
A motorcycle is going on an over bridge of radius $R$. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the over bridge, the normal force in it:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains the same
D) Fluctuates
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In order to find the change in the normal force acting on a motorcycle ascending on a over bridge, draw a free body diagram of the motor cycle along the curvature of the over bridge and find out the variables causing the change to the normal force.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, it is given that the radius of the over bridge is $R$ and the motorcycle is ascending on the over bridge with a constant speed. We are asked to find how the normal force acting on the motor cycle changes.
In order to explain the changes in the normal force acting on the motorcycle, we are using the diagram given below.
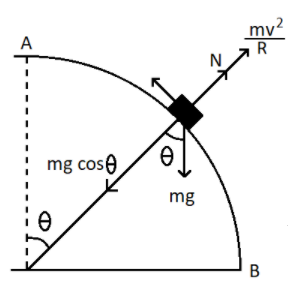
From the figure, we know that,
$N = mg\cos \theta - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$
Where, $N$ is the normal force acting on the motorcycle
$m$ is the mass of the motorcycle
$v$ is the velocity of the motorcycle
$\theta $ is the angle between the weight and the component of the weight in the direction towards the centre of curvature of the bridge.
$R$ is the radius of curvature of the bridge
$g$ is the gravitational constant
In the equation, it is clear that the terms $m$, $v$, $R$and $g$ are constant values (the motorcycle is going with a uniform velocity). The only variable is $\theta $ with the movement of the motorcycle.
So the normal force acting on the motorcycle will be changed only by the value of $\cos \theta $ as it moves.
In the figure, if the vehicle is moving from point B to point A, the value of $\theta $ will get decreased and the value of $\cos \theta $ will get increased. Thus the normal force acting will also be increased and it will be maximum at poi A.
That is, as the motorcycle is ascending on the over bridge with a uniform velocity, the normal force in it will get increased.
Final answer is option (A), Increases.
Note: In the mechanics, the normal force is defined as the component of a contact force that is perpendicular to the surface to which the body has contact. For example, the surface of a table or floor that prevents an object from falling. All bodies in contact experience a normal force perpendicular to the surface in contact. It balances the resultant force acting on the body in the direction perpendicular to the surface of contact.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, it is given that the radius of the over bridge is $R$ and the motorcycle is ascending on the over bridge with a constant speed. We are asked to find how the normal force acting on the motor cycle changes.
In order to explain the changes in the normal force acting on the motorcycle, we are using the diagram given below.

From the figure, we know that,
$N = mg\cos \theta - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$
Where, $N$ is the normal force acting on the motorcycle
$m$ is the mass of the motorcycle
$v$ is the velocity of the motorcycle
$\theta $ is the angle between the weight and the component of the weight in the direction towards the centre of curvature of the bridge.
$R$ is the radius of curvature of the bridge
$g$ is the gravitational constant
In the equation, it is clear that the terms $m$, $v$, $R$and $g$ are constant values (the motorcycle is going with a uniform velocity). The only variable is $\theta $ with the movement of the motorcycle.
So the normal force acting on the motorcycle will be changed only by the value of $\cos \theta $ as it moves.
In the figure, if the vehicle is moving from point B to point A, the value of $\theta $ will get decreased and the value of $\cos \theta $ will get increased. Thus the normal force acting will also be increased and it will be maximum at poi A.
That is, as the motorcycle is ascending on the over bridge with a uniform velocity, the normal force in it will get increased.
Final answer is option (A), Increases.
Note: In the mechanics, the normal force is defined as the component of a contact force that is perpendicular to the surface to which the body has contact. For example, the surface of a table or floor that prevents an object from falling. All bodies in contact experience a normal force perpendicular to the surface in contact. It balances the resultant force acting on the body in the direction perpendicular to the surface of contact.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




