




How to Add and Subtract Powers: Rules, Methods & Practice
Algebra is one of the very important parts of mathematics. To understand algebra, one must know how to use exponents and radicals. The power over the given base number is known as exponents/index. For example, $4^2=4 \times 4$, where 4 is the base and 2 is the exponent. The Addition of powers is the process of adding exponents or powers of a number irrespective of whether the base is the same. In this article, we will learn about the addition and subtraction of powers with numerical bases.
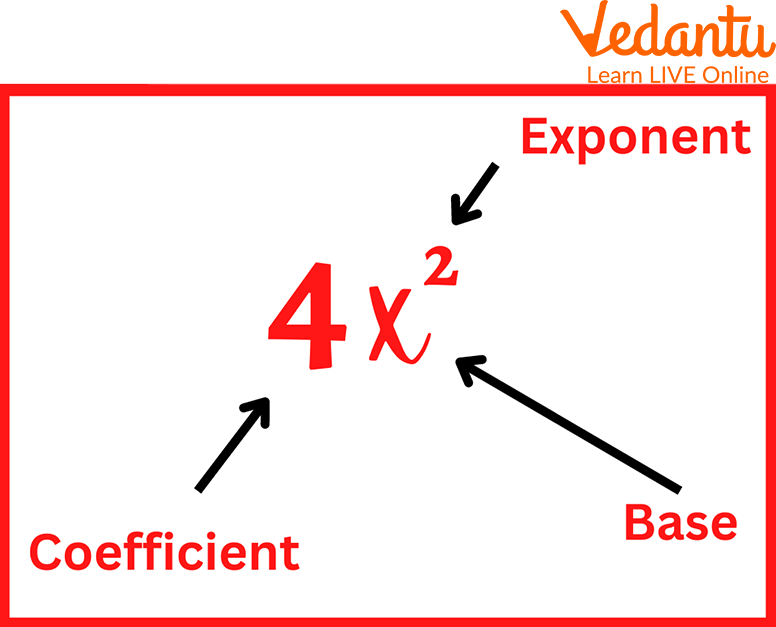
Introduction to Powers
Addition and Subtraction of Powers with Numerical Bases
Addition and subtraction are the two primary operations of mathematics. But we cannot directly add or subtract powers, we can only perform addition or subtraction only on the variables that have the same base and the same power. We can only add powers in multiplication and subtract powers in the division.
$3^4+2^5=$
$=3^4$
$=3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3$
$=81$
Also, $2^5$
$=2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2$
$=32$
Therefore, $3^4+2^5= 81 + 32$
$=113$
Addition of Numbers with Powers
Adding numbers with power can be done when the base and powers are the same. There would be times when the base and powers are different, but we can still add those expressions. Let us have a look at the ways of adding powers.
Check if they got the same base and also the same power.
The usual form of addition of powers with same base is $x^{n}+x^{n}=2x^{n}$.
For example, $4^{2}+4^{2}$
$=2(4^{2})=2 \times 4 \times 4$
$=32$
If the base and power differ, then the expression will be calculated with individual terms.
The usual form is like $z^{n}+x^{m}$.
Addition and Subtraction of Powers
To add and subtract powers, you must first ensure that the base and power of the two terms we use to add or subtract are the same. If they are the same, then you only have to add together their coefficients and let the base and power remain identical.
$3^3+2^5 =?$
$=(3 \times 3 \times 3 )(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2)$
$=(27)+(32)$
$=59$
$3^3+2^5=59$
Laws of Indices
The First Law: Multiplication
If the two terms have identical bases (in this case, " $\mathrm{x}$ ") and are to be multiplied, their indices will be added.
Let’s see the addition of indices with different powers, $x^m \times x^n=x^{m+n}$
Example: $5^2 \times 5^1=5^{2+1}=5^3$
The Second Law is: Division
If the two terms have an identical base (in this case, " $\mathrm{x}$ ") and are to be divided, their indices will be subtracted.
$\dfrac{x^m}{x^n}=x^{m-n}$
Example: $\dfrac{2^3}{2^2}=2^{3-2} =2^{1} = 2$
The third law: Brackets
If a term with an exponent is raised to a power, then the powers are multiplied.
$\left(x^m\right)^n=x^{m \times n}$
Example: $\left(3^2\right)^2=3^{2 \times 2}=3^{4}$
Solved Examples
Q 1. Find the value of $9^5$.
Ans: $9^5=9 \times 9 \times 9 \times 9 \times 9= 59,049$
Q 2. Find the value of $81+2^4=?$
Ans: $2^4$
$=2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 $
$=16$
Therefore, 81 + 16 = 97.
Q 3. Find the value of $2^6+3^5$
Ans: Since $2^6+3^5$ can be written in expanded form ad
$=(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 )+(3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3)$
$=(64)+(243)$
$=307$
Practice Questions
Q 1. $\left(2^3\right)^2=$? (Ans: $64 .$)
Q 2. Find the value of $4^{-5}$. (Ans: $=\dfrac{1}{1024}$)
Q 3. $8^2 \times 4^1=$? (Ans: 256)
Summary
In this article, we have learned about the addition of power. Adding exponents refers to the simple addition of numbers but in the form of exponents or power. This article taught us that the variables and exponents must be the same to add or subtract with powers. The power of a number tells us how many times a number is to be used in multiplication. Powers are also known as Indices or Exponents. For example, $7^{2}$ could be called “7 to the power of 2” “7’’to the second power”, or simply “7 squared”. In the end, we added the practice problem to check the command over the topic. So after going through the article, give it a try!
FAQs on Addition and Subtraction of Powers Explained
1. What is the rule for adding and subtracting powers?
The rule for adding and subtracting powers (also called exponents) is that you can only add or subtract expressions with the same base and the same exponent. For example, $2^3 + 5^3$ cannot be simplified directly since the bases are different. If the bases and exponents are the same, you add or subtract the coefficients: for example, $3x^2 + 4x^2 = 7x^2$. You do not combine the exponents when adding or subtracting powers; only like terms are combined.
2. What are the 7 rules of exponents?
The seven rules of exponents (also known as laws of exponents) are fundamental for simplifying powers in mathematics:
- Product Rule: $a^m imes a^n = a^{m+n}$
- Quotient Rule: $\frac{a^m}{a^n} = a^{m-n}$
- Power of a Power: $(a^m)^n = a^{mn}$
- Power of a Product: $(ab)^n = a^n b^n$
- Power of a Quotient: $\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)^n = \frac{a^n}{b^n}$
- Zero Exponent: $a^0 = 1$ (where $a \neq 0$)
- Negative Exponent: $a^{-n} = \frac{1}{a^n}$
3. How to add and subtract numbers in scientific notation with different exponents?
To add or subtract numbers in scientific notation with different exponents, you first need to express both numbers with the same exponent:
- Step 1: Adjust the numbers so that the exponents of 10 match.
- Step 2: Add or subtract the coefficients (the numbers in front) while keeping the common exponent.
$3.2 \times 10^4 + 4.5 \times 10^3$
Rewrite $4.5 \times 10^3$ as $0.45 \times 10^4$ so both have the 104 exponent.
Now combine:
$3.2 \times 10^4 + 0.45 \times 10^4 = 3.65 \times 10^4$
This method allows accurate addition or subtraction in scientific notation.
4. How do you add and subtract like terms with exponents?
To add and subtract like terms with exponents, make sure the base and the exponent of each term are identical. Only then can you add or subtract the numerical coefficients:
- Combine the coefficients, keeping the base and exponent unchanged.
- For example, $5x^3 + 2x^3 = 7x^3$ and $9y^2 - 4y^2 = 5y^2$.
- Terms with different exponents or different bases cannot be combined.
5. How do you simplify expressions involving addition and subtraction of exponents?
To simplify expressions with addition and subtraction of exponents, follow these steps:
- Group like terms with the same base and exponent.
- Add or subtract the coefficients of these terms.
- Keep the base and exponent the same.
If bases or exponents differ, you cannot combine the terms, but you can use exponent rules if multiplication or division is involved.
6. What mistakes should be avoided when adding or subtracting powers?
Some common mistakes when working with addition or subtraction of powers include:
- Combining terms with different exponents or bases (e.g., $x^2 + x^3$ cannot be simplified).
- Mistakenly adding exponents when only adding coefficients is allowed.
- Forgetting to align exponents in scientific notation before performing operations.
7. How are addition and subtraction of exponents used in real-life problems?
In real-life scenarios, addition and subtraction of exponents are applied in:
- Scientific calculations: Combining measurements expressed in scientific notation.
- Physics and Chemistry: Adding or subtracting quantities like mass or energy represented with exponents.
- Financial modeling: Handling exponential growth or decay calculations.
8. What is the difference between multiplication and addition of powers with the same base?
The key difference between multiplying and adding powers with the same base is:
- Multiplication: When multiplying, add the exponents: $a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}$
- Addition: When adding, combine coefficients if exponents and bases are the same: $ka^n + ma^n = (k + m)a^n$
9. How can Vedantu help you master addition and subtraction of exponents?
Vedantu offers live online classes, comprehensive study materials, and practice worksheets on topics like addition and subtraction of powers. With guided lessons, immediate doubt resolution, and detailed explanations from experienced teachers, students can build a strong foundation in exponents and other key concepts. Interactive quizzes and personalized learning plans ensure students master this topic efficiently.
10. Why is understanding addition and subtraction of exponents important for mathematics exams?
A solid grasp of addition and subtraction of exponents is critical for success in mathematics exams. Many algebraic expressions and scientific problems require combining like terms using exponents, and mistakes can lead to incorrect answers. Mastery of these concepts, as emphasized in Vedantu’s curriculum, equips students to solve equations accurately and quickly, boosting their performance in school and competitive tests.























