
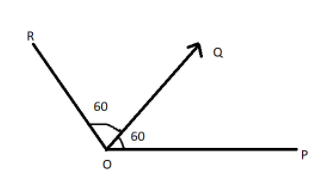
Three coplanar forces each of magnitude $F$ act on a particle at $O$ as shown in the figure. The resultant force is:
A) $2F$ along $OQ$
B) $2F$ along $OP$
C) $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}F$ along $OR$
D) Zero
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Both forces on one plane are coplanar force structures. It can be simultaneous, non-competitive, non-parallel or parallel. The graphical statistics or algebra will solve all these structures. A coplanar force structure is a system of two or more forces whose action lines are crossed by both at one point in particular. However, the universal point may not necessarily be in touch with all the different vectors. These are the simplest powers in which one of several graphic or algebraic alternatives may be solved.
Complete step by step solution:
The single force of the same effect, known as the consequent force or the resulting force, means the arithmetical sum of the different forces for forces that act in the same way and have the same line of operation. If two forces do not have the same action, a method called vector addition of forces may be used to find the magnitude and direction of the resulting force.
There are two visual methods for inserting vectors such as the force triangle and a force parallelogram. The corresponding force is the arithmetic differential of the two powers in the opposite directions along the same line of motion. There are no effects when three or more coplanar forces at a time and the vector diagram closes. The powers at the point of operation are in harmony.
Along vertical, components of $R$ and $Q$ cancel out .But along horizontal, the components of, $OP$ $OQ$ and $OR$ are $F$, $\dfrac {F} {2} $and $\dfrac {F} {2} $ respectively, which make a total of $2F$ along $OP$.
Note: Coplanar forces mean the forces on an aeroplane. If several forces operate on a person, they are called a power system or a force system. It is regarded as a coplanar force structure in a system where all powers lie on the same plane. This article therefore deals with a system of forces which operate on the same plane and which either share or converge on a similar line of action. If the powers have a similar line of movement, they are known as hills, whereas they are known as concourse when they converge at a common point.
A coplanar or non-coplanar force device can be used. If all forces in a system lie on the same basis, then the coplanar is known as the force system.
Complete step by step solution:
The single force of the same effect, known as the consequent force or the resulting force, means the arithmetical sum of the different forces for forces that act in the same way and have the same line of operation. If two forces do not have the same action, a method called vector addition of forces may be used to find the magnitude and direction of the resulting force.
There are two visual methods for inserting vectors such as the force triangle and a force parallelogram. The corresponding force is the arithmetic differential of the two powers in the opposite directions along the same line of motion. There are no effects when three or more coplanar forces at a time and the vector diagram closes. The powers at the point of operation are in harmony.
Along vertical, components of $R$ and $Q$ cancel out .But along horizontal, the components of, $OP$ $OQ$ and $OR$ are $F$, $\dfrac {F} {2} $and $\dfrac {F} {2} $ respectively, which make a total of $2F$ along $OP$.
Note: Coplanar forces mean the forces on an aeroplane. If several forces operate on a person, they are called a power system or a force system. It is regarded as a coplanar force structure in a system where all powers lie on the same plane. This article therefore deals with a system of forces which operate on the same plane and which either share or converge on a similar line of action. If the powers have a similar line of movement, they are known as hills, whereas they are known as concourse when they converge at a common point.
A coplanar or non-coplanar force device can be used. If all forces in a system lie on the same basis, then the coplanar is known as the force system.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




