




How to Use Skip Counting by 6 in Everyday Math
The practice of counting by skipping over some numbers is known as skip counting. For instance, if we start with 0 and decide to skip over some numbers by 3, the following numbers will be 3, 6, 9, and so on. As a result, when we skip count by 6, we go through 6 digits at once.

Skip counting by 6
Skip Counting
Skip counting is a way of counting that involves removing some numbers. It is also possible to think of it as a way to count by increasing the previous number each time. One way to count is to skip a fixed number of places along the counting line.
For instance, when we skip count by 10, we begin at 0 and move on to the next number until we reach 10.
Skip counting by 10 requires counting every tenth number beginning with the given number. Starting at zero, we count 0, 10, 20, 30, and so on. You'll notice that we skipped the numbers between each time and jumped right to the number that comes after our current one.
Ways to Skip Counting
Skip counting by adding or subtracting:
Skip counting can also refer to adding or taking away a specific amount from each successive number. To skip count by 6, we would count as 6, 12, 18, 24, and so on. Remember that each number in this series is six more than the previous one. Let us take the example of adding or subtracting skip counting by 6:
$\begin{array}{l}6 + 0 = 6\\6 + 6 = 12\\12 + 6 = 18\\18 + 6 = 24\end{array}$
Skip counting on the number line:
Using the number line, we can skip count by simply moving forward a certain number to create a sequence. Beginning with the first number on the number line, work your way forward and to the right when adding, or you can deduct from the largest number on the number line before moving to the left.
Let us take the example of skip counting by 6 on a number line:
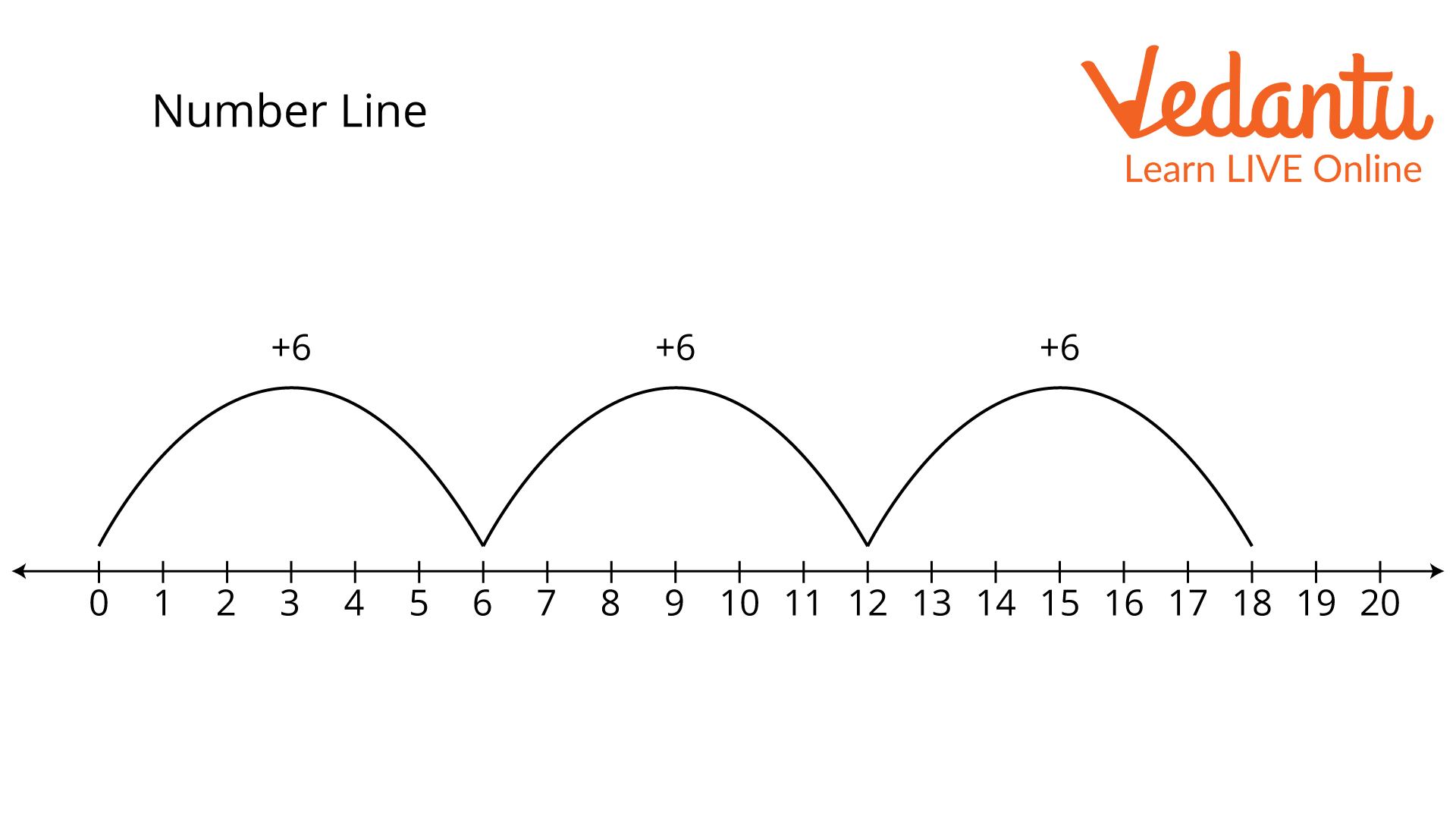
Number line
Skip Counting by 6
As we all know, skip counting involves removing some numbers from the total. Thus, skipping past 6 must mean skipping counting by 6. As a result, we start at 0 and go directly to the next number, which is 6, 12, 18, 24, and so on, without counting any of them.
In other words, skip counting by six or count in groups of six, start with six, add six to reach the next number, and then keep adding six to the previous number to keep counting by six.
Skip Counting by 6 charts
A skip counting by 6 charts of the first 500 numbers is provided below because it is impossible to skip count by 6 infinitely continuously:
Conclusion
Why do you think that skipping counts is so simple? By this point, you need to be aware of what skip counting is and the many types of it. Skip counting is enjoyable and easy, isn't it? Next time, we'll practice skipping a larger number.
We can also get the required number by multiplying it by the number.
FAQs on Skip Counting by 6 Made Easy
1: What is the purpose of skip counting?
Skip counting is crucial for the growth of number sense and as the foundation for multiplication and division. Skip counting serves as the basis for multiplication and division, as well as the development of calculating speed and number sense.
Additionally, it's crucial to assist kids in switching from counting by ones to number facts when performing calculations.
2: How to perform skip counting?
When counting backwards or forwards, any number can be skipped over, and any number can be the first skip. To skip counting by a certain amount, keep adding numbers to the starting number.
3: Where can skip counting be used?
In multiplication tables, skip counting is mostly used to obtain the answer to a specific multiple. If you needed to get a multiple of 20, for instance, while reading out the multiplication table for 4, you would skip count by 4 until you reached 20 and calculate the multiple, which would be 5.























