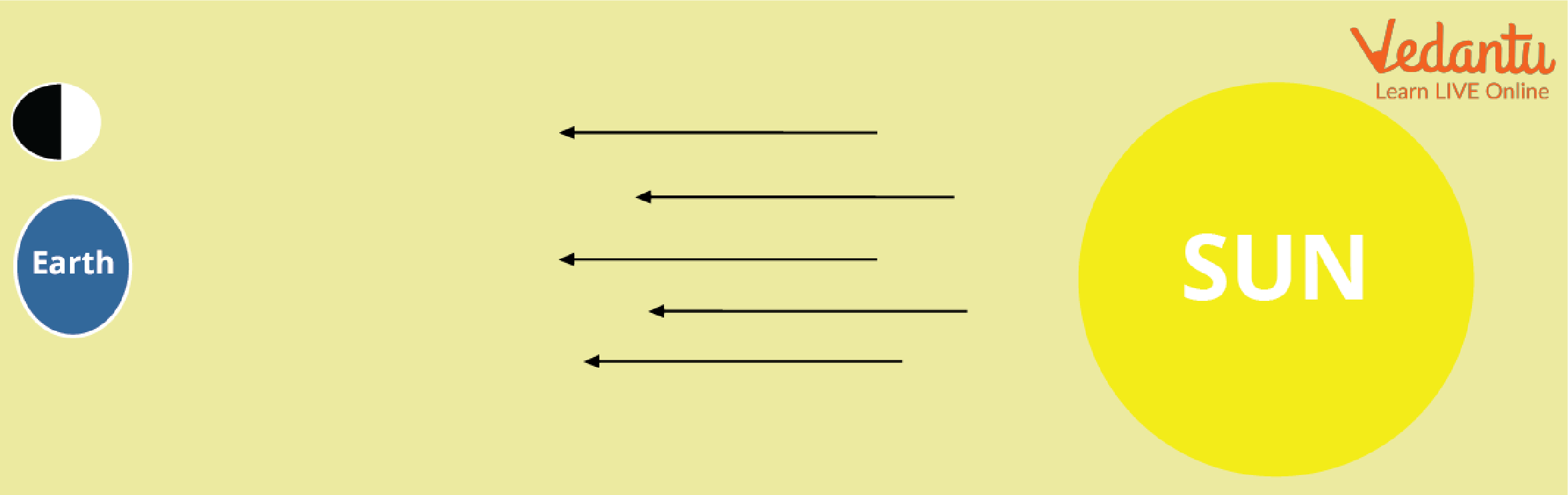
First Quarter Moon
We view half of the lit side of the moon around a week later and this is called the First Quarter moon.
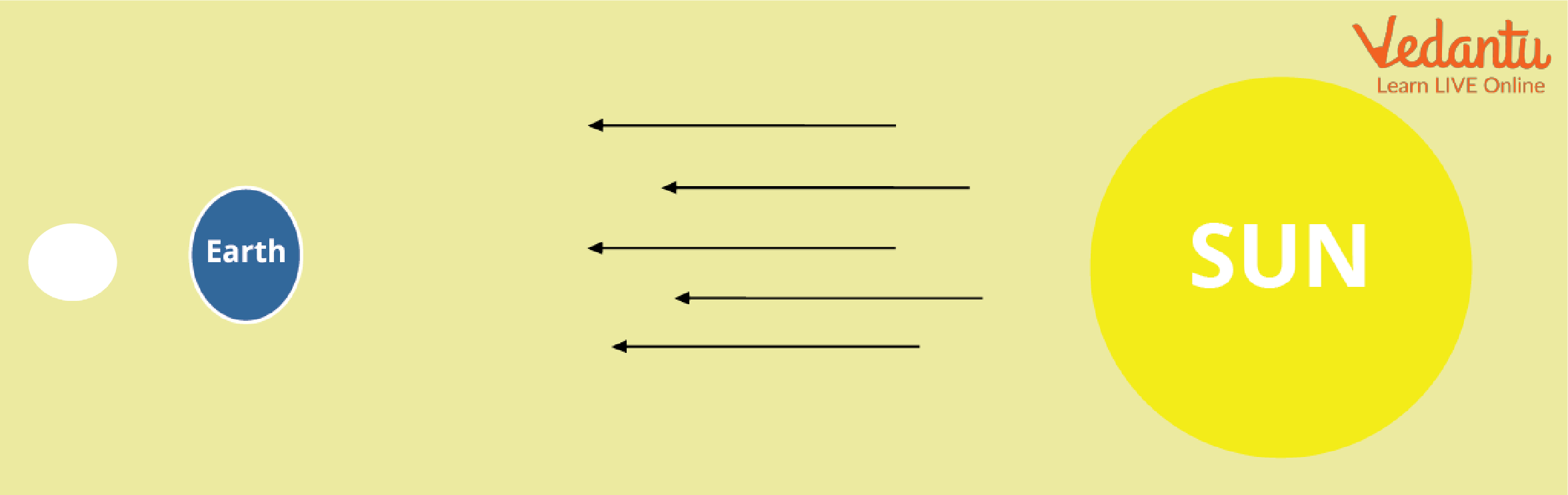
Full Moon
A full moon appears nearly two weeks after the new moon day. The entire illuminated side of the moon is visible from the earth.
Third Quarter Moon
A third-quarter moon appears after three weeks of the new moon. We can see half of the lighted surface of the moon from earth.
Four weeks after the new moon, another new moon appears and the cycle starts again.
Task to Observe
Observe the moon over a period of 28 days. You will see its different phases. Note down your observation in a diary date-wise. On certain nights, you will find that the Moon has disappeared altogether. This is the ‘New Moon’. Such nights are dark and we call such a night ‘Amavasya’ in India. Gradually you will see a half-moon. The size of the Moon will still increase, i.e., start waxing and reach the first quarter. On the 14th day of the new moon, you will see the full moon. The sky is bright and we call it ‘Purnima’ in India. The Moon will again start waning. It will gradually become a semi-circle and then crescent-shaped and by the 28th day, it will disappear again. This is again a new moon night.
Interesting Facts of Moon
The Moon is the only natural satellite of the earth.
The surface of the moon is actually quite black.
In comparison to the sun, the moon is 400 times smaller and 400 times closer to the earth.
The tides in the ocean are caused by the moon.
FAQs on Phases of the Moon Explained for Kids: Shapes, Sizes & Cycles
1. What are the phases of the Moon for kids?
The phases of the Moon are the different ways the Moon looks to us from Earth. The Moon doesn't make its own light; it reflects sunlight. As the Moon travels around the Earth, we see different amounts of its sunlit part. These changing views are what we call the phases of the Moon, making it look like it's changing shape every night.
2. What are the four main shapes of the Moon we see?
While there are eight main phases, they can be simplified into four key shapes that are easy for kids to spot:
- New Moon: The Moon is not visible in the sky.
- First Quarter: The Moon looks like a half-circle.
- Full Moon: The Moon looks like a complete, bright circle.
- Third Quarter (or Last Quarter): The Moon again looks like a half-circle, but the opposite half is lit.
3. Why does the Moon seem to change its shape?
The Moon itself is always a round sphere, like a ball, and its actual shape never changes. It only appears to change shape because of its movement around the Earth. As the Moon orbits our planet, the Sun lights up different parts of it. Our view of this sunlit part changes from night to night, creating the illusion of different shapes.
4. What are the names of the 8 main Moon phases?
The eight main phases of the Moon, in order, are:
- New Moon: The start of the cycle, where the Moon is not visible.
- Waxing Crescent: A small sliver of the Moon becomes visible.
- First Quarter: Half the Moon is lit.
- Waxing Gibbous: More than half the Moon is lit.
- Full Moon: The entire side facing us is lit.
- Waning Gibbous: The lit part starts to shrink.
- Third Quarter: The other half of the Moon is lit.
- Waning Crescent: Only a small sliver is left before it disappears into the New Moon again.
5. Does the Moon have its own light?
No, the Moon does not produce its own light. It shines because its surface reflects the light from the Sun. It acts like a giant mirror in the sky. The bright glow we see from the Moon is just sunlight bouncing off its surface and travelling to our eyes on Earth.
6. How long does it take to see all the Moon's phases?
It takes the Moon about 29.5 days to go through its entire cycle of phases, from one New Moon to the next. This is called a lunar month, and it's the reason our calendar months are about 30 days long. So, if you watch the sky for about a month, you will see all the different shapes of the Moon.
7. Does the Moon actually change its size?
No, the Moon's actual size always stays the same. Sometimes it looks much bigger, especially when it is near the horizon. This is an optical trick played by our brains called the Moon Illusion. The Moon isn't really bigger; it just appears that way when compared to trees and buildings on the horizon.
8. Why can we sometimes see the Moon during the day?
We can sometimes see the Moon during the daytime because it is our closest celestial neighbour and it's bright enough to be seen even when the Sun is out. Its visibility depends on its phase and where it is in the sky. After a Full Moon, for example, it is often visible in the morning sky. The sky is blue because of our atmosphere, but the Moon is still up there, reflecting sunlight.





















