
In the potentiometer circuit suppose, $ \in = 12V$, $l = 1{\text{m}}$. If the galvanometer current is zero when $x = 0.75{\text{m}}$
A) Find the potential difference $V$
B) If $V = emf$of the battery, find its internal resistance.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:In this question, draw the circuit diagram and then use the definition and expression of potential gradient and internal resistance and then find the potential difference and the internal resistance of the circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the diagram of the potentiometer as,
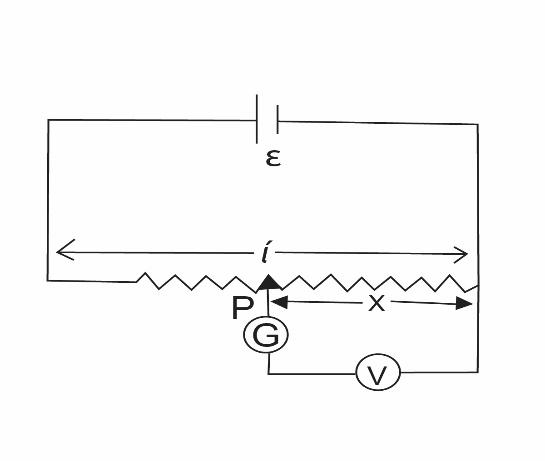
In this question, the null point is given as $X = 0.75{\text{m}}$
A) We know that potential gradient of a cell is the potential drop per unit length. It is expressed as $ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{V}{l}$
where $K$ is potential gradient, $V$ is voltage and $l$ is the length
Potential gradient,
Now, we substitute the values in the above equation as,
$ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{{12}}{1} = 12$
Now we will calculate the potential difference as,
$ \Rightarrow V = KL$
Where, $L$ is the null point distance
Now, we will substitute the values as,
$ \Rightarrow V = 12 \times 0.75$
After calculation, we will get
$\therefore V = 9\;{\text{V}}$
Hence, the potential difference is $9V.$
B) As we know that the internal resistance of a cell is opposition to the current flow provided by the cells and batteries which results in the generation of heat in the circuit.
The expression of internal resistance in an electrical circuit is $E = I\left( {r + R} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow E = Ir + IR$
$ \Rightarrow E = Ir + V$
Where $r$ - the internal resistance of an electrical circuit, $E$ is the electromotive force, so in this case $V$ is the E. M.F of the cell.
Hence,
$E = V + Ir$
$ \Rightarrow E = E + Ir$
After calculation we get
$\therefore r = 0$
Thus, the internal resistance of the circuit is Zero.
Note:The potential gradient mainly depends on various properties such as-i) Current passing through the potentiometer wire ii) Specific resistance of the material of the potentiometer iii) Area of cross section of the potentiometer wire. Internal resistance is used to limit the current flow in a circuit to prevent the short circuit problem in an electrical circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the diagram of the potentiometer as,

In this question, the null point is given as $X = 0.75{\text{m}}$
A) We know that potential gradient of a cell is the potential drop per unit length. It is expressed as $ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{V}{l}$
where $K$ is potential gradient, $V$ is voltage and $l$ is the length
Potential gradient,
Now, we substitute the values in the above equation as,
$ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{{12}}{1} = 12$
Now we will calculate the potential difference as,
$ \Rightarrow V = KL$
Where, $L$ is the null point distance
Now, we will substitute the values as,
$ \Rightarrow V = 12 \times 0.75$
After calculation, we will get
$\therefore V = 9\;{\text{V}}$
Hence, the potential difference is $9V.$
B) As we know that the internal resistance of a cell is opposition to the current flow provided by the cells and batteries which results in the generation of heat in the circuit.
The expression of internal resistance in an electrical circuit is $E = I\left( {r + R} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow E = Ir + IR$
$ \Rightarrow E = Ir + V$
Where $r$ - the internal resistance of an electrical circuit, $E$ is the electromotive force, so in this case $V$ is the E. M.F of the cell.
Hence,
$E = V + Ir$
$ \Rightarrow E = E + Ir$
After calculation we get
$\therefore r = 0$
Thus, the internal resistance of the circuit is Zero.
Note:The potential gradient mainly depends on various properties such as-i) Current passing through the potentiometer wire ii) Specific resistance of the material of the potentiometer iii) Area of cross section of the potentiometer wire. Internal resistance is used to limit the current flow in a circuit to prevent the short circuit problem in an electrical circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




