
A solid current-carrying conductor of radius R is having current per unit area ( $J$ ) as $J = \dfrac{{\alpha r}}{R}$ where $\alpha$ is a constant and $r$ is the distance from the axis. Find the magnetic field at a distance $x$ from the axis of the wire.
Assume $x > R$.
A) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}\alpha {x^2}}}{{3R}}$
B) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}\alpha {x^2}}}{{2R}}$
C) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}\alpha {R^2}}}{x}$
D) $Zero$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We apply Amperes’ Circuital Law. The magnetic field is directly proportional to the current, which acts as its source. Like Gauss’ Law, Amperes’ Circuital Law is very useful when calculating magnetic fields of current distributions with high symmetry.
Complete step by step solution:
The Amperes’ Circuital Law relates current to the magnetic field created by it.
This law states that the integral of magnetic field density $B$ along an imaginary closed path is equal to the product of current enclosed by the path and permeability of the medium.
$\oint {\vec B.d\vec l = {\mu _0}} I$
where, $\oint {\vec B.d\vec l}$ is line integral of B around a closed path
${\mu _0} = 4\pi \times {10^{ - 15}}N{A^{ - 2}}$ is the permeability of free space
$I$ is current
The magnetic field lines encircle the current-carrying wire, and the magnetic field lines lie in a plane perpendicular to the wire.
A closed- loop called the Amperian loop is designated to find a magnetic field using this law. We assume the loop consists of small elemental rings of thickness dr.
The length of the small element mentioned as $dl$ of the elemental rings taken here is its circumference, i.e., $2\pi x.dx$
Take an elemental ring of thickness $dx$ at a distance of $x$ from the center.
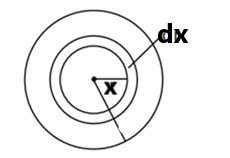
By Amperes’ Circuital Law,
$\oint {B.dl = {\mu _0}} I$
$\therefore B \times 2\pi x = {\mu _0}I$……..$(1)$
Now,
$\Rightarrow dI = J \times area$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\alpha x}}{R} \times (2\pi x)dx$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}{x^2}dx$
Integrating to find the total current from the center to a distance x:
$\Rightarrow I = \int\limits_0^x {\dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}} {x^2}.dx$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}[\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}]_0^x{\text{ }}$
The formula of basic integration used is, ${\text{ }}\int {{x^n}} .dx = \dfrac{{{x^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}} + C$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}.\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}$
Applying the current calculated in the equation $(1)$, we get
$\Rightarrow B \times 2\pi x = {\mu _0}I$
$\Rightarrow B \times 2\pi x = {\mu _0}\dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}.\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}$
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\alpha {x^2}}}{{3R}}$
The correct answer is [A], $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}\alpha {x^2}}}{{3R}}$.
Note: Whenever a body with the non-uniform current is mentioned, its total current is calculated by integration. Only the current inside the closed path is taken into consideration because only that current contributes to the magnetic field.
Complete step by step solution:
The Amperes’ Circuital Law relates current to the magnetic field created by it.
This law states that the integral of magnetic field density $B$ along an imaginary closed path is equal to the product of current enclosed by the path and permeability of the medium.
$\oint {\vec B.d\vec l = {\mu _0}} I$
where, $\oint {\vec B.d\vec l}$ is line integral of B around a closed path
${\mu _0} = 4\pi \times {10^{ - 15}}N{A^{ - 2}}$ is the permeability of free space
$I$ is current
The magnetic field lines encircle the current-carrying wire, and the magnetic field lines lie in a plane perpendicular to the wire.
A closed- loop called the Amperian loop is designated to find a magnetic field using this law. We assume the loop consists of small elemental rings of thickness dr.
The length of the small element mentioned as $dl$ of the elemental rings taken here is its circumference, i.e., $2\pi x.dx$
Take an elemental ring of thickness $dx$ at a distance of $x$ from the center.

By Amperes’ Circuital Law,
$\oint {B.dl = {\mu _0}} I$
$\therefore B \times 2\pi x = {\mu _0}I$……..$(1)$
Now,
$\Rightarrow dI = J \times area$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\alpha x}}{R} \times (2\pi x)dx$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}{x^2}dx$
Integrating to find the total current from the center to a distance x:
$\Rightarrow I = \int\limits_0^x {\dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}} {x^2}.dx$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}[\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}]_0^x{\text{ }}$
The formula of basic integration used is, ${\text{ }}\int {{x^n}} .dx = \dfrac{{{x^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}} + C$
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}.\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}$
Applying the current calculated in the equation $(1)$, we get
$\Rightarrow B \times 2\pi x = {\mu _0}I$
$\Rightarrow B \times 2\pi x = {\mu _0}\dfrac{{2\pi \alpha }}{R}.\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}$
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\alpha {x^2}}}{{3R}}$
The correct answer is [A], $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}\alpha {x^2}}}{{3R}}$.
Note: Whenever a body with the non-uniform current is mentioned, its total current is calculated by integration. Only the current inside the closed path is taken into consideration because only that current contributes to the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




