How Can Economic Activities Around Us Class 6 Questions and Answers Help You Prepare for Exams?
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14 Economic Activities Around Us (2025-26)
1. What are the three main sectors of economic activities described in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14?
The three main sectors of economic activities are:
- Primary Sector: Activities involving the extraction of natural resources, like farming and fishing.
- Secondary Sector: Activities that process raw materials into finished goods, such as manufacturing.
- Tertiary Sector: Service-oriented activities, including transport, banking, and trade.
2. How are economic activities classified in Chapter 14 Economic Activities Around Us?
Economic activities in Chapter 14 are classified based on the nature of work involved:
- Primary activities use natural resources directly.
- Secondary activities process or manufacture products from primary goods.
- Tertiary activities provide services that support primary and secondary production.
3. What is the difference between the primary and secondary sectors in the context of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14?
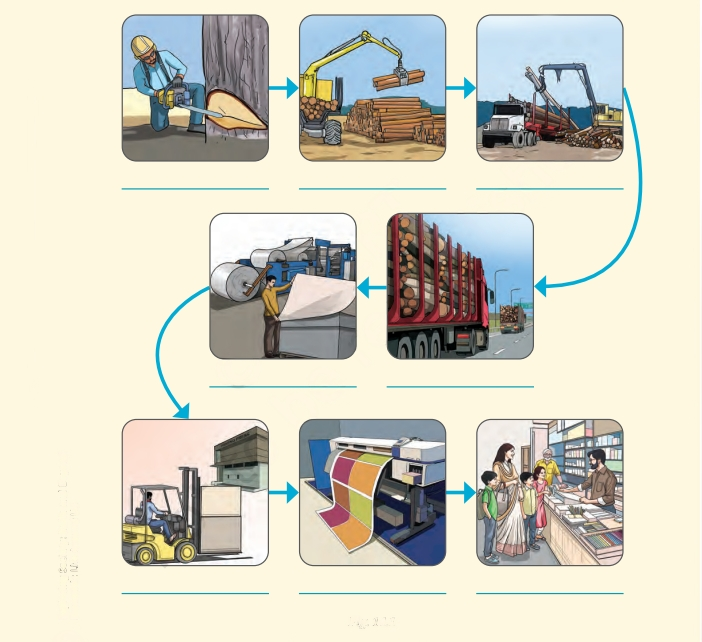
The primary sector focuses on obtaining raw materials from nature, such as farming and fishing, while the secondary sector transforms these raw materials into finished products through manufacturing or processing, like making bread from wheat or fabric from cotton.
4. How does the secondary sector depend on the tertiary sector? (CBSE 2025–26)
The secondary sector relies on the tertiary sector for essential services, such as transportation of raw materials to factories, distribution of finished products to markets, financial transactions, and advertising. Without these support services, the manufacturing process would be disrupted.
5. Explain the interdependence of primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors using an example from Chapter 14.
All three sectors are interconnected:
- A farmer (primary) grows wheat.
- A mill (secondary) turns wheat into flour.
- A bakery (secondary) bakes bread, which is then transported and sold in shops (tertiary) to consumers.
6. Why is it important for students to understand economic activities as per NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 14?
Understanding economic activities helps students learn how people earn livelihoods and how various sectors contribute to society and economic development. It also fosters awareness of interconnected roles in the economy.
7. What types of questions are covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14 for this chapter?
The solutions cover short answer questions, long answer explanations, conceptual reasoning, labeling activities, and flow diagram-based questions, addressing all aspects of economic activities and their sectoral connections.
8. How does Chapter 14 help students prepare for Social Science exams as per CBSE guidelines?
Chapter 14 offers stepwise, CBSE-aligned answers that clarify each concept, provide exam-oriented content, and use clear explanations with examples. This thorough coverage ensures students are well-prepared for both objective and descriptive exam sections.
9. What misconceptions do students commonly have about economic sectors, and how does Chapter 14 address them?
Students often confuse the sectors or assume single-sector independence. Chapter 14 clarifies sectoral interdependence, provides real-life examples, and explains the unique role of each sector, correcting common mistakes in understanding economic chains.
10. How can labeling economic activities in a neighborhood, as suggested in Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions, enhance understanding?
Labeling neighborhood activities encourages students to identify real-life examples of each sector, visualize how sectors are interconnected, and analyze their dependence, building deeper, application-based comprehension.
11. Why is transportation considered part of the tertiary sector in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14?
Transportation is categorized under the tertiary sector because it provides services that support the movement of goods and people. It links primary producers and manufacturers to markets, enabling the flow of products in the economy.
12. Can you provide a stepwise method to solve a question on sector interdependence as per the NCERT Solutions?
Yes.
- Identify all economic activities in the scenario.
- Classify each as primary, secondary, or tertiary sector.
- Draw arrows to indicate dependencies or the flow of goods/services between sectors.
- Explain what would happen if any sector’s activity stopped, supporting your answer with the example provided.
13. What is the benefit of using NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14 for quick revision?
The solutions provide concise, stepwise answers that cover key concepts, definitions, and examples, making them ideal for rapid revision and last-minute exam preparation in alignment with the latest CBSE syllabus.
14. How does Class 6 Social Science Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions help in understanding the significance of each economic sector in daily life?
The solutions illustrate how each sector—primary, secondary, and tertiary—is vital for providing goods and services in daily life. Real examples show their impact on community development, livelihoods, and access to various resources.
15. According to NCERT Solutions, what would be the economic impact if one sector ceased to function in the production chain?
If any sector (primary, secondary, or tertiary) stops functioning, it disrupts the flow of goods or services, leading to shortages, loss of livelihoods, and economic imbalance. For example, if the primary sector fails, there are no raw materials for the subsequent sectors.