
The structure of \[{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\] crystal is:
(A) \[{\text{CsCl}}\]type
(B) \[{\text{NaCl}}\]type
(C) \[{\text{KCl}}\]type
(D) Anti-fluorite
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Sodium oxide has a chemical formula \[{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}{\text{.}}\] The main use of this chemical is in ceramics and in the formation of glasses. It is a base anhydride of sodium hydroxide \[{\text{(NaOH)}}{\text{.}}\] This means that when water is added to sodium oxide, sodium hydroxide is formed. The reaction is as follows –
\[N{a_2}O{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{H_2}O{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}2NaOH\]
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium oxide or \[{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\] possesses the structure of anti-fluorite. Sodium ions are smaller in size than the oxide ions so they go to the voids. Moreover, the number of sodium ions present is twice that of the oxide ions so all the tetrahedral voids get filled by sodium ions. The oxide ions are larger in size so they occupy the face and corners of the lattice. Therefore, the structure formed is all the oxide ions occupy the face and corners while the sodium ions occupy the tetrahedral voids.
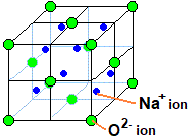
The anti-fluorite structure is derived from fluorite structure by interchanging the positive and negative positions in the lattice crystal.
Hence, the correct answer is (D) i.e., anti-fluorite.
Note: Sodium oxide is widely used in the manufacturing of ceramic and glass products. Also, sodium oxide is insoluble in water, but when added to water, it would result in the formation of sodium hydroxide.
\[N{a_2}O{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{H_2}O{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}2NaOH\]
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium oxide or \[{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\] possesses the structure of anti-fluorite. Sodium ions are smaller in size than the oxide ions so they go to the voids. Moreover, the number of sodium ions present is twice that of the oxide ions so all the tetrahedral voids get filled by sodium ions. The oxide ions are larger in size so they occupy the face and corners of the lattice. Therefore, the structure formed is all the oxide ions occupy the face and corners while the sodium ions occupy the tetrahedral voids.

The anti-fluorite structure is derived from fluorite structure by interchanging the positive and negative positions in the lattice crystal.
Hence, the correct answer is (D) i.e., anti-fluorite.
Note: Sodium oxide is widely used in the manufacturing of ceramic and glass products. Also, sodium oxide is insoluble in water, but when added to water, it would result in the formation of sodium hydroxide.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




