
A metal ring is kept horizontally and a magnet bar is dropped through the ring with its length along the axis of the ring. The acceleration of the falling magnet:
A) Is equal to g
B) Is less than g
C) Is more than g
D) Depends on the diameter of the ring and the length of the magnet bar.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First we should remember that a magnet bar has two poles, namely, the South Pole and the North Pole. And the same type of pole, north-north or south-south repel each other but the different types of two poles of a magnet bar attract each other. We can analyze the above problem with the help of Lenz’s law. Lenz’s law states that the direction of the electric current which is induced in a conductor by a changing magnetic field such that the magnetic field created by the induced current opposes the initial changing magnetic field.
Complete answer:
Step 1: consider the following figure
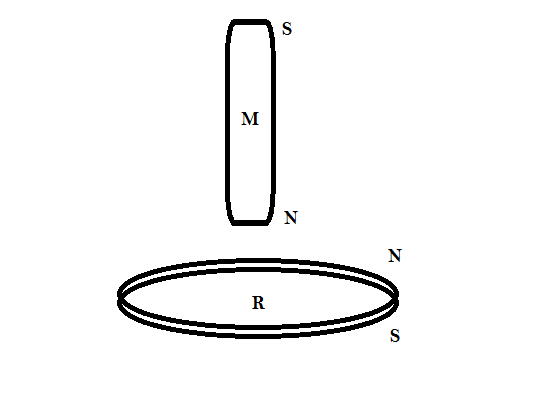
Let us suppose that the north pole of the magnetic bar is entering first in the metal ring then according to Lenz’s law, that is, the current induced in a circuit due to a change in a magnetic field is directed to oppose the change in flux and to exert a mechanical force which opposes the motion. Therefore the force of repulsion between the ring and the bar will oppose the motion of the bar. It is very important here that in which direction the current is generated because of the magnetic flux change. Thus the bar will slow down when dropped through the ring and the acceleration of the ring will be less than g.
Step 2: Now consider the following figure
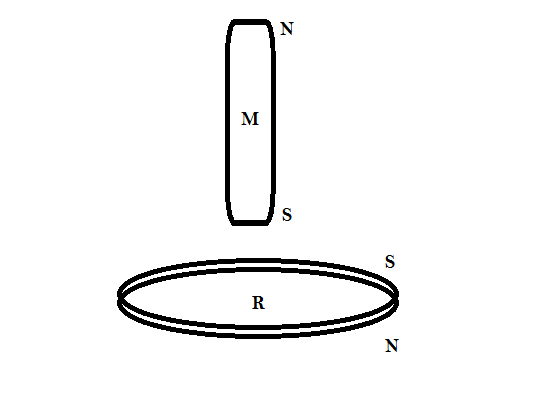
Now consider another case when the south pole of the magnetic bar is entering first in the metal ring. Now the direction of the current in the ring will be opposite of the direction of the current when the North Pole was entering first. Therefore the direction of the magnetic fields line will also be reversed. Eventually, the electromagnetic field will be generated and this time the South Pole of the ring and South Pole of the magnetic bar will repel each other. Thus again the bar will slow down while passing through the ring.Thus the acceleration of the magnetic bar will be less than g.
The correct answer is option B.
Note: Magnetic flux is the number of imaginary lines passing through the one unit area in a magnetic field. When a magnetic bar is allowed to go through a coil, pipe, loop, etc. then the magnetic flux forces the free electron in a particular direction. It generates current in the circuit and eventually an electromagnetic effect in the circuit.
Complete answer:
Step 1: consider the following figure

Let us suppose that the north pole of the magnetic bar is entering first in the metal ring then according to Lenz’s law, that is, the current induced in a circuit due to a change in a magnetic field is directed to oppose the change in flux and to exert a mechanical force which opposes the motion. Therefore the force of repulsion between the ring and the bar will oppose the motion of the bar. It is very important here that in which direction the current is generated because of the magnetic flux change. Thus the bar will slow down when dropped through the ring and the acceleration of the ring will be less than g.
Step 2: Now consider the following figure

Now consider another case when the south pole of the magnetic bar is entering first in the metal ring. Now the direction of the current in the ring will be opposite of the direction of the current when the North Pole was entering first. Therefore the direction of the magnetic fields line will also be reversed. Eventually, the electromagnetic field will be generated and this time the South Pole of the ring and South Pole of the magnetic bar will repel each other. Thus again the bar will slow down while passing through the ring.Thus the acceleration of the magnetic bar will be less than g.
The correct answer is option B.
Note: Magnetic flux is the number of imaginary lines passing through the one unit area in a magnetic field. When a magnetic bar is allowed to go through a coil, pipe, loop, etc. then the magnetic flux forces the free electron in a particular direction. It generates current in the circuit and eventually an electromagnetic effect in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




