
An observer 1.6 m tall is $20 \sqrt{3}$ m away from a tower. The angle of elevation from his eye to the top of the tower is 30°. The height of the tower is
A) 21.6 m
B) 23.2 m
C) 24.72 m
D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Use the trigonometric applications involving heights and distances. The distance between the man and the pole is given and the angle of elevation is given. A Trigonometric approach will be the best.
Complete step by step solution:
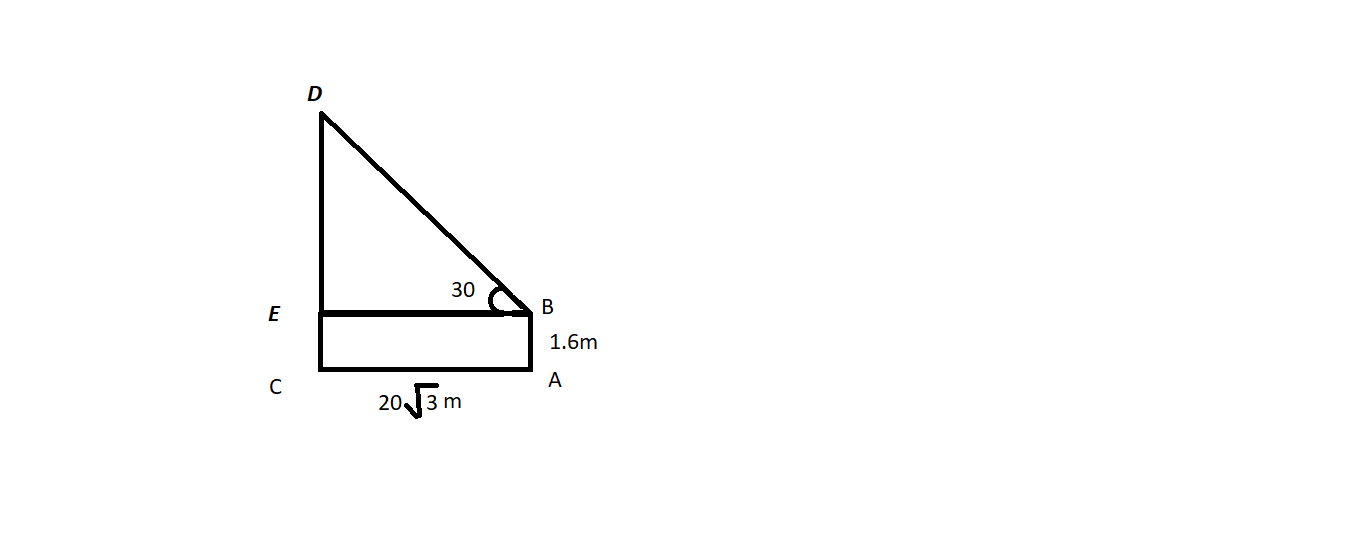
In the above given figure A,
Let $AB$ be the observer and $CD$ tower
Draw $BE$ perpendicular to $CD$
This will represent the distance between the man’s eye and the point E on the pole
Then $CE = AB = 1.6m$
Also,
$BE = AC = 20\sqrt 3 m$
Using the trigonometric applications in the right angled triangle $DEB$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{P}{B}$
Where, $\theta $is the angle of inclination, $P$ is perpendicular of the triangle and $B$ is the base of the triangle.
Therefore, in triangle $DEB$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{DE}}{{BE}}$
Now, we know that
$\tan {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3}} $ and
It is given that
$BE = 20\sqrt 3 m$
Putting the values in the above equation, we get,
$\dfrac {1} {{\sqrt 3}} = \dfrac{{DE}}{{20\sqrt 3}} $
Therefore,
$DE = 20m$
Now,
Height of the tower, $CD = DE + CE$
$CD = 20 + 1.6$
$CD = 21.6m$
Therefore, the height of the tower is $21.6m$.
Note: The key application of trigonometry is either to calculate the distance between two or more points or to calculate the height of the object or angle that any object subtends at the specified point without calculating the distance, height or angle actually.
Complete step by step solution:

In the above given figure A,
Let $AB$ be the observer and $CD$ tower
Draw $BE$ perpendicular to $CD$
This will represent the distance between the man’s eye and the point E on the pole
Then $CE = AB = 1.6m$
Also,
$BE = AC = 20\sqrt 3 m$
Using the trigonometric applications in the right angled triangle $DEB$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{P}{B}$
Where, $\theta $is the angle of inclination, $P$ is perpendicular of the triangle and $B$ is the base of the triangle.
Therefore, in triangle $DEB$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{DE}}{{BE}}$
Now, we know that
$\tan {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3}} $ and
It is given that
$BE = 20\sqrt 3 m$
Putting the values in the above equation, we get,
$\dfrac {1} {{\sqrt 3}} = \dfrac{{DE}}{{20\sqrt 3}} $
Therefore,
$DE = 20m$
Now,
Height of the tower, $CD = DE + CE$
$CD = 20 + 1.6$
$CD = 21.6m$
Therefore, the height of the tower is $21.6m$.
Note: The key application of trigonometry is either to calculate the distance between two or more points or to calculate the height of the object or angle that any object subtends at the specified point without calculating the distance, height or angle actually.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




