




How to Identify P Pi D Pi Bonds in Compounds with Examples
P Pi D Pi Bonds are a special type of pi bonding important for understanding molecular structures in JEE Main Chemistry. These bonds result from the sideways overlap between a p orbital from one atom and a d orbital from another. This concept regularly appears in the JEE Main syllabus, especially in the context of oxoanions and molecules where third-period elements like sulphur or phosphorus form multiple bonds with second-period elements like oxygen.
What are Pi Bonds and P Pi D Pi Bonds?
A pi (π) bond forms when atomic orbitals overlap laterally (sideways), sharing electrons above and below the bond axis. The most common is the pπ–pπ bond, where two p orbitals overlap. When a p orbital overlaps with a d orbital, it creates a pπ–dπ bond. This bonding is possible only when one atom (typically from the third period or higher) possesses energetically available and vacant d orbitals, while the other has a filled p orbital with a lone pair.
Distinction: Sigma, P Pi P Pi, and P Pi D Pi Bonds
For the JEE Main exam, it's essential to distinguish between:
| Bond Type | Orbitals Involved | Example | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma (σ) | Head-on overlap (s/p/pz) | C–H in CH4 | Strongest |
| Pπ–Pπ | Sideways p–p overlap | C=C in alkenes, O2 | Strong |
| Pπ–Dπ | Sideways p–d overlap | S=O in SO2, SO3, SO42– | Strong (often stronger than Pπ–Pπ) |
A sigma bond uses direct overlap, while both pπ–pπ and pπ–dπ use lateral overlap, but with different types of orbitals. Recognising these differences for MCQs on bond types is crucial.
How is a P Pi D Pi Bond Formed?
A pπ–dπ bond forms when a filled p orbital (usually from O or F) overlaps sideways with an empty d orbital (from S, P, Cl, etc). The most important condition is that the d orbital must be energetically accessible, which is possible for main group elements from the third period onwards. The larger size and availability of d orbitals in these atoms allow for effective sideways overlap, leading to delocalized π bonding in structures like sulfate and phosphate ions.
Mechanism: Orbital Overlap in P Pi D Pi Bonding
When the oxygen atom in SO2 or SO3 possesses a lone pair in its p orbital, and sulphur has low-lying empty 3d orbitals, the sideways overlap between these orbitals allows the π-electrons to delocalize. This delocalization across p and d orbitals explains the observed resonance and partial double-bond character in multiple S–O bonds.
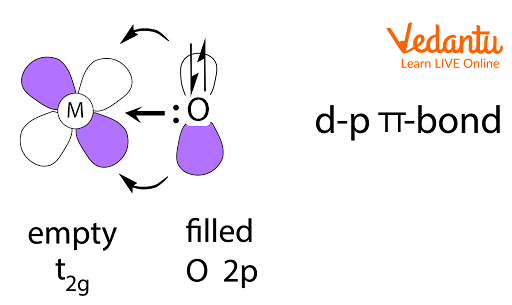
The illustration shows pπ–dπ bond example, an important visual for identifying possible overlap directions in structures like SO42–.
Key JEE Examples of P Pi D Pi Bonds
Memorise these classic cases for JEE Main:
- SO2 (Sulphur dioxide): Sulphur uses its 3d orbitals to form pπ–dπ bonds with oxygen. Each S–O bond has partial double-bond character due to resonance. Number of pπ–dπ bonds in SO2: 2.
- SO3 (Sulphur trioxide): Similar resonance phenomenon, with 3 S–O bonds, each involving pπ–dπ overlap.
- SO42– (Sulfate ion): Four equivalent S–O bonds, all exhibit partial double-bond character thanks to delocalisation of π electrons via pπ–dπ bonding. Number of pπ–dπ bonds: 4.
- PO43– (Phosphate ion): P (3rd period) forms multiple pπ–dπ bonds with O, following the same mechanism.
For each, the multiple resonance structures allow delocalization, which arises only because central atoms have accessible d orbitals.
How to Identify a P Pi D Pi Bond (JEE MCQ Guide)
Use this checklist for exam questions:
- If the central atom is from the 3rd period or below (e.g., S, P, Cl, Si).
- Bonded to second-period atoms (usually O or F with lone pairs available).
- The molecule shows resonance, suggesting delocalisation.
- Bonds appear to be 'double' in some forms, but not pure pπ–pπ (as with C=O).
- Each equivalent bond implies possible pπ–dπ contribution (count S–O bonds).
Apply this logic in compounds like p-block oxoanions. Avoid assigning d orbital participation to elements from the second period (e.g., C, N, O, F)—they lack empty d orbitals.
Why is P Pi D Pi Bonding Important?
P Pi D Pi bonds explain why some molecules violate the octet rule and exhibit unusual bond lengths. In chemical bonding theory, these bonds underpin the equivalent S–O lengths in sulphates, where without d orbital involvement, classic single–double bond patterns would emerge. In coordination chemistry and transition metal complexes, d orbitals are crucial for pi back bonding and electron delocalisation as well.
Applications and Practice: JEE Focus
Expect multiple-choice and assertion-reason questions in JEE Main Chemistry involving:
- Counting number and type of pi bonds in molecules like SO3, SO2, SO42–.
- Explaining resonance by invoking d orbital overlap in p-block oxoanions.
- Comparing bond order, strength, and lengths using pπ–dπ bond reasoning.
- Identifying why hybridization in SO42– is not possible for second-period central atoms.
- Differentiating between pπ–pπ (as in O2) vs. pπ–dπ (as in SO3).
Mastering this concept supports questions related to resonance, bond order, and complex ion geometry—useful for both quick MCQs and advanced assertions.
Practice Problem Set: P Pi D Pi Bonds (JEE Level)
- How many pπ–dπ bonds are present in SO3 and SO42–?
- Explain, with orbital reason, why CO2 does NOT show pπ–dπ bonding.
- Among SiO44–, SO42–, PO43–, and ClO4–, which has all equivalent M–O bonds?
- Draw resonance structures of SO2 showing pπ–dπ interaction.
- Assign bond order to each S–O bond in SO42– and justify your answer.
Work through these using the checklist above. For a stepwise guide and solved examples, the p-block revision notes page is recommended.
For comprehensive JEE Main Chemistry preparation, use Vedantu’s expert-curated resources and practice with questions focused on the role of pπ–dπ bonds in bonding and structure. This topic integrates NCERT knowledge with advanced application, making it vital for boosting accuracy on exam day.
FAQs on Understanding P Pi D Pi Bonds in Chemistry
1. What are pπ and dπ bonds?
Pπ and dπ bonds are types of pi bonds formed by the sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, where a p orbital from one atom overlaps with a d orbital from another atom. This bonding is commonly observed in molecules with third-period elements or beyond that have vacant d orbitals available for bonding.
- Pπ-dπ bonds occur when a lone pair from a p orbital (such as oxygen) is shared with an empty d orbital (such as sulfur in SO₂ or SO₄²⁻).
- These bonds play an important role in resonance structures and in expanding the octet.
- They are significant in inorganic chemistry for understanding bonding in compounds like SO₂, SO₃, and SO₄²⁻.
2. What is p pi d pi bonding?
P pi d pi bonding (pπ–dπ bonding) is a type of pi bond formed by the lateral overlap of a filled p orbital with a vacant d orbital in another atom.
- Common in compounds where elements from the third period or beyond (e.g., sulfur, phosphorus) bond with oxygen or nitrogen.
- Facilitates delocalization of electrons and resonance, especially in ions like SO₂ and SO₄²⁻.
- Enhances molecular stability and allows for expanded octet configurations.
3. Which molecules show pπ-dπ bonding?
Molecules containing a central atom with vacant d orbitals and surrounding atoms with available p orbitals can exhibit pπ-dπ bonding. Examples include:
- SO₂ (Sulfur dioxide)
- SO₃ (Sulfur trioxide)
- SO₄²⁻ (Sulfate ion)
- PO₄³⁻ (Phosphate ion)
4. How do you identify pπ-dπ bonds in a compound?
To identify pπ-dπ bonds, look for the following features in the molecule or ion:
- Presence of a central atom from the third period or beyond (e.g., sulfur, phosphorus) with vacant d orbitals.
- Lone pairs available on oxygen or neighboring atoms for p orbital overlap.
- Resonance structures that involve d orbital participation for electron delocalization.
- Expanded octet on the central atom.
5. How many pπ-dπ bonds are present in SO₂ and SO₄²⁻?
SO₂ contains 2 pπ-dπ bonds (one with each oxygen atom), while SO₄²⁻ contains 2 pπ-dπ bonds (from delocalized pi bonding involving S and O).
- Each pπ-dπ bond forms by overlap between an oxygen p orbital and a sulfur d orbital.
- These bonds contribute to resonance stabilization and expanded octet on sulfur.
6. What is the difference between pπ-pπ and pπ-dπ bonds?
Pπ-pπ bonds form by lateral overlap between two p orbitals (e.g., C=O, O₂), typically found in second-period elements.
Pπ-dπ bonds result from the overlap of a filled p orbital with an empty d orbital, as seen in compounds containing third-period elements (e.g., SO₄²⁻).
- Pπ-pπ: Both atoms use p orbitals.
- Pπ-dπ: One atom uses p, the other uses d orbital.
- Pπ-dπ bonding enables the central atom to expand its octet.
7. Why are d orbitals available for bonding in third-period elements but not in second-period elements?
Third-period elements (like sulfur, phosphorus) have energetically accessible and vacant 3d orbitals, which can participate in bonding, especially for forming pπ-dπ bonds.
- Second-period elements (C, N, O) lack vacant d orbitals, so they cannot expand their octet or form pπ-dπ bonds.
- This explains why only heavier main group elements can utilize d orbitals in bonding.
8. Is resonance always involved in pπ-dπ bonding?
Resonance often involves pπ-dπ bonding when multiple valid Lewis structures can be drawn with electrons delocalized over p and d orbitals.
- For ions like SO₄²⁻ and SO₂, pπ-dπ bonds explain the observed bond order and delocalization.
- Not all pπ-dπ bonds are strictly due to resonance, but resonance structures frequently illustrate how p and d orbitals overlap.
9. Can phosphorus form a d-pi d-pi bond?
Yes, phosphorus can use its vacant 3d orbitals to form pπ-dπ or even dπ-dπ bonding in certain compounds, such as phosphates (PO₄³⁻) or other polyatomic ions.
- This ability allows phosphorus to expand its octet and form multiple bonds involving d orbitals.
10. How to calculate the number of sigma and pi bonds in compounds like SO₂ and SO₄²⁻?
To determine the number of sigma and pi bonds in molecules:
- Draw the Lewis structure or resonance forms of the compound.
- Each pair of bonded atoms has one sigma bond.
- Double bonds contain one sigma and one pi bond.
- For SO₂: Total 2 sigma bonds (S–O), and 1 pi bond (delocalized as pπ-dπ across S–O bonds by resonance).
- For SO₄²⁻: 4 sigma bonds (S–O), and 2 delocalized pπ-dπ bonds (spread across all four S–O bonds).
11. Can pπ-dπ bonds exist in organic compounds?
Pπ-dπ bonds are extremely rare in organic compounds because organic molecules primarily involve second-period elements (C, N, O) that lack low-energy d orbitals.
- Such bonding is instead observed in inorganic compounds with heavier elements like sulfur and phosphorus.
12. How does the presence of pπ-dπ bonds affect molecular geometry and bond angles?
The presence of pπ-dπ bonds allows the central atom to expand its octet, leading to delocalization and partial double-bond character across multiple bonds.
- This often results in equal bond lengths (as seen in SO₂ and SO₄²⁻).
- Bond angles may be slightly larger than expected due to reduced repulsion between electron domains, and overall symmetry or resonance stabilization may increase.























