
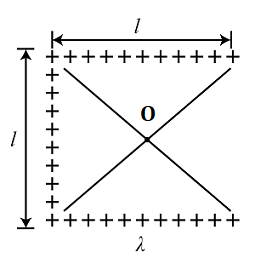
Three sides of a square of side \[l\] are occupied by positive charges of density $\lambda {\text{C}}/m$. The net electric field at the centre $O$ is:
(A) \[\dfrac{{\sqrt 2 {\text{k}}\lambda }}{l}\]
(B) $\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 {\text{k}}\lambda }}{l}$
(C) $\dfrac{{2{\text{k}}\lambda }}{l}$
(D) $\dfrac{{{\text{k}}\lambda }}{l}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Electric Field is the region produced around it by an electric charge whose influence is observed when in that region where the field exists, another charge is brought.
Formula Used: We will use the following formula to find out the solution of this problem:
\[E = \dfrac{{2\lambda }}{{x\sqrt {{l^2} + 4{x^2}} }}\]
Where
${\text{E}}$ is the net electric field
$\lambda $ is the electric charge density
$l$ is the length of the side of square
\[x\] is the distance from line charge
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
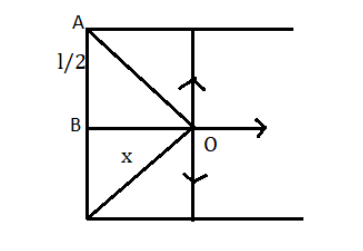
We have been given that the sides of the square are occupied by positive charges of density ${Q_{density}} = \lambda {\text{C}}/m$
The electric fields here are equal and opposite to each other due to the line charge of the top and bottom of the square. They cancel each other, and because of the line on the left side of the square, the net electric field at \[O\] is only the field.
In simpler words, we have
\[{E_{top}} = {E_{bottom}}\]
The charges on top and bottom are equal magnitude and opposite in polarity.
According to the question and the figure drawn above, we can observe that
\[x = \dfrac{l}{2}\]
Now we will put the values of \[x\] in the above formula, we get
\[E = \dfrac{{2\lambda }}{{k\dfrac{l}{2}\sqrt {{l^2} + \dfrac{{4{l^2}}}{4}} }}\]
We can rewrite this equation as
\[E = k\dfrac{{4\lambda }}{{\sqrt 2 l}}\]
Upon further simplifying, we get
\[E = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 k\lambda }}{l}\]
Therefore, the correct option is (B.)
Note: An electric field surrounds an electric charge and also exerts force at the same time on other charges in the field. It either attracts them or repels them. The electric field is defined mathematically as a vector field that connects the force per unit of charge exerted on an infinitesimal positive test charge to each point in space at that particular point. The volt per meter is the SI unit of electric field strength. Electric field strength is also denoted by Newtons per coulomb. Electric fields are generated by electrical charges, or by magnetic fields that vary in time.
Formula Used: We will use the following formula to find out the solution of this problem:
\[E = \dfrac{{2\lambda }}{{x\sqrt {{l^2} + 4{x^2}} }}\]
Where
${\text{E}}$ is the net electric field
$\lambda $ is the electric charge density
$l$ is the length of the side of square
\[x\] is the distance from line charge
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:

We have been given that the sides of the square are occupied by positive charges of density ${Q_{density}} = \lambda {\text{C}}/m$
The electric fields here are equal and opposite to each other due to the line charge of the top and bottom of the square. They cancel each other, and because of the line on the left side of the square, the net electric field at \[O\] is only the field.
In simpler words, we have
\[{E_{top}} = {E_{bottom}}\]
The charges on top and bottom are equal magnitude and opposite in polarity.
According to the question and the figure drawn above, we can observe that
\[x = \dfrac{l}{2}\]
Now we will put the values of \[x\] in the above formula, we get
\[E = \dfrac{{2\lambda }}{{k\dfrac{l}{2}\sqrt {{l^2} + \dfrac{{4{l^2}}}{4}} }}\]
We can rewrite this equation as
\[E = k\dfrac{{4\lambda }}{{\sqrt 2 l}}\]
Upon further simplifying, we get
\[E = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 k\lambda }}{l}\]
Therefore, the correct option is (B.)
Note: An electric field surrounds an electric charge and also exerts force at the same time on other charges in the field. It either attracts them or repels them. The electric field is defined mathematically as a vector field that connects the force per unit of charge exerted on an infinitesimal positive test charge to each point in space at that particular point. The volt per meter is the SI unit of electric field strength. Electric field strength is also denoted by Newtons per coulomb. Electric fields are generated by electrical charges, or by magnetic fields that vary in time.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




