
The electron in the beam of a television tube moves horizontally from south to north. The vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field points down. The electron is deflected towards
A.West
B.No deflection
C.East
D.North to south
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When the electron beam of a television tube moves horizontally from south to north, then-current moves from the opposite direction of the flow of electrons that is current is moving from south to north. Then charged particles will be deflected in the opposite direction of the earth’s magnetic field.
Complete answer:
According to Fleming’s left hand-thumb rule, if we stretch our left hand and arrange the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger in such a way that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. In this way, if the forefinger points toward the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger points toward the direction of flow of charged particles then the thumb points in the direction of magnetic force experienced by a positively charged particle.
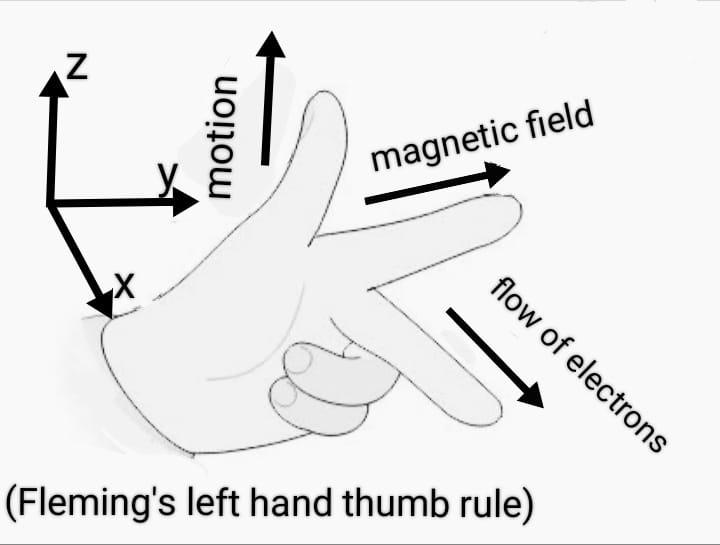
As a result, negatively charged particles deflected in the opposite direction of the deflection of a positively charged particle.
Here the given phenomena can be explained by Fleming’s left-hand thumb rule.
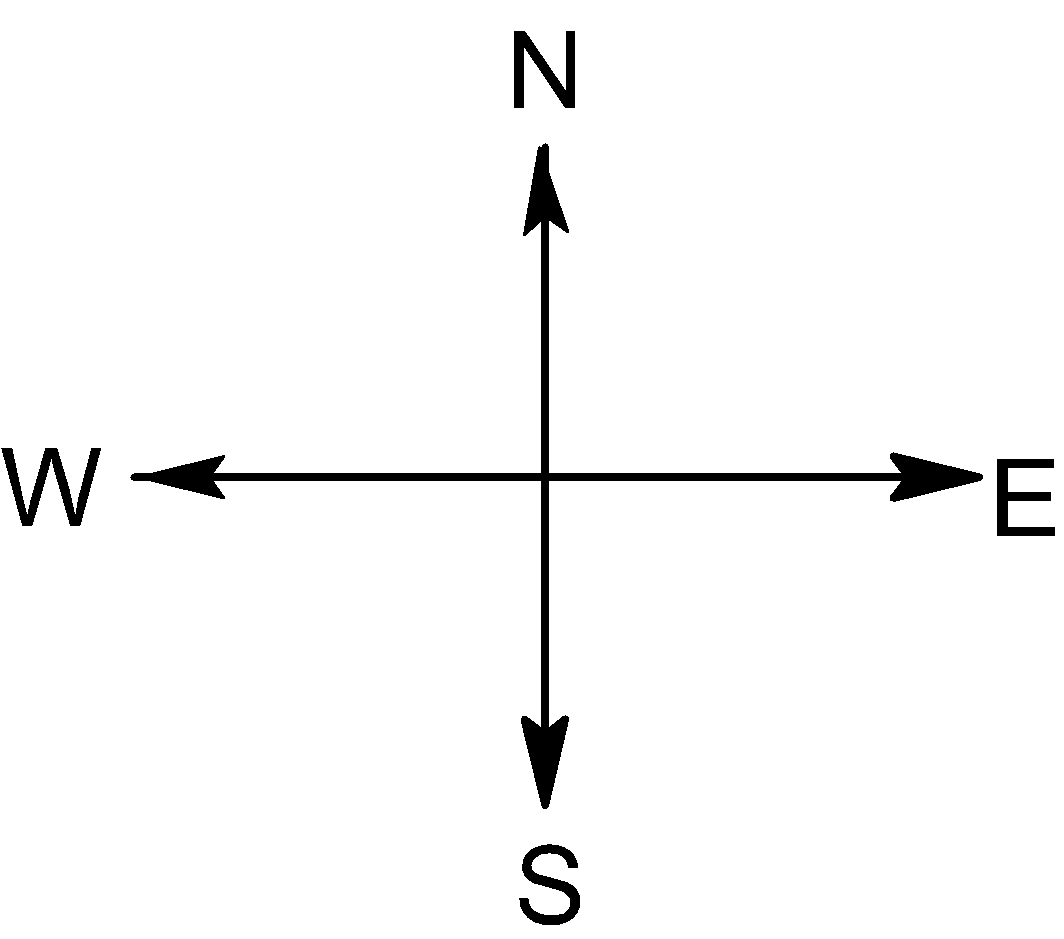
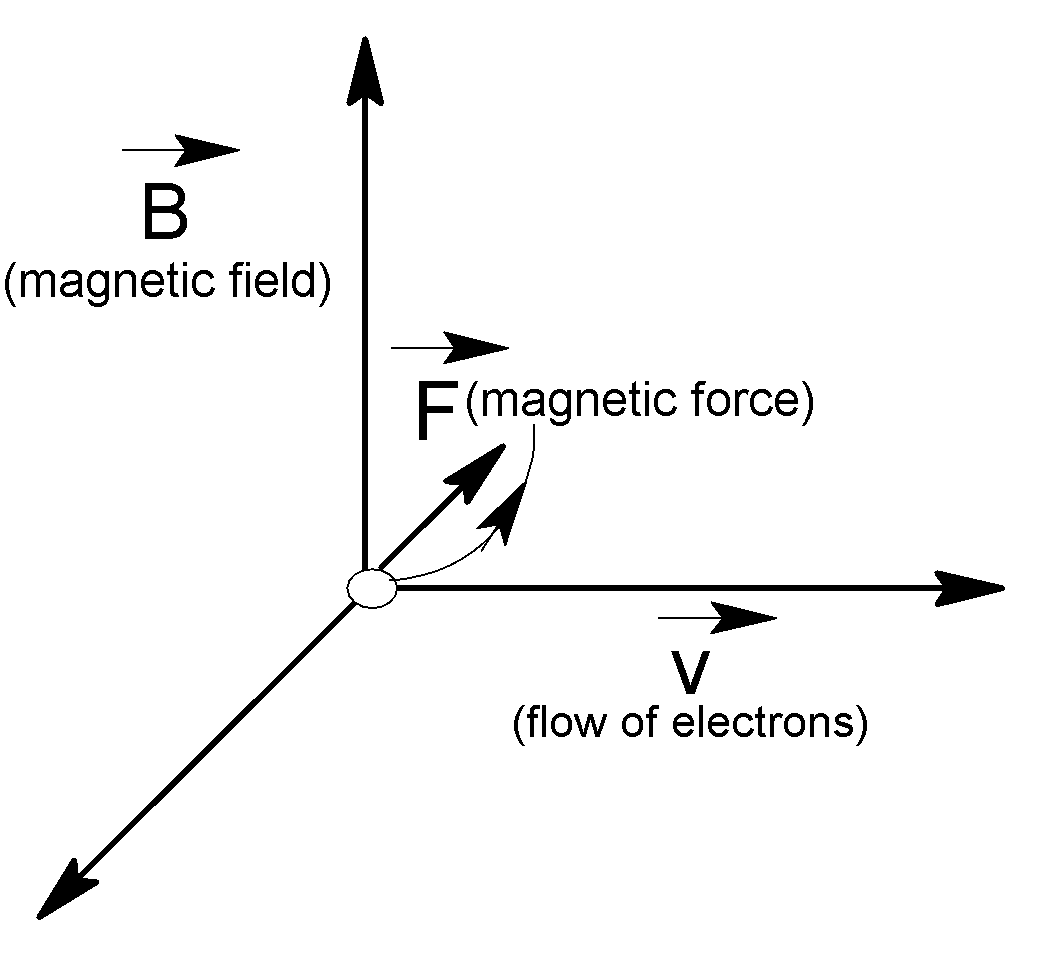
The electron in the beam of the television tube moves horizontally from south ($S$) to north ($N$) and the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field points down which means a vertical component of the magnetic field points toward the direction of the west ($W$). According to Fleming’s rule, the electron experiences force toward the direction of the east ($E$).
The negatively charged particle, an electron, is deflected in the direction of the east ($E$).
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Only a moving charged particle experiences a magnetic force in the presence of the magnetic field. For example protons, electrons, alpha particles, etc are charged particles and they are deflected but a neutron which is a neutral particle i.e zero charged does not deflect in the presence of the magnetic field.
Complete answer:
According to Fleming’s left hand-thumb rule, if we stretch our left hand and arrange the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger in such a way that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. In this way, if the forefinger points toward the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger points toward the direction of flow of charged particles then the thumb points in the direction of magnetic force experienced by a positively charged particle.

As a result, negatively charged particles deflected in the opposite direction of the deflection of a positively charged particle.
Here the given phenomena can be explained by Fleming’s left-hand thumb rule.


The electron in the beam of the television tube moves horizontally from south ($S$) to north ($N$) and the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field points down which means a vertical component of the magnetic field points toward the direction of the west ($W$). According to Fleming’s rule, the electron experiences force toward the direction of the east ($E$).
The negatively charged particle, an electron, is deflected in the direction of the east ($E$).
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Only a moving charged particle experiences a magnetic force in the presence of the magnetic field. For example protons, electrons, alpha particles, etc are charged particles and they are deflected but a neutron which is a neutral particle i.e zero charged does not deflect in the presence of the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




