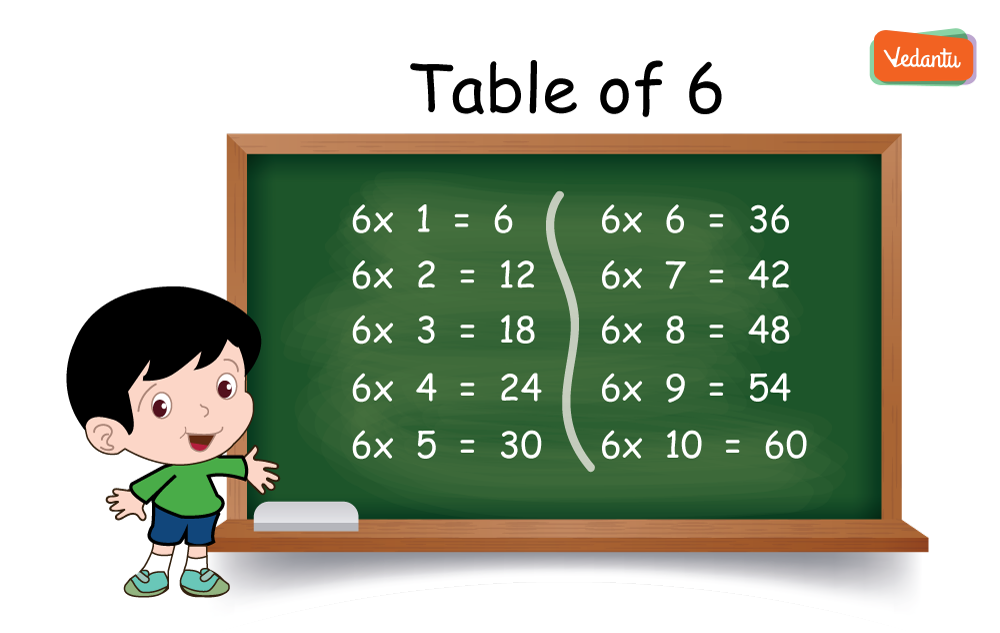
How to Quickly Learn and Remember the Table of 6
FAQs on Table of 6 – Simple Multiplication Guide
1. What are the rules followed by a multiplication table of 6?
Each multiplication table follows the most basic and general rule of addition. It includes adding the same number repetitively.
For example, when we add 6 four times, we get 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = 24, which is equivalent to 6 × 4 = 24.
2. What is the divisibility rule of 6?
Any number which is divisible by 2 and 3 both is also divisible by 6. This is because of the fact that a multiple of 6 is also the multiple of 2 and 3 both.
Recently Updated Pages
Minuend in Maths: Definition, Explanation & Examples

Math Words That Start With Y – Key Terms Explained for Students

Addition and Subtraction Worksheets: Practice with Integers, Fractions

Consecutive Numbers: Definition, Examples & Key Properties

Compare Numbers in Maths: Easy Steps & Examples

More Than Symbol in Math: Meaning, Uses & Easy Examples

Trending pages
Greater Than and Less Than Symbols: Easy Guide for Maths Students

Greater Than Symbol: Meaning, Examples, and Shortcuts

Number Names from 1 to 50 in English Words

Maths Made Easy: Key Concepts, Formulas & Smart Practice

What Is Money? Simple Guide for Kids

Factors of 100: Complete Concept Explanation & Methods