Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology – Download Free PDF with Solution
Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 is all about biotechnology. It is comparatively a newer division of science and engineering where biological forms are developed and made better using certain scientific techniques. This chapter will explain how such techniques are developed and utilized.
To understand the concepts of this chapter, refer to the Biotechnology notes prepared by the experts. Find out how the experts have explained these concepts in a concise format and develop your knowledge. Learn how you can answer the exercise questions from the solutions framed by the experts to sharpen your answering skills.
Access Maharashtra Board Solutions for Biology Class 12 Chapter 12 Biotechnology
Choose The Correct Option.
1. The bacterium which causes a plant disease called crown gall is ………………
Helicobacter pylori
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Theophilus aquaticus
Bacillus thuringiensis
Ans: The correct option is (b) Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
The Agrobacterium tumefaciens attacks the plant if there is any injury or wound in the plant. The gram-negative bacteria contain the Ti plasmid that is responsible for the tumour in the host cells. When the bacteria enter the plant, the tumour-causing genes in the Ti plasmid cause the growth of tumours in the host plant. This results in the formation of galls on various parts of the plant such as roots, branches, stems, etc. Hence, the disease caused by this bacteria is called crown gall disease.
2. The enzyme nuclease hydrolyses ……………… of polynucleotide chain of DNA.
Hydrogen bond
Phosphodiester bonds
Glycosidic bonds
Peptide bonds
Ans: The correct option is (b) Phosphodiester bonds.
The nuclease enzymes are capable of hydrolysing the phosphodiester bonds in the polynucleotide chain of DNA. There are two types of nuclease enzymes- exonuclease which breaks the phosphodiester bonds outside the polynucleotide chain of the DNA and endonuclease which breaks the phosphodiester bonds inside the polynucleotide chain of the DNA. Some nucleases act as both endonucleases and exonucleases.
3. In vitro amplification of DNA or RNA segments is known as ………………………
Chromatography
Southern blotting
Polymerase chain reaction
Gel electrophoresis
Ans: The correct option is (c) Polymerase chain reaction.
PCR is an amplification technique that is generally used to create millions to billions of copies of DNA from a small segment of DNA. It consists of mainly three steps that are denaturation, annealing and extension. This technique is very important in DNA fingerprinting, gene therapy, parental testing and detecting point mutations. The PCR method is becoming very useful in various fields of science as it is a faster method.
4. Which of the following is the recognition sequence of restriction enzyme hind III?
5’---A-A-G-C-T
3’---T-T-C-G-A-A---5’
5’---G-A-A-T-T-C---3’
3’---C-T-T-A-A-G---5’
5’---C-G-A-T-T-C---3’
3’---G-C-T-A-A-G---5’
5’---G-G-C-C---3’
3’---C-C-G-G---5’
Ans: The correct option is (a) 5’---A-A-G-C-T-T---3’
3’---T-T-C-G-A-A---5’
Hind III is an endonuclease that is isolated from the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae. This endonuclease identifies and cuts the DNA at a specific segment which is 5’---A-A-G-C-T-T---3’. Hence, the recognition sequence of the HindIII restriction enzyme is 5’---A-A-G-C-T-T---3’. This restriction enzyme works in the presence of magnesium ion, which acts as a cofactor.
5. Recombinant protein ………………….. is used to dissolve blood clots present in the body.
Insulin
Tissue plasminogen activator
Relaxin
Erythropoietin
Ans: The correct option is (b) Tissue plasminogen activator.
The Tissue plasminogen activator is a serine protease enzyme that is produced from the cells that form the inner lining of blood vessels or endothelial cells. Tissue plasminogen activator plays a very important role in the breakdown and dissolution of blood clots that occur in the body. It is also made in the laboratory to treat various problems related to the heart and lungs.
6. Recognition sequence of restriction enzymes is generally ..………………………. nucleotide long.
2 to 4
4 to 8
8 to 10
14 to 18
Ans: The correct option is (b) 4 to 8.
The recognition sequence of restriction enzymes is the specific sites or sequences on the nucleotide sequence that the restriction enzyme recognises and cleaves. There is a specific recognition sequence for a specific restriction enzyme. Generally, the recognition sequence is 4 to 8 nucleotides long. The recognition sequence of HindIII endonuclease is 5’---A-A-G-C-T-T---3’.
Very Short Answer Type Questions.
1. Name the vector which is used in production of human insulin through recombinant DNA technology.
Ans: The cloning vector which is used in the synthesis of human insulin through recombinant DNA technology is pBR322. The pBR322 is present as a circular plasmid in the E.coli bacteria. It is extracted from the bacteria and cut by restriction enzymes. After this, the human insulin-producing genes are inserted into the gap of the cloning vector. The genetically modified plasmid is now introduced into the bacteria such as E. coli or yeast such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae. As these bacterial or yeast cells divide, human insulin is produced.
2. Which cells from Langerhans of pancreas do produce a peptide hormone insulin?
Ans: The beta cells that form about 75 percent of each islet of Langerhans of the pancreas are responsible for the production of the peptide hormone insulin.
Whenever there are high glucose levels in the blood, the beta cells secrete insulin that uptakes the excess glucose from the blood and transports it to the liver. In the liver, the glucose is converted into glucagon.
On the other hand, if there are low glucose levels in the blood, the alpha cells of the islet of Langerhans secrete the glucagon hormone that converts the glucagon to glucose.
Thus, both alpha and beta cells regulate blood glucose levels.
3. Give the role of Ca⁺⁺ ions in the transfer of recombinant vector into bacterial host cell.
Ans: In recombinant DNA technology, the entry of the recombinant vector into the host is one of the important steps. As the bacterial cell wall is made up of hard lipopolysaccharides, hence, it is very difficult to insert the recombinant vector into the host cell. The calcium ions play a very important role in the transfer of the recombinant vector into the bacterial host cell. They facilitate the binding of the vector into the host cell by increasing the ability of the bacterial host cell to incorporate the plasmid vector.
4. Expand the following acronyms which are used in the field of protechnology.
YAC
RE
dNTP
PCR
GMO
MAC
Ans: The acronyms are expanded below:
a. YAC: Yeast Artificial Chromosome
YACs are the human-made chromosomes in the laboratory using the DNA from yeast. The desired DNA sequence can be inserted into the YACs and then the recombinant DNA is incorporated into the yeast cell to make multiple copies of recombinant DNA.
b. RE: Restriction Enzyme
Restriction enzymes are molecular scissors that can cut the DNA sequences at specific locations.
c. dNTP: Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphate
During the third step of the polymerase chain reaction, the dNTPs help in enlarging the growing strand of DNA. This happens in the presence of the enzyme Taq DNA polymerase.
d. PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction
PCR is an amplification technique that is generally used to create millions to billions of copies of DNA from a small segment of DNA. It consists of mainly three steps that are denaturation, annealing, and extension.
e. GMO: Genetically Modified Organisms
GMOs are organisms whose genes have been modified by using various genetic engineering techniques to obtain the expression of desired genes.
f. MAC: Mammalian Artificial Chromosome
Mammalian artificial chromosomes contain functional human chromosomes that can replicate.
5. Fill in the blanks and complete the chart.
GMO | Purpose |
i. Bt cotton | ………………………… |
ii. ………………….. | Delay the softening of tomato during ripening. |
iii. Golden rice | ………………………….. |
iv. Holstein cow | ………………………….. |
Ans: The complete chart is:
GMO | Purpose |
i. Bt cotton | Bt cotton is resistant to the attack of pests such as bollworms.
|
ii. Flavr savr tomato
| Delay the softening of tomato during ripening. |
iii. Golden rice | It is rich in vitamin-A.
|
iv. Holstein cow | High milk production
|
Short Answer Type Questions.
1. Explain the properties of a good and ideal cloning vector for rDNA technology.
Ans: There are some properties that a good and ideal cloning vector should have:
The cloning vector should have the ability of self-replication so that it can easily replicate inside the cell of the host organism.
The vector should be small in size so that it can be easily incorporated inside the host cell.
There should be some antibiotic resistance genes within the cloning vectors.
The cloning vector should have restriction sites and multiple cloning sites.
The introduction of desired DNA into the cloning vector should not interfere with the cloning ability of the vector.
2. A PCR machine can rise temperature upto 100℃ but after that, it is not able to lower the temperature below 70℃ automatically. Which step of PCR will be hampered first in this faulty machine? Explain why?
Ans: The step of PCR which will be hampered in this faulty machine is annealing. This is because annealing occurs at temperatures ranging from 40-60°C. After the first step of PCR, the temperature of the machine is reduced from 100°C to less than 70°C. This allows the binding of the DNA primers to the complementary ends of a single strand of template DNA. The temperature of the machine depends upon the length of primers and their sequence. Hence, if the machine is faulty, the annealing process will not happen properly.
3. In the process of rDNA technology, if two separate restriction enzymes are used to cut vector and donor DNA then which problem will arise in the formation of rDNA or chimeric DNA? Explain.
Ans: The rDNA technology involves the formation of recombinant DNA using the DNA from two species one is cloning vector DNA and the other is donor DNA. This is done with the help of restriction enzymes. The restriction enzymes are known to cut the DNA strand at specific sites known as restriction sites. If we use two different restriction enzymes to cut the donor DNA and cloning vector then the complementary base pairing will not occur and hence, the recombinant DNA will not be formed.
4. Match and write the pairs.
Recombinant protein | It’s used in or for |
i. Platelet derived growth factor | a. Anaemia |
ii. α-antitrypsin | b. Cystic fibrosis |
iii. Relaxin | c. Haemophilia A |
iv. Erythropoietin | d. Diabetes |
v. Factor VIII | e. Emphysema |
vi. DNAse | f. Parturition |
g. Atherosclerosis |
Ans: The correct matches are:
Recombinant protein | It’s used in or for |
i. Platelet derived growth factor | g. Atherosclerosis
|
ii. α-antitrypsin | e. Emphysema
|
iii. Relaxin | f. Parturition
|
iv. Erythropoietin | a. Anaemia
|
v. Factor VIII | c. Haemophilia A
|
vi. DNA ase | b. Cystic fibrosis
|
Long Answer Type Questions.
1. Define and explain terms.
Biopiracy
Biopatent
Bioethics
Ans: The terms are defined below:
Biopiracy: Biopiracy is the stealing and then getting patent of biological or natural products that once belonged to some indigenous group. These indigenous groups originally had knowledge about these products. Examples of some Indian traditional products that are patented by other countries are: neem, turmeric, basmati rice etc.
Biopatent: Biopatent is the patenting of biotechnological products, tools, processes, strains of microorganisms etc. so that others cannot use them for commercial purpose but for a limited time period .
Bioethics: Bioethics are the concerns and moral values that are related to the use or not use of certain things that are related to life. Examples of some topics that fall under bioethics are genetically modified organisms, invitro fertilisation etc.
2. Explain the steps in the process of rDNA technology with suitable diagrams.
Ans: The steps involved in the process of rDNA technology are:
As a first step, the desired DNA is isolated from the donor organism.
The isolated donor DNA is then cut using restriction enzymes that cut the DNA at specific sites. This results in many small fragments of DNA.
The desired gene containing a DNA fragment is screened and then incorporated into the cloning vector DNA. This results in the formation of recombinant DNA or rDNA.
The rDNA is then inserted into the host cell to make multiple copies of the desired fragment of DNA.
These desired DNA fragments are used to transform the desired host cells to obtain the desired gene expression.
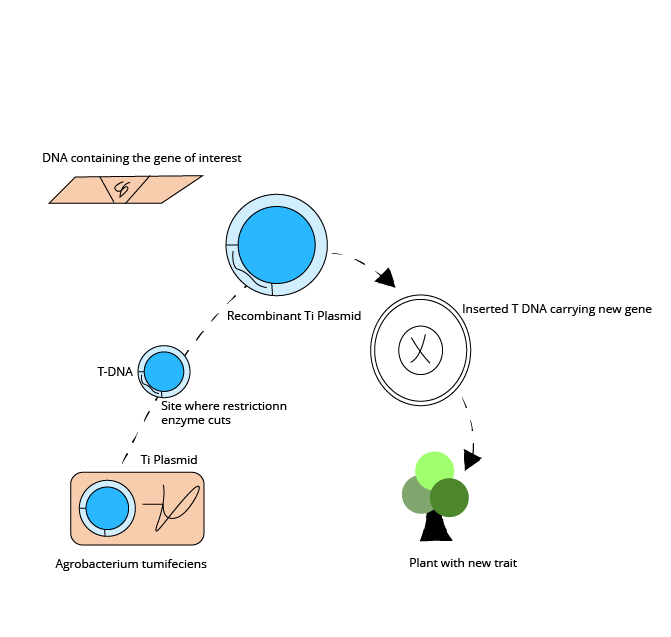
Steps in rDNA technology
3. Explain the gene therapy. Give two types of it.
Ans: Gene therapy is the treatment of certain diseases using nucleic acid polymers that will replace or alter the mutated gene with the correct gene. This will treat the genetic abnormalities.
There are two types of gene therapy:
Somatic Cell Gene Therapy: It involves the introduction of therapeutic genes into the somatic cells such as bone marrow, endocrine cells etc. of the affected person. As the healthy genes are incorporated into somatic cells, the modified information will not pass on to the next generation.
Germline Gene Therapy: It involves the administration of normal or therapeutic genes into the germline cells such as sperm, eggs etc. As the therapeutic genes are incorporated into the germline cells, the modified information will pass on from generation to generation.
4. How are transgenic mice used in cancer research?
Ans: Transgenic mice are widely used in cancer research in the following ways:
The introduction of particular oncogenes or cancer-causing genes into these mice will develop some cancer and we can study the development of cancer inside the transgenic mice.
Scientists can study transgenic mice to study the biological functioning of oncogenes.
Transgenic mice are also used to study the development of breast cancer and its treatment.
Scientists can do research on transgenic mice for malignant cancer and treatment of different types of cancer.
5. Give the steps in PCR or polymerase chain reaction with suitable diagrams.
Ans: PCR is an amplification technique that is generally used to create millions to billions of copies of DNA from a small segment of DNA. It consists of mainly three steps that are denaturation, annealing and extension.
Denaturation: In this step, the double strand of the desired DNA segment is denatured into two single-stranded DNA. The temperature of the PCR machine remains between 90-98°C.
Annealing: After the denaturation of DNA strands, the temperature of the machine is reduced from 90°C to less than 70°C. This allows the pairing of the DNA primers to the complementary ends of a single strand of template DNA. This process is called annealing.
Elongation: In this step, the enzyme Taq DNA polymerase adds nucleotides using the single stranded DNA as template. This step occurs in the temperature range of 70-75°C. This is the elongation of DNA.
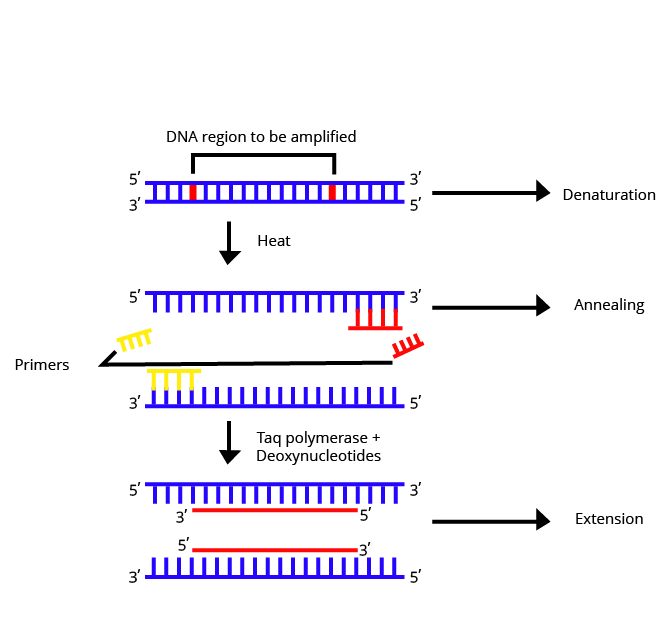
Steps in PCR Technique
6. What is a vaccine? Give advantages to oral vaccines or edible vaccines.
Ans: A vaccine is a biological product in which weakened or dead microorganisms are used to increase the immunity of the human body against a specific disease causing organism. Hence, this vaccine acts as a prevention to a certain disease.
There are several advantages of oral or edible vaccines. These are:
The introduction of oral vaccines reduced the threat of several blood borne pathogens that can enter our body during administration of needles or syringes.
The oral vaccines can be given by any medical personnel without any special training.
The oral or edible vaccines can be easily taken by anyone as they are not painful when compared to injections.
Oral vaccines can be easily manufactured on a mass level and they don't require any special areas.
The traditional vaccines cost high as they required cold chain storage to remain stable. But, this is not the case with oral vaccines.
7. Enlist different types of restriction enzymes commonly used in rDNA technology? Write on their role.
Ans: The different types of restriction enzymes used in rDNA technology are:
Type I Restriction Enzyme: These restriction enzymes do cleaving of sequence and methylation at the same time.
Type II Restriction Enzyme: These restriction enzymes are widely used in rDNA technology as they separately function as nuclease and methylase. Type II restriction enzymes cut the DNA sequence at specific palindromic sites.
Type III Restriction Enzyme: These enzymes cut the nucleotide sequence on specific sites but at non-palindromic sequences.
The role of restriction enzymes is: They play a very important role in recombinant DNA technology. These enzymes are used to cut the DNA sequence at specific locations to get the desired DNA sequence or fragment.
8. Enlist and write in brief about the different biological tools required in rDNA technology.
Ans: The different biological tools required in rDNA technology are:
Host Prganism: This is the organism into which the cloning vector containing desired DNA will be incorporated. The host organisms used in rDNA technology are generally bacteria.
Genomic DNA: This is the desired DNA which will be used in rDNA technology to obtain the desired product.
Restriction Enzymes: The restriction enzymes, especially endonucleases, act on the genomic DNA and cut it at specific recognition sites to form the sticky ends.
Ligase: The ligase enzyme helps in the binding of sticky ends of the sequence with the sequence of a plasmid containing cloning vectors.
Cloning Vectors: The desired gene-containing sequence is inserted into the cloning vector such as bacteriophage, pBR322. The cloning vector is then incorporated into the host organism to produce multiple copies of the desired recombinant vector.
Importance of Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology
Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 of the Maharashtra Board deals with the different aspects of biotechnology. In this chapter, you will find the definition of this interdisciplinary domain of science and technology.
Biotechnology deals with the formation and alteration of various biological forms for the benefit of humans and the ecosystem. This is a unique branch of science where the techniques are developed to create new breeds for food, medicines, etc. The prime focus of biotechnology is to progress and make these aspects more sustainable.
Biotechnology has been modernized by the introduction of DNA technology. Previously, it was based on the use of microorganisms to prepare food, medicine, and other important products. Now, we can alter the genetic impression of a species using biotechnological methods and can prepare higher quality products or outcomes in particular fields.
This chapter also explains the cores of these technologies used in biotechnology. One of its cores is genetic engineering. As mentioned earlier, the genetic impression of various species can be altered using various methods. It is done to create better species for better outcomes.
Another core is chemical engineering. In this domain, various biotechnological processes are adopted to develop products like vaccines, enzymes, antibodies, therapeutics, etc in a sterile environment. To understand these concepts, refer to the Biotechnology Class 12 notes prepared by the experts.
Benefits of Biotechnology Class 12 Notes PDF
If you follow the Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 notes, you will find a simpler explanation of all the concepts. All these concise explanations have been formulated in an easier format so that you can memorize them.
You will also be able to recall these simplified concepts faster and can answer the fundamental questions without any hassle.
There is no need to waste time making notes when the experts have already covered the entire chapter for you.
Clarify doubts related to the biotechnological terms, definitions, methods, exercise questions, etc with these notes and stay ahead of the competition.
Get to know the latest biotechnological techniques and advancements in a simpler format from these notes to enhance your knowledge.
Download Maharashtra Solutions Class 12th Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology PDF
Get the free PDF version of the Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology notes Chapter 12 Biotechnology and prepare this chapter exceptionally. Get a simpler description of the concepts, scientific terms, definitions, etc. in this chapter and make your preparation better. Find out how the experts have answered all exercise questions to develop better answering skills.
FAQs on Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology - PDF
1. What is biotechnology?
The process of genetic manipulation of organisms for various purposes is called biotechnology.
2. What is cloning?
Cloning is a biotechnological process where an entire copy of the genetic impression of an organism is replicated.
3. Why do we perform genetic engineering?
We perform genetic engineering to alter the genetic impression of an organism to make it better or to fulfill our particular requirements. One of the biggest successes of biotechnology is mass-producing insulin and reducing its price.
4. What is DNA?
Deoxyribose nucleic acid is the unit of hereditary material present in the chromosomes of living organisms. It maintains a sequence and carries the genetic information of an organism.
5. Why is the sequence of DNA determined?
The sequence of DNA is determined so that it can be cloned or identified as a gene. The determination results in performing various biotechnological functions.























