Master Grassroots Democracy Class 6 With Our Easy To Follow Solution Guide
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 Grassroots Democracy - Part 3 Local Government In Urban Areas (2025-26)
1. What are the stepwise NCERT solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 as per the CBSE 2025–26 textbook?
The stepwise NCERT solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 are prepared in line with the CBSE 2025–26 textbook. Each answer follows the NCERT-approved format, providing clear steps, supporting explanations, and relevant references from textbook intext and exercise questions. All solutions emphasize the official answer structure to help students write precise answers during exams.
2. Where can I find the official NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 in English medium?
You can access the official NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 in English medium as a PDF download or online view on trusted platforms like Vedantu, which aligns with the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus and presents every answer according to the NCERT answer key and marking pattern.
3. Does the answer key for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 provide CBSE-approved explanations for all exercise and intext questions?
Yes, the answer key for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 delivers CBSE-approved, syllabus-aligned explanations for all textbook exercise and intext questions. The solutions offer stepwise reasoning and use official NCERT patterns to clarify important concepts and ensure correctness as per the latest guidelines.
4. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 12 help in understanding Grassroots Democracy – Part 3 Local Government in Urban Areas?
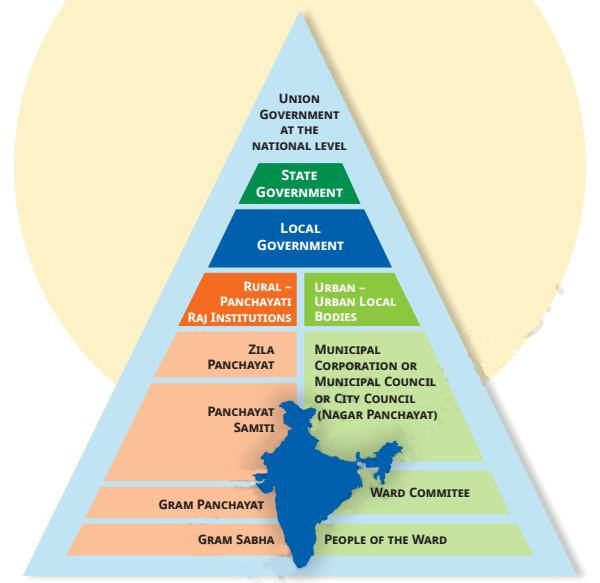
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 12 assist students by breaking down complex topics of local government in urban areas into simple steps. Using official NCERT formats, each solution explains the roles and powers of municipal bodies, election processes, and the importance of grassroots democracy, enhancing chapter understanding and exam preparation.
5. Can I download the NCERT Social Science Book Class 6 Solutions PDF for Chapter 12 free of cost?
Yes, you can download the NCERT Social Science Book Class 6 Solutions PDF for Chapter 12 free of cost from reliable educational websites like Vedantu. These PDF solutions strictly follow the CBSE and NCERT 2025–26 pattern, ensuring students have access to accurate and updated answers for all questions.
6. What is the correct NCERT answer format for writing Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 solutions in exams?
The correct NCERT answer format for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 includes using full sentences, presenting facts stepwise, supporting each point with textbook evidence, and concluding with a summary line when required. This CBSE-approved method improves clarity, structure, and scoring in answers.
7. Are these Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 answers as per the most recent CBSE 2025–26 guidelines?
All answers for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 are updated as per the most recent CBSE 2025–26 guidelines and align with the official NCERT syllabus, ensuring students prepare according to the latest exam standards and curriculum updates.
8. How can NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 help clarify doubts about municipal government rules?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 address doubts by offering detailed, textbook-based explanations of municipal government rules, such as functions of different officials, sources of revenue, and the election process, allowing students to grasp all administrative aspects easily and accurately.
9. Are the provided NCERT solutions for Social Science Class 6 Chapter 12 suitable for both intext and exercise questions?
The provided NCERT solutions for Social Science Class 6 Chapter 12 comprehensively cover both intext and exercise questions, offering official, stepwise answers that match the CBSE 2025–26 marking scheme and the NCERT textbook answer key for all question types asked in the chapter.
10. What is the best approach to solve Chapter 12 Class 6 Social Science questions as per NCERT guidelines?
The best approach involves reading the question carefully, identifying keywords, writing answers stepwise following NCERT structure, and including facts/examples from the chapter "Grassroots Democracy – Part 3 Local Government in Urban Areas." It is recommended to review official NCERT solutions to ensure your answer meets CBSE 2025–26 standards.
11. How can I use Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 NCERT solutions to avoid common mistakes in exam answers?
By referencing the NCERT solutions for Chapter 12, students can learn the correct answer structure, avoid missing key points, and understand how to frame complete responses. Each textbook answer follows a logical, stepwise format that highlights important details, preventing common errors often made in exams.
12. Do the NCERT Social Science Class 6 solutions include stepwise explanations for all activity-based questions in Chapter 12?
Yes, NCERT Social Science Class 6 solutions include detailed, stepwise explanations for all activity-based, intext, and exercise questions in Chapter 12. The answers are created to follow the official NCERT answer pattern and address student doubts with clarity and textbook alignment.
13. Are there differences between English and Hindi medium answers for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12?
No, the content and logic of the answers for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 remain the same in both English and Hindi medium. Only the language differs; the solutions follow the same NCERT answer structure and CBSE guidelines regardless of medium.
14. How do NCERT solutions for Class 6 Social Science ensure alignment with textbook terminology and examples in Chapter 12?
NCERT solutions for Class 6 Social Science use the exact terminology and examples presented in Chapter 12 of the textbook, following a CBSE-approved pattern. This ensures students’ answers include all crucial points expected by examiners and match the official answer key for full marks.