
A flip coil consists of N turns of circular coils which lie in a uniform magnetic field. Plane of the coils is perpendicular to the magnetic field as shown in the figure. The coil is connected to a current integrator which measures the total charge passing through it. The coil is turned through $180^\circ $ about the diameter. The charge passing through the coil is:
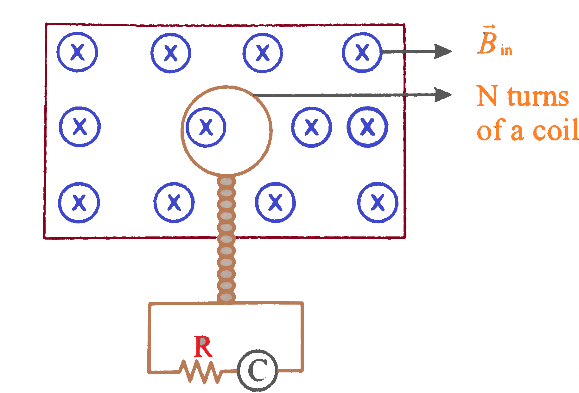
A) $\dfrac{{NBA}}{R}$ ;
B) $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 NBA}}{{2R}}$;
C) $\dfrac{{NBA}}{{\sqrt 2 R}}$;
D) $\dfrac{{2NBA}}{R}$;
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A flip coil is a device which is used for determining the magnetic field intensity. It is made up of a small coir wire which is then suddenly rotated through $180^\circ $ and a galvanometer is used to measure the net current.
Formula Used:
$N{\phi _B} = NBA\cos \theta $;
Where:
N = Number of turns;
${\phi _B}$= Magnetic Flux Density;
B = Magnetic field;
A = Area;
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Find the change in the magnetic flux:
The formula for magnetic flux is given as:
$N{\phi _B} = NBA\cos \theta $ ;
Here there would be two fluxes: one would be the initial flux ${\phi _i}$which would be at $\sin 90^\circ $and the final flux would be at$\cos 180^\circ $. This is so because the coil has taken a $180^\circ $turn. The magnetic flux would be:
$N{\phi _B} = N\left( {BA\sin 90^\circ - BA\cos 180^\circ } \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow N{\phi _B} = N\left( {BA - \left( { - BA} \right)} \right)$;
Simplify the above equation:
$ \Rightarrow N{\phi _B} = 2NBA$;
Put the area of the circle in the above equation:
$N{\phi _B} = 2NB\left( {\pi {r^2}} \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow N{\phi _B} = 2\pi {r^2}NB$;
Step 2: Find out the average induced EMF is:
\[\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right| = \left| {N\dfrac{{\Delta {\phi _B}}}{{\Delta t}}} \right|\] ; …(\[\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right|\] = Magnitude of EMF )
Put the value of $N{\phi _B} = 2\pi {r^2}NB$in the above equation:
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right| = \left| {\dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{\Delta t}}} \right|\]; …..(Average EMF)
Step 3: Find out the average induced current.
$\Rightarrow$ ${I_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right|}}{R}$ ; …(Here ${I_{avg}}$= Induced current; $R$= Resistance )
Enter the value of average induced EMF\[\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right| = \left| {\dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{\Delta t}}} \right|\] in the above equation:
$\Rightarrow$ ${I_{avg}} = \dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{R\Delta t}}$;
Step 4: Find out the total charge due to induction:
${Q_{net}} = {I_{avg}}\Delta t$; …(Here${Q_{net}}$= Net charge )
Put the value of average current induced ${I_{avg}} = \dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{R\Delta t}}$in the above equation.
$\Rightarrow$ ${Q_{net}} = \dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{R}{\text{ or }}\dfrac{{2NBA}}{R}$;
Option D is correct. The charge passing through the coil is ${Q_{net}} = \dfrac{{2NBA}}{R}$.
Note: The process is lengthy and many parameters seem to be missing like time,etc so go step by step. First find out the change in the magnetic flux then put the value of the change in magnetic flux in the average induced EMF, after that find out the value of induced current by placing the value of induced Emf in the induced current equation. The net finds out the total net charge by the formula ${Q_{net}} = {I_{avg}}\Delta t$.
Formula Used:
$N{\phi _B} = NBA\cos \theta $;
Where:
N = Number of turns;
${\phi _B}$= Magnetic Flux Density;
B = Magnetic field;
A = Area;
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Find the change in the magnetic flux:
The formula for magnetic flux is given as:
$N{\phi _B} = NBA\cos \theta $ ;
Here there would be two fluxes: one would be the initial flux ${\phi _i}$which would be at $\sin 90^\circ $and the final flux would be at$\cos 180^\circ $. This is so because the coil has taken a $180^\circ $turn. The magnetic flux would be:
$N{\phi _B} = N\left( {BA\sin 90^\circ - BA\cos 180^\circ } \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow N{\phi _B} = N\left( {BA - \left( { - BA} \right)} \right)$;
Simplify the above equation:
$ \Rightarrow N{\phi _B} = 2NBA$;
Put the area of the circle in the above equation:
$N{\phi _B} = 2NB\left( {\pi {r^2}} \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow N{\phi _B} = 2\pi {r^2}NB$;
Step 2: Find out the average induced EMF is:
\[\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right| = \left| {N\dfrac{{\Delta {\phi _B}}}{{\Delta t}}} \right|\] ; …(\[\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right|\] = Magnitude of EMF )
Put the value of $N{\phi _B} = 2\pi {r^2}NB$in the above equation:
\[ \Rightarrow \left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right| = \left| {\dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{\Delta t}}} \right|\]; …..(Average EMF)
Step 3: Find out the average induced current.
$\Rightarrow$ ${I_{avg}} = \dfrac{{\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right|}}{R}$ ; …(Here ${I_{avg}}$= Induced current; $R$= Resistance )
Enter the value of average induced EMF\[\left| {{\varepsilon _{avg}}} \right| = \left| {\dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{\Delta t}}} \right|\] in the above equation:
$\Rightarrow$ ${I_{avg}} = \dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{R\Delta t}}$;
Step 4: Find out the total charge due to induction:
${Q_{net}} = {I_{avg}}\Delta t$; …(Here${Q_{net}}$= Net charge )
Put the value of average current induced ${I_{avg}} = \dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{{R\Delta t}}$in the above equation.
$\Rightarrow$ ${Q_{net}} = \dfrac{{2\pi {r^2}NB}}{R}{\text{ or }}\dfrac{{2NBA}}{R}$;
Option D is correct. The charge passing through the coil is ${Q_{net}} = \dfrac{{2NBA}}{R}$.
Note: The process is lengthy and many parameters seem to be missing like time,etc so go step by step. First find out the change in the magnetic flux then put the value of the change in magnetic flux in the average induced EMF, after that find out the value of induced current by placing the value of induced Emf in the induced current equation. The net finds out the total net charge by the formula ${Q_{net}} = {I_{avg}}\Delta t$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




