
A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass slab for different values of the angle of incidence $\left( {\angle i} \right)$. He then measures the corresponding values of the angle of refraction $\left( {\angle r} \right)$ and the angle of emergence $\left( {\angle e} \right)$ for every value of the angle of incidence. On analyzing these measurements of angles, his conclusion would be
$\left( a \right)$ $\angle i > \angle r > \angle e$
$\left( b \right)$ $\angle i = \angle e > \angle r$
$\left( c \right)$ $\angle i,\angle r,\angle e$
$\left( d \right)$ $\angle i = \angle e,\angle r$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint Angle of incidence is the adequate angle of emergence and angle of incidence is bigger than the angle of refraction additionally angle of refraction is less than angle emergence. By using all the above concepts we can answer the question.
Complete Step by Step Solution We discovered, that once a ray of light passes from rarer medium to denser medium, it diverges toward the normal, and once this refracted lightweight emerges, then it goes away from the normal, once the incident and also the emerging medium is the same then the angle of incidence and also the angle of emerging perpetually are equal.
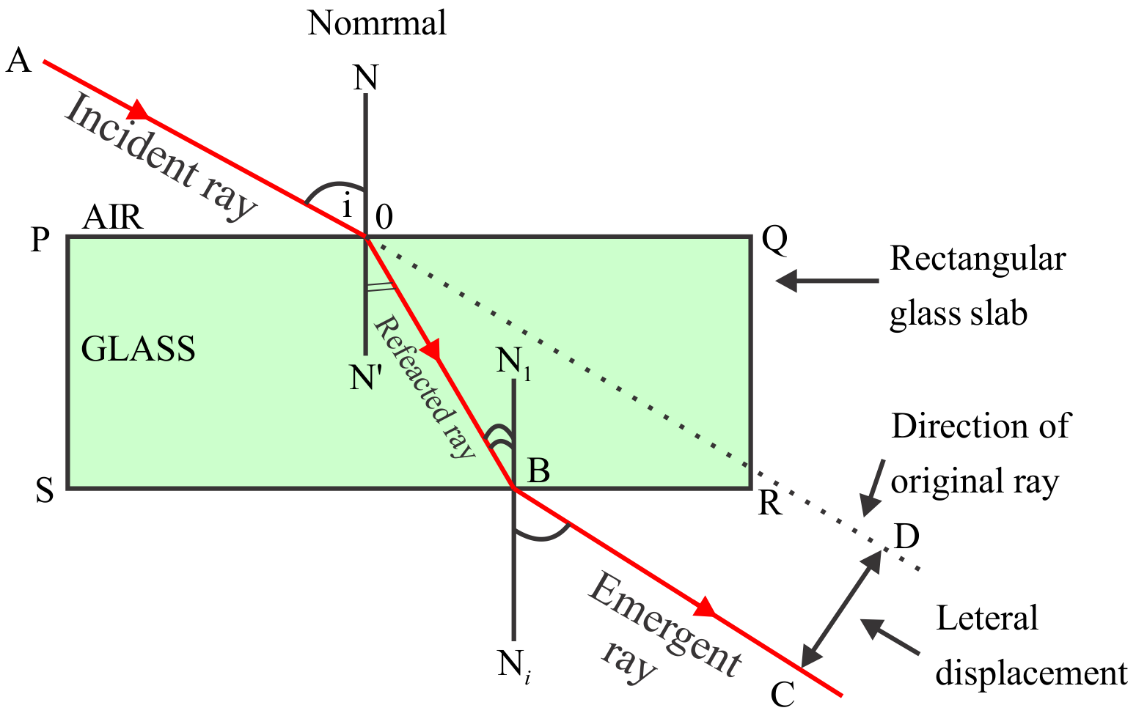
As the incident ray is parallel to the emerging ray so we will conclude that the angle of incidence is adequate the angle of emergence
And mathematically we can write it as,
$\angle i = \angle e$
And also the ray traveling from the rarer medium which is air, to the denser medium which is glass slab. The ray will slightly bend towards the normal after the refraction.
Thus we can say that the angle of refraction is smaller than the angle of incidence.
$\angle i > \angle r$
Therefore, $\angle i = \angle e > \angle r$ will be the correct option. That is an option$b$.
Note
It may be noted that this is, in general, true only if the normal at the point of incidence and the point of emergence are parallel to each other as in the case of rectangular slabs of the second medium. In the case of a prism, the conventional at the purpose of incidence isn't parallel to the conventional at the purpose of emergence. They are equal only for the angle of minimum deviation.
Complete Step by Step Solution We discovered, that once a ray of light passes from rarer medium to denser medium, it diverges toward the normal, and once this refracted lightweight emerges, then it goes away from the normal, once the incident and also the emerging medium is the same then the angle of incidence and also the angle of emerging perpetually are equal.

As the incident ray is parallel to the emerging ray so we will conclude that the angle of incidence is adequate the angle of emergence
And mathematically we can write it as,
$\angle i = \angle e$
And also the ray traveling from the rarer medium which is air, to the denser medium which is glass slab. The ray will slightly bend towards the normal after the refraction.
Thus we can say that the angle of refraction is smaller than the angle of incidence.
$\angle i > \angle r$
Therefore, $\angle i = \angle e > \angle r$ will be the correct option. That is an option$b$.
Note
It may be noted that this is, in general, true only if the normal at the point of incidence and the point of emergence are parallel to each other as in the case of rectangular slabs of the second medium. In the case of a prism, the conventional at the purpose of incidence isn't parallel to the conventional at the purpose of emergence. They are equal only for the angle of minimum deviation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




