
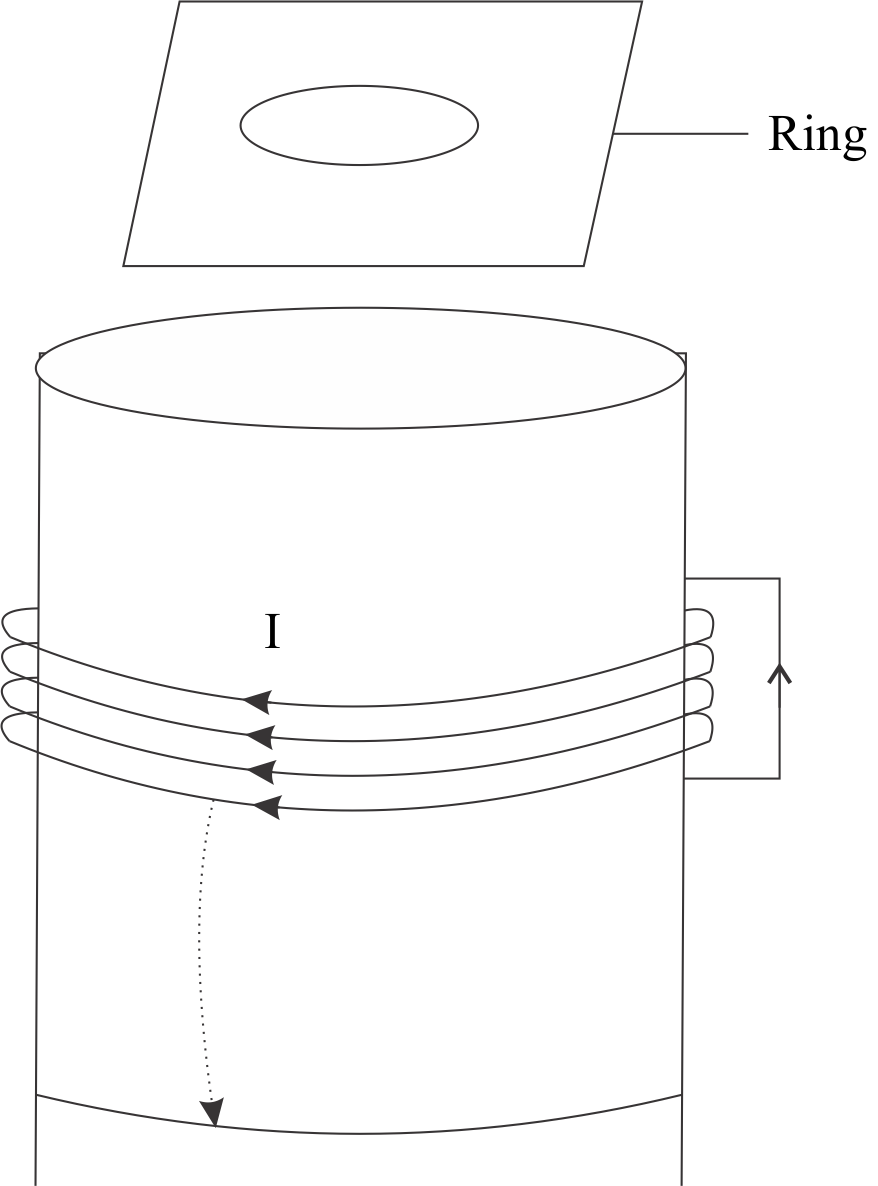
A metal ring kept (surrounded by a cardboard) on the top of a fixed solenoid carries a current \[I\]as shown in figure . The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is switched off , then:
(A) Magnetic flux linked with the metal ring increases.
(B) Current induced in the metal ring is in clockwise direction.
(C) Metal rings will not remain on the cardboard.
(D) Both (A) and (B) are correct.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint This question will be solved by Lenz Law. The ring will experience some mutual induction due to the current flowing in solenoid. These changes in the ring will be determined by the use of Faraday’s laws of mutual induction and Lenz Law.
Complete Step-by-step Solution We have been given a solenoid and a ring as shown in the diagram
Let us assume that the current in the solenoid is changing. This will cause the change in magnetic flux in the ring( which here acts as secondary coil) . A current will get induced in the ring due to mutual induction. We will now determine what are the changes taking place in the ring . First of all, let's first define what Lenz law is : It states that “ the direction of the induced current is such that it opposes the cause producing it i.e. it resists any change in its flux and current flows accordingly” . So if the current in the primary is increasing , the current in the secondary will flow in such a way that it reduces the effect of that current and vice-versa.
Here, the current is switched off which means the magnetic flux linked with the solenoid is decreasing , so the flux linked with the ring also decreases . The current in the ring will flow in such a direction that it tends to resist this decrease in flux.
The current in the solenoid is in clockwise direction. The flux is decreasing so the induced current will flow in the same direction as that of the primary coil. The induced current in the ring will be in clockwise direction .
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note
Lenz law is based on conservation of energy. We have to keep in mind that here we have assumed the magnetic flux is changing. If the flux through the coil is constant, there will be no induced current.
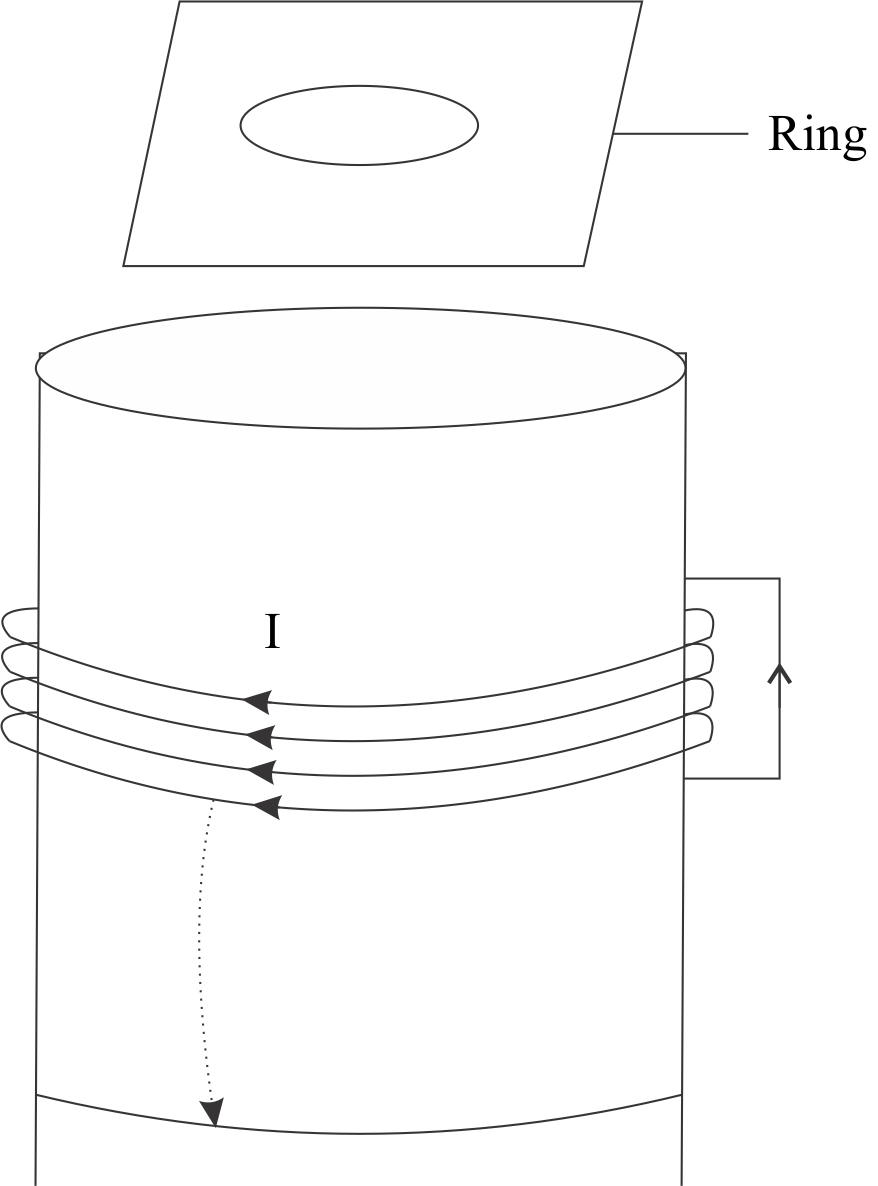
Complete Step-by-step Solution We have been given a solenoid and a ring as shown in the diagram

Let us assume that the current in the solenoid is changing. This will cause the change in magnetic flux in the ring( which here acts as secondary coil) . A current will get induced in the ring due to mutual induction. We will now determine what are the changes taking place in the ring . First of all, let's first define what Lenz law is : It states that “ the direction of the induced current is such that it opposes the cause producing it i.e. it resists any change in its flux and current flows accordingly” . So if the current in the primary is increasing , the current in the secondary will flow in such a way that it reduces the effect of that current and vice-versa.
Here, the current is switched off which means the magnetic flux linked with the solenoid is decreasing , so the flux linked with the ring also decreases . The current in the ring will flow in such a direction that it tends to resist this decrease in flux.
The current in the solenoid is in clockwise direction. The flux is decreasing so the induced current will flow in the same direction as that of the primary coil. The induced current in the ring will be in clockwise direction .
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note
Lenz law is based on conservation of energy. We have to keep in mind that here we have assumed the magnetic flux is changing. If the flux through the coil is constant, there will be no induced current.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




