
The standard quantity used for comparison is called
(A) Scale
(B) Unit
(C) Magnitude
(D) All
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint Every physical quantity needs a standard for its specification which is required for identification, comparisons and for expressing other physical quantities as well. All the comparisons with physical quantities are made in terms of units.
Complete step-by-step solution
Measuring a physical quantity includes comparison with certain basic internationally approved reference standards called units. A physical quantities measurement is written in terms of the standard unit with the numerical value. Each unit has its symbol.
For example:
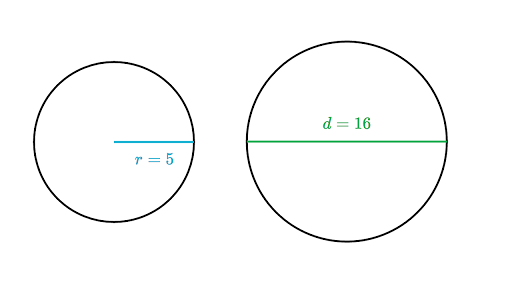
From the diagram, the radius of the circle is 5 cm.
The diameter of the circle is 10 cm. Here cm is the standard unit giving meaning to the numerical value 5 and 10.
There are many systems of units like S.I, CGS, FPS, MKS and more but the S.I units system is the standard scheme for international usage in scientific work. The S.I system has seven base/fundamental units from which other units are derived called secondary derived units. Using these base units the dimensional formulae of physical quantities are also derived.
Besides the above seven fundamental units two supplementary units exist.
So, B is the correct option.
Note: The units of other physical quantities are derived from the base units.
For example: Unit of length is m and unit of time is s from this unit of velocity \[m{s^{ - 1}}\] is derived. The units can be converted from one to other forms of the same physical quantity like kg, g, mg, dg all are the units for measuring mass.
Complete step-by-step solution
Measuring a physical quantity includes comparison with certain basic internationally approved reference standards called units. A physical quantities measurement is written in terms of the standard unit with the numerical value. Each unit has its symbol.
For example:
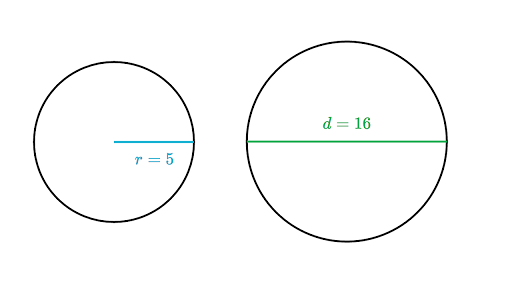
From the diagram, the radius of the circle is 5 cm.
The diameter of the circle is 10 cm. Here cm is the standard unit giving meaning to the numerical value 5 and 10.
There are many systems of units like S.I, CGS, FPS, MKS and more but the S.I units system is the standard scheme for international usage in scientific work. The S.I system has seven base/fundamental units from which other units are derived called secondary derived units. Using these base units the dimensional formulae of physical quantities are also derived.
| Quantity | Unit | Symbol |
| Length | Meter | m |
| Mass | Kilogram | Kg |
| Time | Second | S |
| Temperature | Kelvin | K |
| Amount of substance | Mole | Mol |
| Electric current | Ampere | A |
| Luminous intensity | Candela | Cd |
Besides the above seven fundamental units two supplementary units exist.
| Quantity | Unit | Symbols |
| Plane angle | Radian | Rad |
| Solid angle | Steradian | Sr |
So, B is the correct option.
Note: The units of other physical quantities are derived from the base units.
For example: Unit of length is m and unit of time is s from this unit of velocity \[m{s^{ - 1}}\] is derived. The units can be converted from one to other forms of the same physical quantity like kg, g, mg, dg all are the units for measuring mass.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




