
What is conformation in alkanes?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Alkanes contain C-C sigma bonds. The charge distribution of the sigma molecular orbital is symmetrical near the internuclear axis of the C–C bond. This charge distribution will remain undisturbed for any rotation about its axis. This allows unrestricted rotation of the C–C single bond.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The rotation of the C-C single bond yields various spatial arrangements of atoms in space that are interchangeable.
The spatial arrangements of atoms that can be modified into one another by rotation around a C-C single bond are called conformations.
Alkanes can therefore have an infinite number of conformations by rotating around C-C single bonds.
Conformations of ethane
Ethane comprises a carbon-carbon single bond with each carbon atom attached to three hydrogen atoms.
Suppose we retain one carbon atom stationary and rotate the other carbon atom around the C-C axis. In that case, this rotation yields a vast no.of spatial arrangements of hydrogen atoms connected to one carbon atom for the hydrogen atoms bonded to the other carbon atom.
These are known as conformational isomers (conformers).
I) Eclipsed conformation - Here hydrogen atoms connected to two carbons are close to each other.
ii) Staggered conformation - Here hydrogens are far apart from each other.
These two conformations can be represented by many projections one of them is Sawhorse projections.
Sawhorse projections
In this, front carbon is demonstrated at the lower end of the line, whereas the rear carbon is exhibited at the upper end.
Each carbon has three lines connecting it to three hydrogen atoms.
The lines are inclined at an angle of 120° to each other.
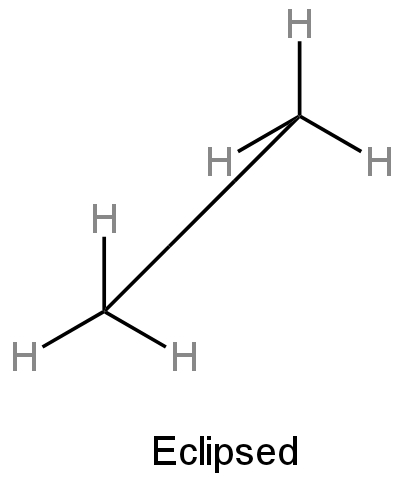
Image: Eclipsed conformation of ethane
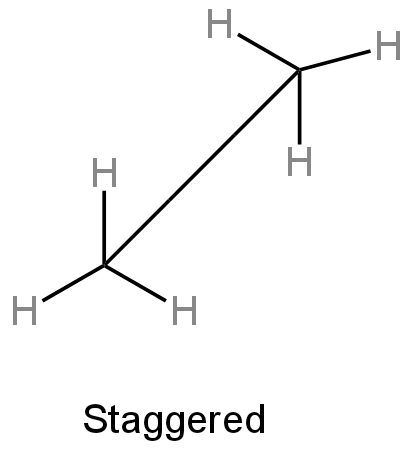
Image: Staggered conformation of ethane
Note: The rotation around a C-C single bond is not entirely free.
It is hindered by a small energy barrier of 1-20 kJ/mol due to weak repulsion between the adjacent bonds. This category of repulsive interaction is called torsional strain.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The rotation of the C-C single bond yields various spatial arrangements of atoms in space that are interchangeable.
The spatial arrangements of atoms that can be modified into one another by rotation around a C-C single bond are called conformations.
Alkanes can therefore have an infinite number of conformations by rotating around C-C single bonds.
Conformations of ethane
Ethane comprises a carbon-carbon single bond with each carbon atom attached to three hydrogen atoms.
Suppose we retain one carbon atom stationary and rotate the other carbon atom around the C-C axis. In that case, this rotation yields a vast no.of spatial arrangements of hydrogen atoms connected to one carbon atom for the hydrogen atoms bonded to the other carbon atom.
These are known as conformational isomers (conformers).
I) Eclipsed conformation - Here hydrogen atoms connected to two carbons are close to each other.
ii) Staggered conformation - Here hydrogens are far apart from each other.
These two conformations can be represented by many projections one of them is Sawhorse projections.
Sawhorse projections
In this, front carbon is demonstrated at the lower end of the line, whereas the rear carbon is exhibited at the upper end.
Each carbon has three lines connecting it to three hydrogen atoms.
The lines are inclined at an angle of 120° to each other.

Image: Eclipsed conformation of ethane

Image: Staggered conformation of ethane
Note: The rotation around a C-C single bond is not entirely free.
It is hindered by a small energy barrier of 1-20 kJ/mol due to weak repulsion between the adjacent bonds. This category of repulsive interaction is called torsional strain.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




