
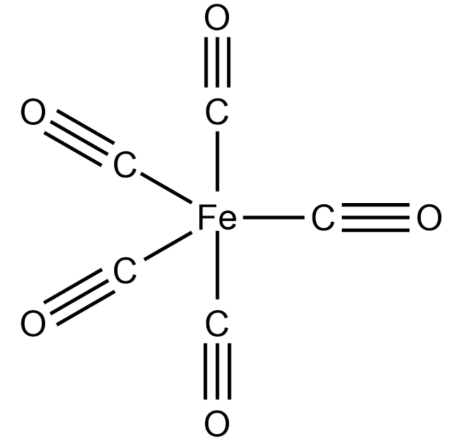
What is the shape of $Fe{{(CO)}_{5}}$the molecule and which of the following d-orbitals involved in hybridization?
(A) Tetrahedral, ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$
(B) Trigonal bipyramidal, ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$
(C) Trigonal bipyramidal, ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}}}$
(D) Square pyramidal
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Finding the hybridization of the central metal atom will tell the structure of the complex. Hybridization is the process of combining and mixing of atomic orbitals from the same atom to form an entirely new hybrid orbital having the same energy.
Complete step by step solution:
-In simple words, the concept of intermixing of two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels giving rise to the degenerate type of orbitals.
-In hybridization, the atomic orbitals of only similar energy can take parts such as the mixing of two ‘s’ orbitals or two ‘p’ orbitals or an ‘s’ orbital with a ‘p’ orbital or ‘s’ orbital with a ‘d’ orbital.
-The atomic orbitals taking part in hybridization can be both, full-filled or half-filled orbitals provided they must have similar energy.
-Finding the hybridization of $Fe{{(CO)}_{5}}$complex,
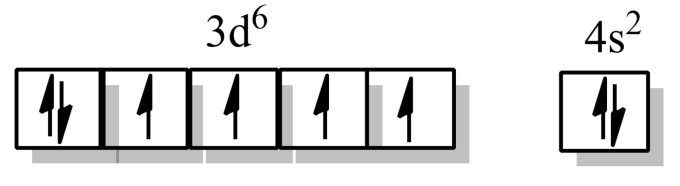
Electronic configuration of Fe in the ground state- $[Ar]3{{d}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}$
Electronic configuration of Fe in an excited state- $[Ar]3{{d}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}$, as the iron in the complex, is in zero oxidation state.
According to Valence Bond theory,
From spectrochemical series, CO being a strong field ligand thus will cause the pairing of electrons.
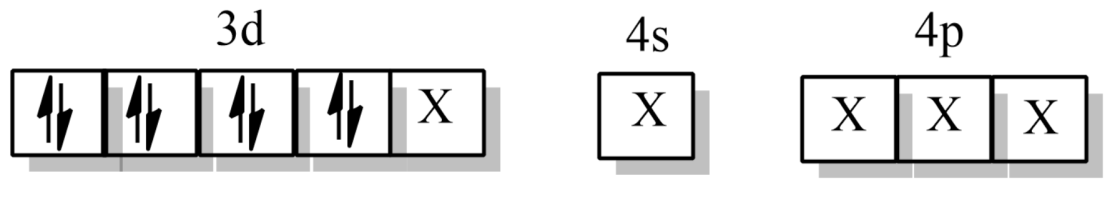
where X is the orbitals occupied by the ligand CO.
Therefore, hybridization will be $ds{{p}^{3}}$.
-According to Crystal field theory,
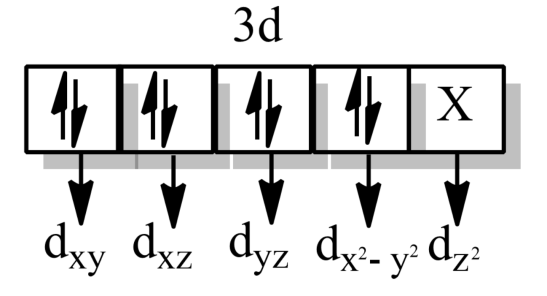
-When the hybridization is $ds{{p}^{3}}$, the shape will be trigonal bipyramidal and the d-orbital involved in hybridization will be $d{{z}^{2}}$.
So, the correct option is (C).
Note: When the coordination number is 2, the geometry of the complex is linear. When the coordination number is 3, the geometries can be trigonal planar geometry, trigonal pyramid geometry, or T-shaped. When the coordination number is 4, the geometries can be tetrahedral or square planar. When the coordination number is 5, the geometries can be square pyramidal or trigonal bipyramidal. When the coordination number is 6, the geometries can be a hexagonal planar, trigonal prism, or octahedral.
Complete step by step solution:
-In simple words, the concept of intermixing of two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels giving rise to the degenerate type of orbitals.
-In hybridization, the atomic orbitals of only similar energy can take parts such as the mixing of two ‘s’ orbitals or two ‘p’ orbitals or an ‘s’ orbital with a ‘p’ orbital or ‘s’ orbital with a ‘d’ orbital.
-The atomic orbitals taking part in hybridization can be both, full-filled or half-filled orbitals provided they must have similar energy.
-Finding the hybridization of $Fe{{(CO)}_{5}}$complex,
Electronic configuration of Fe in the ground state- $[Ar]3{{d}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}$
Electronic configuration of Fe in an excited state- $[Ar]3{{d}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}$, as the iron in the complex, is in zero oxidation state.
According to Valence Bond theory,

From spectrochemical series, CO being a strong field ligand thus will cause the pairing of electrons.

where X is the orbitals occupied by the ligand CO.
Therefore, hybridization will be $ds{{p}^{3}}$.
-According to Crystal field theory,

-When the hybridization is $ds{{p}^{3}}$, the shape will be trigonal bipyramidal and the d-orbital involved in hybridization will be $d{{z}^{2}}$.

So, the correct option is (C).
Note: When the coordination number is 2, the geometry of the complex is linear. When the coordination number is 3, the geometries can be trigonal planar geometry, trigonal pyramid geometry, or T-shaped. When the coordination number is 4, the geometries can be tetrahedral or square planar. When the coordination number is 5, the geometries can be square pyramidal or trigonal bipyramidal. When the coordination number is 6, the geometries can be a hexagonal planar, trigonal prism, or octahedral.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




