
State and prove Pascal’s Law of transmission of fluid pressure.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, the concept of Pascal's law is used, that is it states that if a static pressure is applied from outside of a confined fluid, the pressure is evenly distributed throughout every portion of fluid.
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that Pascal's law states that if a static pressure is applied from outside of a confined fluid, the pressure is evenly distributed throughout every portion of fluid. According to the law, if \[F\] is the applied force, \[P\]is the transmitted pressure, and \[A\] is the area of applied pressure then from Pascal’s law relation of these three will be
\[ \Rightarrow F = P \times A\]
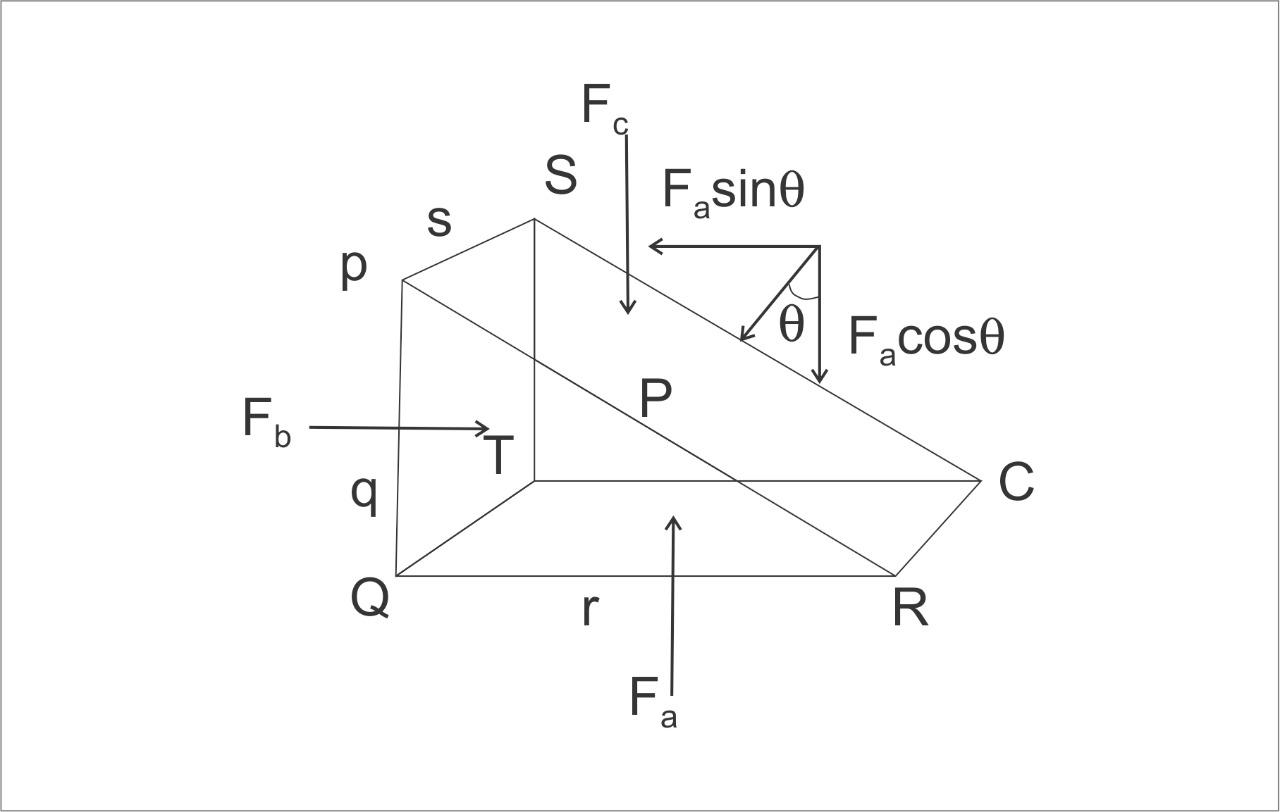
Fig: Pressure and Force distribution in triangular prism
Now, we assume a right angled prismatic triangle containing a fluid of density\[\rho \].the prism being very small, we consider every point at the same depth, and gravitational effect on prism is also the same in those points.
Let \[ps\], \[qs\]and \[rs\] be the area of surfaces \[PSUR\], \[PSTQ\] and \[TURQ\] of the prism.
And also, pressure on those surfaces be, \[{P_b}\] and \[{P_c}\] respectively.
A force is exerted by the pressure in surfaces, in \[PRUS\] face the force be \[{F_a}\], in \[PSTQ\] the force be \[{F_b}\] and in \[TURQ\] the force be \[{F_c}\].
Now, we write the expression for the forces at different surfaces as,
\[ \Rightarrow {F_a} = {P_a} \times ps\]
$ \Rightarrow {F_b} = {P_b} \times qs$
\[ \Rightarrow {F_c} = {P_c} \times rs\]
As it is right angled triangular prism,
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{q}{p}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{r}{p}\]
As we know that the total force inside the prism will be zero, as equilibrium is attained.
Breaking the \[{F_a}\] force into horizontal and vertical directions as \[{F_a}\sin \theta \] and \[{F_a}\cos \theta \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow {F_a}\sin \theta = {F_b}......(1)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_a}\cos \theta = {F_c}......(2)\]
Replacing \[{F_a}\] with \[{P_a} \times ps\] and the value of \[{F_b}\] with \[{P_b} \times qs\] putting values of \[\sin \theta \] in equation\[(1)\]
$ \Rightarrow {P_a} \times ps \times \dfrac{q}{p} = {P_b} \times qs.....(3)$
Similarly, from equation \[(2)\] putting the values we get
$ \Rightarrow {P_a} \times ps \times \dfrac{r}{p} = {P_c} \times rs......(4)$
Now, from equation \[(3)\] and \[(4)\] we get,
\[{P_a} = {P_b}\] And \[{P_a} = {P_c}\]
\[\therefore {P_a} = {P_b} = {P_c}\]
So, the pressure distributed in the fluid is equal in every direction.
Note: As we know that the Pascal Law has wide application for example it is used in the hydraulic press, which is the great achievement of Pascal’s Law application, in modern planes it is used for brakes, landing and various purposes.
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that Pascal's law states that if a static pressure is applied from outside of a confined fluid, the pressure is evenly distributed throughout every portion of fluid. According to the law, if \[F\] is the applied force, \[P\]is the transmitted pressure, and \[A\] is the area of applied pressure then from Pascal’s law relation of these three will be
\[ \Rightarrow F = P \times A\]

Fig: Pressure and Force distribution in triangular prism
Now, we assume a right angled prismatic triangle containing a fluid of density\[\rho \].the prism being very small, we consider every point at the same depth, and gravitational effect on prism is also the same in those points.
Let \[ps\], \[qs\]and \[rs\] be the area of surfaces \[PSUR\], \[PSTQ\] and \[TURQ\] of the prism.
And also, pressure on those surfaces be, \[{P_b}\] and \[{P_c}\] respectively.
A force is exerted by the pressure in surfaces, in \[PRUS\] face the force be \[{F_a}\], in \[PSTQ\] the force be \[{F_b}\] and in \[TURQ\] the force be \[{F_c}\].
Now, we write the expression for the forces at different surfaces as,
\[ \Rightarrow {F_a} = {P_a} \times ps\]
$ \Rightarrow {F_b} = {P_b} \times qs$
\[ \Rightarrow {F_c} = {P_c} \times rs\]
As it is right angled triangular prism,
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{q}{p}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{r}{p}\]
As we know that the total force inside the prism will be zero, as equilibrium is attained.
Breaking the \[{F_a}\] force into horizontal and vertical directions as \[{F_a}\sin \theta \] and \[{F_a}\cos \theta \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow {F_a}\sin \theta = {F_b}......(1)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_a}\cos \theta = {F_c}......(2)\]
Replacing \[{F_a}\] with \[{P_a} \times ps\] and the value of \[{F_b}\] with \[{P_b} \times qs\] putting values of \[\sin \theta \] in equation\[(1)\]
$ \Rightarrow {P_a} \times ps \times \dfrac{q}{p} = {P_b} \times qs.....(3)$
Similarly, from equation \[(2)\] putting the values we get
$ \Rightarrow {P_a} \times ps \times \dfrac{r}{p} = {P_c} \times rs......(4)$
Now, from equation \[(3)\] and \[(4)\] we get,
\[{P_a} = {P_b}\] And \[{P_a} = {P_c}\]
\[\therefore {P_a} = {P_b} = {P_c}\]
So, the pressure distributed in the fluid is equal in every direction.
Note: As we know that the Pascal Law has wide application for example it is used in the hydraulic press, which is the great achievement of Pascal’s Law application, in modern planes it is used for brakes, landing and various purposes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




