
Given below is the table showing shapes of some molecules having lone pairs of electrons. Fill up the blanks left in it.
Molecule Type bp lp Shape Example \[A{{B}_{2}}{{E}_{2}}\] 2 P Bent \[{{H}_{2}}O\] \[A{{B}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}\] 3 2 Q \[Cl{{F}_{3}}\] \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\] 5 R S \[Br{{F}_{5}}\] \[A{{B}_{4}}{{E}_{2}}\] 4 2 T U
(A) P-2, Q - Square pyramidal, R - 2, S - T-shaped, T - Square planar, U - \[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\]
(B) P-4, Q - T-shaped, R - 5, S - square planar, T - Square pyramidal, U - \[S{{O}_{3}}\]
(C) P-2, Q - T-shaped, R - 1, S - square pyramidal, T - Square planar, U - \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\]
(D) P-3, Q - Square planar, R - 2, S - T-shaped, T - Square pyramidal, U - \[BrC{{l}_{3}}\]
| Molecule Type | bp | lp | Shape | Example |
| \[A{{B}_{2}}{{E}_{2}}\] | 2 | P | Bent | \[{{H}_{2}}O\] |
| \[A{{B}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}\] | 3 | 2 | Q | \[Cl{{F}_{3}}\] |
| \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\] | 5 | R | S | \[Br{{F}_{5}}\] |
| \[A{{B}_{4}}{{E}_{2}}\] | 4 | 2 | T | U |
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Understand the description of molecule type and find out which letter represents the bond pair and which one represents the number of lone pairs. Draw the structure of the compound to find out the shape as well as to give an example.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first define the molecule type and find out the letter representing the number of lone pairs(lp).
In the molecule type,
-Central atom-A
-Neighbouring atoms-B
-lone pair-E
- For molecule type \[BrC{{l}_{3}}\], the number of lone pairs is 2. Hence the value of P is 2.
-We will now try to find out the shape of the molecule type \[A{{B}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}\]i.e. draw the structure of \[Cl{{F}_{3}}\].
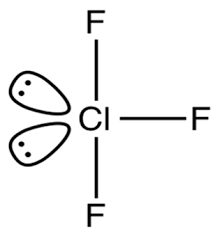
-From the above structure, we can conclude that the molecule is T-shaped. Hence the answer for Q is T-shaped.
-For the molecule type \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\]the number of lone pairs is 1. Let us draw the structure of molecule type \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\].
Structure of \[Br{{F}_{5}}\] (Molecule type - \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\]):
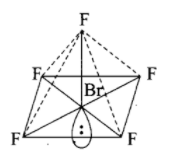
From the above diagram, it is clear that the shape is square pyramidal. Hence the value of R is 1 and the answer for S is square pyramidal.
-Let us draw the structure of molecule type \[A{{B}_{4}}{{E}_{2}}\]: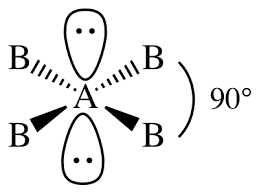
From the above structure, we can conclude that the shape of the molecule is square planar.
Example: \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\]
Hence the answer for T is square planar and U is \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\].
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: While drawing the structures for different molecule types, always highlight the lone pairs to easily calculate the number of lone pairs. Remember that the shape and geometry of a molecule are not always the same. When lone pairs are present, the shape of the molecule is different from the geometry of the molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first define the molecule type and find out the letter representing the number of lone pairs(lp).
In the molecule type,
-Central atom-A
-Neighbouring atoms-B
-lone pair-E
- For molecule type \[BrC{{l}_{3}}\], the number of lone pairs is 2. Hence the value of P is 2.
-We will now try to find out the shape of the molecule type \[A{{B}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}\]i.e. draw the structure of \[Cl{{F}_{3}}\].

-From the above structure, we can conclude that the molecule is T-shaped. Hence the answer for Q is T-shaped.
-For the molecule type \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\]the number of lone pairs is 1. Let us draw the structure of molecule type \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\].
Structure of \[Br{{F}_{5}}\] (Molecule type - \[A{{B}_{5}}{{E}_{{}}}\]):

From the above diagram, it is clear that the shape is square pyramidal. Hence the value of R is 1 and the answer for S is square pyramidal.
-Let us draw the structure of molecule type \[A{{B}_{4}}{{E}_{2}}\]:

From the above structure, we can conclude that the shape of the molecule is square planar.
Example: \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\]
Hence the answer for T is square planar and U is \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\].
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: While drawing the structures for different molecule types, always highlight the lone pairs to easily calculate the number of lone pairs. Remember that the shape and geometry of a molecule are not always the same. When lone pairs are present, the shape of the molecule is different from the geometry of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




