
The chord joining two points ${\theta _1}{\text{ and }}{\theta _2}$on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ such that $\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{{b^2}}}$ will subtend a right angle at
$
(a){\text{ focus}} \\
(b){\text{ center}} \\
(c){\text{ end of the major axis}} \\
(d){\text{ end of the minor axis}} \\
$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In this question suppose two points ${\theta _1}$ and ${\theta _2}$ such that ${\theta _1} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$ and ${\theta _2} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$through which the chord passes. Then use the concept of slope of line passing through two given points to find the slope of $O{\theta _1}{\text{ and O}}{\theta _2}$ where O is the origin. Use the concept that if two lines are perpendicular then their slopes are related as ${m_1} \times {m_2} = - 1$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
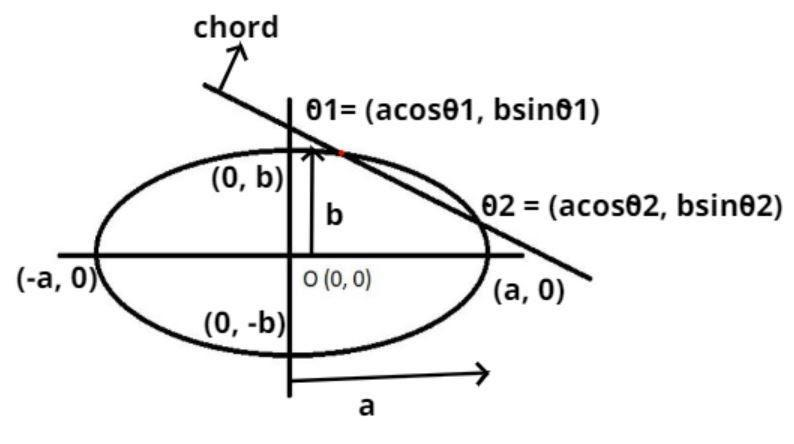
The chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is shown above.
As we know that the ellipse is having a center (O) = (0, 0) is also shown in the figure.
Let us suppose the point ${\theta _1} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$ and ${\theta _2} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$ is also shown in the figure.
Now as we know that the slope between two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$ is given as
Slope (m) = $\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$
So find out the slopes of $\left( {O{\theta _1}} \right)$ and $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$.
Let O = $(x_1, y_1)$ = (0, 0)
${\theta _1} = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$
${\theta _2} = \left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$
So let the slope of $\left( {0{\theta _1}} \right)$ be m1.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _1} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _1} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1}$
Now let the slope of $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$ be m2.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _2} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _2} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2}$
Now multiply the slopes we have
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1} \times \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2}$........................ (1)
Now it is given that
$\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{{b^2}}}$
Now substitute this value in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \times \dfrac{{ - {a^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = - 1$
So multiplication of slopes is (-1) which is the condition of the right angle.
Therefore the chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ will subtend a right angle at origin or center.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: The center of the given ellipse that is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is (0, 0) that is the origin that’s why option (c) is correct. The equation of shifted ellipse or the ellipse whose center is not at origin is given by $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - p} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - q} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ here the center is at (p, q).
Complete step-by-step answer:

The chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is shown above.
As we know that the ellipse is having a center (O) = (0, 0) is also shown in the figure.
Let us suppose the point ${\theta _1} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$ and ${\theta _2} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$ is also shown in the figure.
Now as we know that the slope between two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$ is given as
Slope (m) = $\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$
So find out the slopes of $\left( {O{\theta _1}} \right)$ and $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$.
Let O = $(x_1, y_1)$ = (0, 0)
${\theta _1} = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$
${\theta _2} = \left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$
So let the slope of $\left( {0{\theta _1}} \right)$ be m1.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _1} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _1} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1}$
Now let the slope of $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$ be m2.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _2} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _2} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2}$
Now multiply the slopes we have
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1} \times \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2}$........................ (1)
Now it is given that
$\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{{b^2}}}$
Now substitute this value in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \times \dfrac{{ - {a^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = - 1$
So multiplication of slopes is (-1) which is the condition of the right angle.
Therefore the chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ will subtend a right angle at origin or center.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: The center of the given ellipse that is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is (0, 0) that is the origin that’s why option (c) is correct. The equation of shifted ellipse or the ellipse whose center is not at origin is given by $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - p} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - q} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ here the center is at (p, q).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




