
In the given reaction $PhOMe\xrightarrow[2){{H}_{2}}O]{1)BB{{r}_{3}}}\_\_\_\_\_+\_\_\_\_\_+\_\_\_\_\_$
State the products
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Think about what will happen when boron tribromide reacts with an ether. After boron tribromide has caused cleavage of the ether, hydrolysis occurs and the products are formed.
Complete step by step solution:
Boron tribromide is a reagent that is used to cause the cleavage of dialkyl ether to form an alcohol, boric acid and alkyl bromide. This is a two-step reaction and requires boron tribromide in the first step and hydrolysis with water in the second step. The reaction mechanism is as follows:
i) One mole of phenyl methyl ether reacts with one mole of $BB{{r}_{3}}$ to give an intermediate complex that has benzene bonded to an oxygen atom which is further bonded to boron and two bromine atoms. It also gives a mole of methyl bromide as a byproduct.
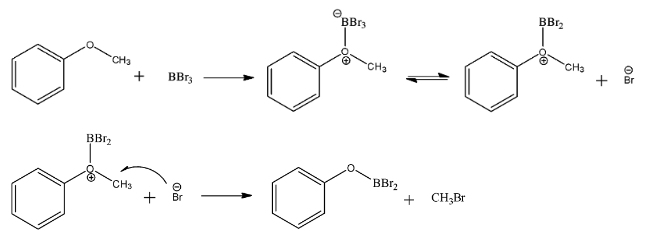
ii) This complex can only be converted to a phenol, which is the aim of the reaction, if it is hydrolyzed by three molecules of water. Two molecules of water first hydrolyze the bonds between boron and bromine, the hydrogen proton is taken by bromine and the hydroxide ion attacks the boron atom. The remaining hydrogen atom hydrolyzes the bond between oxygen and boron where boron gets the hydroxide ion and oxygen the hydrogen proton. The reaction is as follows:
\[PhOBB{{r}_{2}}+3{{H}_{2}}O\to PhOH+{{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}}\]
Hence, the three products that are formed after this reaction are phenol, boric acid, and methyl bromide.
Note: The products formed that we are considering here are all the products that we will find in the vessel of the reaction after both the reagents have been added. We will consider the net products obtained and not just the ones formed in only the first or the second step.
Complete step by step solution:
Boron tribromide is a reagent that is used to cause the cleavage of dialkyl ether to form an alcohol, boric acid and alkyl bromide. This is a two-step reaction and requires boron tribromide in the first step and hydrolysis with water in the second step. The reaction mechanism is as follows:
i) One mole of phenyl methyl ether reacts with one mole of $BB{{r}_{3}}$ to give an intermediate complex that has benzene bonded to an oxygen atom which is further bonded to boron and two bromine atoms. It also gives a mole of methyl bromide as a byproduct.

ii) This complex can only be converted to a phenol, which is the aim of the reaction, if it is hydrolyzed by three molecules of water. Two molecules of water first hydrolyze the bonds between boron and bromine, the hydrogen proton is taken by bromine and the hydroxide ion attacks the boron atom. The remaining hydrogen atom hydrolyzes the bond between oxygen and boron where boron gets the hydroxide ion and oxygen the hydrogen proton. The reaction is as follows:
\[PhOBB{{r}_{2}}+3{{H}_{2}}O\to PhOH+{{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}}\]
Hence, the three products that are formed after this reaction are phenol, boric acid, and methyl bromide.
Note: The products formed that we are considering here are all the products that we will find in the vessel of the reaction after both the reagents have been added. We will consider the net products obtained and not just the ones formed in only the first or the second step.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




