
The terminal C atom in butane is _______ hybridized.
(A) $ds{{p}^{2}}$
(B) $sp$
(C) $s{{p}^{2}}$
(D) $s{{p}^{3}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: There are 2 terminal carbons in the butane chain and both of them have the same hybridization. Both the terminal carbon atoms form 4 single bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
Butane is a member of the alkane group. It has 4 carbons. It has a straight-chain structure.
The formula of butane is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{8}}$
Since it is a member of the alkane group, all the bonds in butane will be a single bond.
So the structure of butane is given below:
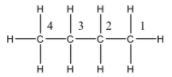
So, there are two terminal carbon atoms in the butane, carbon number one and four.
Both the carbon atoms are connected to three hydrogen atoms and one propyl group.
There are some steps which can help to calculate the hybridization of an atom:
First, look at the atom and count the number of atoms or molecules to which it is connected. If the atom has lone pairs, then it is also counted.
Add both numbers and:
If the number is 4 then it is $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized.
If the number is 3 then it is $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridized
If the number is 2 then it is $sp$hybridized
So, in both the terminal carbon atoms of butane the number is 4 (three hydrogen atoms and one propyl molecule).
Hence, the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
So, the correct answer is an option (d)- $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note: $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization mostly occurs when the carbon atom has a double bond and $sp$hybridization occurs mostly when the carbon atom has a triple bond. $ds{{p}^{2}}$hybridization is shown by heavier elements because they have vacant d-orbitals.
Complete step by step solution:
Butane is a member of the alkane group. It has 4 carbons. It has a straight-chain structure.
The formula of butane is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{8}}$
Since it is a member of the alkane group, all the bonds in butane will be a single bond.
So the structure of butane is given below:

So, there are two terminal carbon atoms in the butane, carbon number one and four.
Both the carbon atoms are connected to three hydrogen atoms and one propyl group.
There are some steps which can help to calculate the hybridization of an atom:
First, look at the atom and count the number of atoms or molecules to which it is connected. If the atom has lone pairs, then it is also counted.
Add both numbers and:
If the number is 4 then it is $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized.
If the number is 3 then it is $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridized
If the number is 2 then it is $sp$hybridized
So, in both the terminal carbon atoms of butane the number is 4 (three hydrogen atoms and one propyl molecule).
Hence, the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
So, the correct answer is an option (d)- $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note: $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization mostly occurs when the carbon atom has a double bond and $sp$hybridization occurs mostly when the carbon atom has a triple bond. $ds{{p}^{2}}$hybridization is shown by heavier elements because they have vacant d-orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




